bio.wikisort.org - Animal
Herpestidae is a family of mammals in the order Carnivora, composed of the mongooses and the meerkat. A member of this family is called a mongoose or a herpestid. They are widespread primarily throughout Africa and south Asia, and are found primarily in forests, savannas, shrublands, and grasslands, though some species can be found in wetlands or deserts. Most mongooses are 30–60 cm (12–24 in) long, plus a 20–40 cm (8–16 in) tail, though the Ethiopian dwarf mongoose can be as small as 18 cm (7 in) plus a 12 cm (5 in) tail, and the white-tailed mongoose can be up to 104 cm (41 in) plus a 47 cm (14 in) tail. Most species do not have population estimates, though one, the Liberian mongoose, is classified as vulnerable with a population size of around 5,000. No herpestid species have been domesticated.

The 34 species of Herpestidae are split into 14 genera within 2 subfamilies: Herpestinae, comprising 23 extant species that are native to southern Europe, Africa and Asia, and Mungotinae, comprising 11 extant species native to Africa. Extinct species have also been placed into both subfamilies, though some older extinct species have not been categorized into a subfamily. Around ten extinct Herpestidae species have been discovered, though due to ongoing research and discoveries the exact number and categorization is not fixed. Herpestidae is believed to have diverged from the existing Feliformia suborder around 21.8 million years ago in the Early Miocene.[1]
Conventions
| IUCN Red List categories | |
|---|---|
| Conservation status | |
| EX | Extinct (0 species) |
| EW | Extinct in the wild (0 species) |
| CR | Critically Endangered (0 species) |
| EN | Endangered (0 species) |
| VU | Vulnerable (1 species) |
| NT | Near threatened (3 species) |
| LC | Least concern (28 species) |
| Other categories | |
| DD | Data deficient (1 species) |
| NE | Not evaluated (1 species) |
Conservation status codes listed follow the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species. Range maps are provided wherever possible; if a range map is not available, a description of the herpestid's range is provided. Ranges are based on the IUCN Red List for that species unless otherwise noted.
Classification
The family Herpestidae consists of 34 extant species belonging to 15 genera in 2 subfamilies and divided into dozens of extant subspecies. This does not include hybrid species or extinct prehistoric species.
- Subfamily Herpestinae
- Genus Atilax: one species
- Genus Bdeogale: three species
- Genus Cynictis: one species
- Genus Herpestes: five species
- Genus Ichneumia: one species
- Genus Paracynictis: one species
- Genus Rhynchogale: one species
- Genus Urva: nine species
- Genus Xenogale: one species
- Subfamily Mungotinae
- Genus Crossarchus: four species
- Genus Dologale: one species
- Genus Helogale: two species
- Genus Liberiictis: one species
- Genus Mungos: two species
- Genus Suricata: one species
|
Herpestids
The following classification is based on the taxonomy described by Mammal Species of the World (2005), with augmentation by proposals accepted by the American Society of Mammalogists since using molecular phylogenetic analysis.[2][3]
Subfamily Herpestinae
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marsh mongoose | A. paludinosus F. Cuvier, 1829 Eleven subspecies
|
Sub-Saharan Africa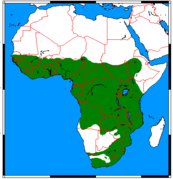 |
Size: 46–64 cm (18–25 in) long, plus 31–41 cm (12–16 in) tail[4] Habitat: Forest, grassland, inland wetlands, neritic marine, and coastal marine[5] Diet: Primarily eats crustaceans as well as other aquatic prey and rodents[5] |
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Black-footed mongoose | B. nigripes Pucheran, 1855 |
Central Africa |
Size: 45–65 cm (18–26 in) long, plus 30–40 cm (12–16 in) tail[4] Habitat: Forest[6] Diet: Primarily eats mammals, as well as reptiles, birds, insects, and centipedes[6] |
LC
|
| Bushy-tailed mongoose | B. crassicauda Peters, 1852 Five subspecies
|
Southeast Africa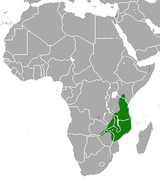 |
Size: 36–52 cm (14–20 in) long, plus 22–29 cm (9–11 in) tail[4] Habitat: Forest, savanna, and shrubland[7] Diet: Omnivorous[7] |
LC
|
| Jackson's mongoose | B. jacksoni Thomas, 1894 |
East-central Africa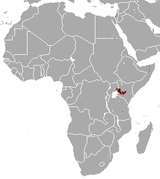 |
Size: 50–58 cm (20–23 in) long, plus 28–33 cm (11–13 in) tail[4] Habitat: Forest[8] Diet: Primarily eats rodents and insects[4][8] |
NT
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yellow mongoose | C. penicillata Cuvier, 1829 Twelve subspecies
|
Southern Africa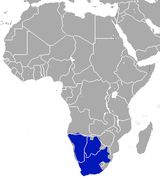 |
Size: 26–46 cm (10–18 in) long, plus 16–30 cm (6–12 in) tail[4] Habitat: Savanna, shrubland, and grassland[9] Diet: Primarily eats insects, as well as rodents, birds, other vertebrates, and arachnids[9] |
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Angolan slender mongoose | H. flavescens Bocage, 1889 Two subspecies
|
Southwestern Africa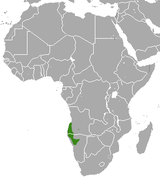 |
Size: 31–36 cm (12–14 in) long, plus 31–37 cm (12–15 in) tail[10] Habitat: Shrubland and rocky areas[11] Diet: Primarily eats invertebrates, small mammals, birds, lizards, and snakes[11] |
LC
|
| Egyptian mongoose | H. ichneumon Linnaeus, 1758 Eleven subspecies
|
Sub-Saharan Africa, Nile river, and Mediterranean (native, green); Iberian peninsula (introduced, red)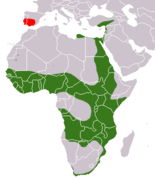 |
Size: 48–60 cm (19–24 in) long, plus 33–55 cm (13–22 in) tail[12] Habitat: Forest, savanna, shrubland, grassland, and inland wetlands[13] Diet: Omnivorous[13] |
LC
|
| Cape gray mongoose | H. pulverulentus Wagner, 1839 Three subspecies
|
Southern Africa |
Size: 29–43 cm (11–17 in) long, plus 20–34 cm (8–13 in) tail[14] Habitat: Shrubland and inland wetlands[15] Diet: Primarily eats small mammals and insects[15] |
LC
|
| Common slender mongoose | H. sanguineus Rüppell, 1836 26 subspecies
|
Sub-Saharan Africa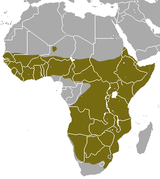 |
Size: 27–35 cm (11–14 in) long, plus 19–33 cm (7–13 in) tail[10] Habitat: Forest, savanna, shrubland, and grassland[16] Diet: Primarily eats small vertebrates and invertebrates[16] |
LC
|
| Somalian slender mongoose | H. ochraceus Gray, 1848 Four subspecies
|
Eastern Africa |
Size: 25–29 cm (10–11 in) long, plus 22–28 cm (9–11 in) tail[10] Habitat: Shrubland and desert[17] Diet: Believed to eat invertebrates and small vertebrates[10][17] |
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| White-tailed mongoose | I. albicauda Cuvier, 1829 Seven subspecies
|
Sub-Saharan Africa, southern Arabic peninsula |
Size: 51–104 cm (20–41 in) long, plus 34–47 cm (13–19 in) tail[4] Habitat: Forest, savanna, shrubland, grassland, and inland wetlands[18] Diet: Primarily eats insects[18] |
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Selous's mongoose | P. selousi Winton, 1896 Four subspecies
|
Southern Africa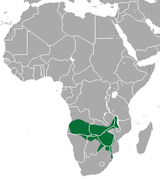 |
Size: 63–90 cm (25–35 in) long, plus 28–43 cm (11–17 in) tail[19] Habitat: Savanna and grassland[20] Diet: Primarily eats invertebrates, as well as small rodents, amphibians, reptiles, and birds[19][20] |
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Meller's mongoose | R. melleri Gray, 1865 Two subspecies
|
Southeastern Africa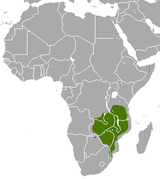 |
Size: 36–57 cm (14–22 in) long, plus 30–42 cm (12–17 in) tail[4] Habitat: Forest, savanna, and shrubland[21] Diet: Primarily eats termites, as well as other invertebrates[4][21] |
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Collared mongoose | U. semitorquata Gray, 1846 Two subspecies
|
Borneo in Southeast Asia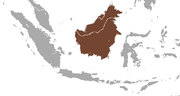 |
Size: 40–46 cm (16–18 in) long, plus 25–31 cm (10–12 in) tail[10] Habitat: Forest[22] Diet: Unknown[10][22] |
NT
|
| Crab-eating mongoose
|
U. urva Hodgson, 1836 Four subspecies
|
Eastern and Southeast Asia |
Size: 45–50 cm (18–20 in) long, plus 25–30 cm (10–12 in) tail[23] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, and grassland[24] Diet: Primarily eats crustaceans, mammals, reptiles, insects, and amphibians[24] |
LC
|
| Indian brown mongoose | U. fusca Waterhouse, 1838 Five subspecies
|
South India, Sri Lanka |
Size: 33–48 cm (13–19 in) long, plus 20–33 cm (8–13 in) tail[23] Habitat: Forest and grassland[25] Diet: Believed to eat a variety of small vertebrates and invertebrates[10][25] |
LC
|
| Indian grey mongoose | U. edwardsii Geoffroy, 1818 Five subspecies
|
India, west Asia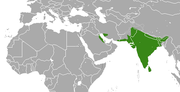 |
Size: 36–45 cm (14–18 in) long, plus 32–45 cm (13–18 in) tail[23] Habitat: Forest, shrubland, and grassland[26] Diet: Primarily eats small mammals, birds, reptiles, eggs, and invertebrates[10][26] |
LC
|
| Javan mongoose | U. javanica Geoffroy, 1818 Nine subspecies
|
Southeast Asia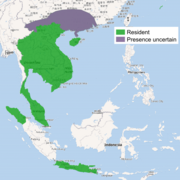 |
Size: 25–37 cm (10–15 in) long, plus 24–27 cm (9–11 in) tail[27] Habitat: Forest, savanna, shrubland, grassland, and inland wetlands[28] Diet: Primarily eats invertebrates, as well as rodents, birds, snakes, lizards, frogs, fish, and fruit[27][28] |
LC
|
| Small Indian mongoose | U. auropunctata Hodgson, 1836 Three subspecies
|
West, south, and southeast Asia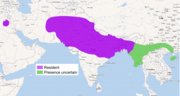 |
Size: 25–37 cm (10–15 in) long, plus 24–27 cm (9–11 in) tail[27] Habitat: Forest, savanna, shrubland, grassland, and inland wetlands[28] Diet: Primarily eats invertebrates, as well as rodents, birds, snakes, lizards, frogs, fish, and fruit[27][28] |
LC
|
| Ruddy mongoose | U. smithii Gray, 1837 Three subspecies
|
India and Sri Lanka |
Size: 39–45 cm (15–18 in) long, plus 35–47 cm (14–19 in) tail[23] Habitat: Forest and shrubland[29] Diet: Primarily eats rodents, birds, and reptiles[10][29] |
LC
|
| Short-tailed mongoose | U. brachyura Gray, 1837 Six subspecies
|
Southeast Asia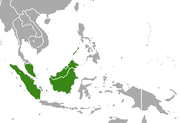 |
Size: 38–45 cm (15–18 in) long, plus 20–25 cm (8–10 in) tail[30] Habitat: Forest and shrubland[31] Diet: Eats invertebrates and small vertebrates[31] |
NT
|
| Stripe-necked mongoose | U. vitticolla Bennett, 1835 Two subspecies
|
Southern India and Sri Lanka |
Size: 25–41 cm (10–16 in) long, plus 22–36 cm (9–14 in) tail[23] Habitat: Forest and shrubland[32] Diet: Eats small mammals, birds, birds' eggs, reptiles, fish, insects, and roots[32] |
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Long-nosed mongoose | X. naso Winton, 1901 |
Central Africa |
Size: 40–61 cm (16–24 in) long, plus 32–43 cm (13–17 in) tail[4] Habitat: Forest and inland wetlands[33] Diet: Omnivorous[33] |
LC
|
Subfamily Mungotinae
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alexander's kusimanse | C. alexandri Thomas, 1907 |
Central Africa |
Size: 37–44 cm (15–17 in) long, plus 24–32 cm (9–13 in) tail[4] Habitat: Forest[34] Diet: Primarily eats invertebrates and fruit, as well as frogs, snakes, and carrion[4][34] |
LC
|
| Angolan kusimanse | C. ansorgei Thomas, 1910 Two subspecies
|
Central Africa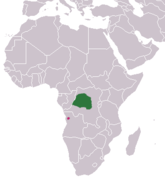 |
Size: 32–35 cm (13–14 in) long, plus 20–22 cm (8–9 in) tail[4] Habitat: Forest[35] Diet: Primarily eats insects, small vertebrates, and eggs[4][35] |
LC
|
| Common kusimanse | C. obscurus F. Cuvier, 1825 |
Western Africa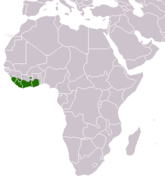 |
Size: 29–37 cm (11–15 in) long, plus 14–21 cm (6–8 in) tail[4] Habitat: Forest and savanna[4][36] Diet: Primarily eats insects, as well as reptiles, small mammals, and fruit[36] |
LC
|
| Flat-headed kusimanse | C. platycephalus Goldman, 1984 |
Western central Africa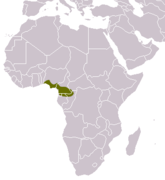 |
Size: 21–47 cm (8–19 in) long, plus 15–21 cm (6–8 in) tail[37] Habitat: Forest and inland wetlands[38] Diet: Primarily eats insects, as well as reptiles, small mammals, and fruit[4][38] |
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pousargues's mongoose | D. dybowskii Pousargues, 1893 |
Central Africa |
Size: 24–30 cm (9–12 in) long, plus 16–22 cm (6–9 in) tail[4] Habitat: Forest, savanna, and grassland[39] Diet: Primarily eats invertebrates[4][39] |
DD
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Common dwarf mongoose | H. parvula Sundevall, 1847 Seven subspecies
|
Southern and eastern Africa |
Size: 18–23 cm (7–9 in) long, plus 14–19 cm (6–7 in) tail[4] Habitat: Savanna and grassland[40] Diet: Primarily eats arthropods, as well as small vertebrates[40] |
LC
|
| Ethiopian dwarf mongoose | H. hirtula Thomas, 1904 Five subspecies
|
Eastern Africa |
Size: 18–26 cm (7–10 in) long, plus 12–20 cm (5–8 in) tail[41] Habitat: Savanna, shrubland, and grassland[42] Diet: Primarily eats invertebrates[4][42] |
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liberian mongoose | L. kuhni Hayman, 1958 |
Western Africa |
Size: 42–55 cm (17–22 in) long, plus 18–21 cm (7–8 in) tail[4] Habitat: Forest[43] Diet: Primarily eats earthworms, as well as small vertebrates, insect larvae, and fruit[43] |
VU
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Banded mongoose | M. mungo Gmelin, 1788 Sixteen subspecies
|
Sub-Saharan Africa |
Size: 30–40 cm (12–16 in) long, plus 19–31 cm (7–12 in) tail[4] Habitat: Forest, savanna, shrubland, and grassland[44] Diet: Primarily eats insects, as well as other invertebrates, reptiles, amphibians, bird eggs, young birds, small mammals, and fruit[44] |
LC
|
| Gambian mongoose | M. gambianus Ogilby, 1835 |
Western Africa |
Size: 34–36 cm (13–14 in) long, plus 20–22 cm (8–9 in) tail[4] Habitat: Forest and savanna[45] Diet: Primarily eats insects, as well as lizards, mice, and snakes[4][45] |
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Meerkat | S. suricatta Schreber, 1776 Three subspecies
|
Southern Africa |
Size: 23–36 cm (9–14 in) long, plus 18–24 cm (7–9 in) tail[4] Habitat: Savanna, shrubland, grassland, and desert[46] Diet: Primarily eats invertebrates[46] |
LC
|
Prehistoric herpestids
In addition to extant herpestids, a number of prehistoric species have been discovered and classified as a part of herpestidae. There is no generally accepted classification of extinct herpestid species. In addition to being placed within extant genera in the extant subfamilies Herpestinae and Mungotinae, several have not been classified within a subfamily. The species listed here are based on data from the Paleobiology Database. Where available, the approximate time period the species was extant is given in millions of years before the present (Mya), also based on data from the Paleobiology Database.[47] All listed species are extinct; where a genus or subfamily within herpestidae comprises only extinct species, it is indicated with a dagger symbol ![]() .
.
- Subfamily Herpestinae
- Genus Herpestes (16 Mya–present)
- H. abdelalii (3.6–2.5 Mya)
- H. auropunctatus
- H. gracilis
- H. microdon
- H. rubrifons
- Genus Ichneumia (3.6 Mya–present)
- I. nims (3.6–2.5 Mya)
- Genus Herpestes (16 Mya–present)
- Subfamily Mungotinae
- Genus Crossarchus
- C. zebra
- Genus Crossarchus
- Unclassified
- Genus Kichechia
 (21–15 Mya)
(21–15 Mya)
- K. savagei (21–15 Mya)
- K. zamanae (21–15 Mya)
- Genus Legetetia
- Genus Ugandictis
 (21–15 Mya)
(21–15 Mya)
- U. napakensis (21–15 Mya)
- Genus Kichechia
References
- Patou, M.; Mclenachan, P. A.; Morley, C. G.; Couloux, A.; Jennings, A. P.; Veron, G. (2009). "Molecular phylogeny of the Herpestidae (Mammalia, Carnivora) with a special emphasis on the Asian Herpestes". Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution. 53 (1): 69–80. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2009.05.038. PMID 19520178.
- "Explore the Database". www.mammaldiversity.org. Retrieved 2021-07-08.
- Rapson, S.; Goldizen, A. W.; Seddon, J. M. (August 2012). "Species boundaries and possible hybridization between the black mongoose (Galerella nigrata) and the slender mongoose (Galerella sanguinea)". Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution. 65 (3): 831–839. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2012.08.005. PMID 22940151.
- Van Rompaey, H.; Colyn, M. (2014). Kingdon, J.; Hoffmann, M. (eds.). The Mammals of Africa. Vol. V. Carnivores, Pangolins, Equids and Rhinoceroses. Bloomsbury Publishing. pp. 326–381. ISBN 978-1-4081-8994-8.
- Do Linh San, E.; Angelici, F. M.; Maddock, A. H.; Baker, C. M.; Ray, J. (2015). "Atilax paludinosus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T41590A45204865. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-4.RLTS.T41590A45204865.en.
- Angelici, F. M.; Do Linh San, E. (2015). "Bdeogale nigripes". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T41592A45205243. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-4.RLTS.T41592A45205243.en.
- White, P. A.; Fischer, C.; Hausser, Y.; Foley, C.; Do Linh San, E. (2016). "Bdeogale crassicauda". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41591A97163568. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T41591A97163568.en.
- De Luca, W.; Rovero, F.; Do Linh San, E. (2015). "Bdeogale jacksoni". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T2675A45196818. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-4.RLTS.T2675A45196818.en.
- Do Linh San, E.; Cavallini, P.; Taylor, P. (2015). "Cynictis penicillata". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T41597A45205726. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-4.RLTS.T41597A45205726.en.
- Hunter, Luke; Barrett, Priscilla (2020). Field Guide to Carnivores of the World (2nd ed.). Bloomsbury Publishing. pp. 56–60. ISBN 978-1-4729-8267-4.
- Rapson, S.; Rathbun, G. B. (2015). "Herpestes flavescens". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T41599A45205933. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-4.RLTS.T41599A45205933.en.
- Bies, LeeAnn (2002). "Herpestes ichneumon". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Archived from the original on July 30, 2020. Retrieved September 8, 2020.
- Do Linh San, E.; Maddock, A. H.; Gaubert, P.; Palomares, F. (2016). "Herpestes ichneumon". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41613A45207211. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T41613A45207211.en.
- Gibbons, Sarah (2014). "Galerella pulverulenta". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Archived from the original on July 27, 2020. Retrieved September 8, 2020.
- Do Linh San, E.; Cavallini, P. (2015). "Herpestes pulverulentus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T41600A45205999. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-4.RLTS.T41600A45205999.en.
- Do Linh San, E.; Maddock, A. H. (2016). "Herpestes sanguineus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41606A45206143. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T41606A45206143.en.
- Taylor, M. E.; Do Linh San, E. (2016) [errata version of 2015 assessment]. "Herpestes ochraceus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T41605A45206073. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-4.RLTS.T41605A45206073.en.
- Do Linh San, E. (2015). "Ichneumia albicauda". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T41620A45208640. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-4.RLTS.T41620A45208640.en.
- Stuart, Chris; Stuart, Mathilde (2015). "Selous's Mongoose". Stuarts' Field Guide to Mammals of Southern Africa. Penguin Random House South Africa. ISBN 978-1-77584-266-8.
- Mateke, C. W.; Bird, T. L. F.; Swanepoel, L. H.; Do Linh San, E. (2016). "Paracynictis selousi". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41622A45209173. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T41622A45209173.en.
- White, P. A.; Mateke, C. W.; Bird, T. L. F.; Swanepoel, L. H.; Do Linh San, E. (2015). "Rhynchogale melleri". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T41623A45209275. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-4.RLTS.T41623A45209275.en.
- Mathai, J.; Hearn, A.; Brodie, J.; Wilting, A.; Duckworth, J. W.; Ross, J.; Holden, J.; Gemita, E.; Hon, J. (2015). "Herpestes semitorquatus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T41616A45208027. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-4.RLTS.T41616A45208027.en.
- Menon, Vivek (2014). "Carnivores". Indian Mammals: A Field Guide. Hachette India. ISBN 978-93-5009-761-8.
- Choudhury, A.; Timmins, R.; Chutipong, W.; Duckworth, J. W.; Mudappa, D.; Willcox, D. H. A. (2016) [errata version of 2015 assessment]. "Herpestes urva". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T41618A45208308. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-4.RLTS.T41618A45208308.en.
- Mudappa, D.; Jathanna, D. (2015). "Herpestes fuscus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T41612A45207051. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-4.RLTS.T41612A45207051.en.
- Mudappa, D.; Choudhury, A. (2016). "Herpestes edwardsii". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41611A45206787. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T41611A45206787.en.
- Smith, Andrew T.; Xie, Yan; Hoffmann, Robert S.; Lunde, Darrin; MacKinnon, John; Wilson, Don E.; Wozencraft, W. Chris, eds. (2010). A Guide to the Mammals of China. Princeton University Press. p. 415. ISBN 978-1-4008-3411-2.
- Chutipong, W.; Duckworth, J. W.; Timmins, R.; Willcox, D. H. A.; Ario, A. (2016). "Herpestes javanicus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T70203940A45207619. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T70203940A45207619.en.
- Mudappa, D.; Choudhury, A. (2016). "Herpestes smithii". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41617A45208195. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T41617A45208195.en.
- Payne, Junaidi; Francis, Charles M.; Phillipps, Karen (1985). A Field Guide to the Mammals of Borneo. Sabah Society. p. 287. ISBN 978-967-99947-1-1.
- Duckworth, J. W.; Mathai, J.; Ross, J.; Wilting, A. (2016). "Herpestes brachyurus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41610A45206655. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T41610A45206655.en.
- Mudappa, D.; Choudhury, A.; Punjabi, G. A. (2016). "Herpestes vitticollis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41619A45208503. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T41619A45208503.en.
- Ray, J.; Bahaa-el-din, L.; Angelici, F. M.; Do Linh San, E. (2015). "Herpestes naso". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T41615A45207915. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-4.RLTS.T41615A45207915.en.
- Angelici, F. M.; Do Linh San, E. (2015). "Crossarchus alexandri". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T41593A45205341. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-4.RLTS.T41593A45205341.en.
- Angelici, F. M.; Do Linh San, E. (2015). "Crossarchus ansorgei". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T41594A45205422. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-4.RLTS.T41594A45205422.en.
- Angelici, F. M.; Do Linh San, E. (2015). "Crossarchus obscurus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T41595A45205532. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-4.RLTS.T41595A45205532.en.
- Stuart, Chris (2017). "Cusimanses". Stuarts' Field Guide to the Larger Mammals of Africa. Penguin Random House South Africa. ISBN 978-1-77584-274-3.
- Angelici, F. M.; Do Linh San, E. (2016). "Crossarchus platycephalus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41596A45205626. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T41596A45205626.en.
- Aebischer, T.; Hickisch, R.; Woolgar, J.; Do Linh San, E. (2015). "Dologale dybowskii". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T41598A45205821. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-4.RLTS.T41598A45205821.en.
- Sharpe, L.; Kern, J.; Do Linh San, E. (2015). "Helogale parvula". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T41609A45206516. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-4.RLTS.T41609A45206516.en.
- Dybas, Mitchell (2013). "Helogale hirtula". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Archived from the original on July 31, 2020. Retrieved September 8, 2020.
- Do Linh San, E.; Hoffmann, M. (2015). "Helogale hirtula". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T41608A45206437. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-4.RLTS.T41608A45206437.en.
- Taylor, M. E.; Greengrass, E. J.; Dunham, A.; Do Linh San, E. (2016). "Liberiictis kuhni". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T11933A45198780. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T11933A45198780.en.
- Gilchrist, J. S.; Do Linh San, E. (2016). "Mungos mungo". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41621A45208886. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T41621A45208886.en.
- Sillero-Zubiri, C.; Do Linh San, E. (2016). "Mungos gambianus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T13922A45199653. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T13922A45199653.en.
- Jordan, N. R.; Do Linh San, E. (2015). "Suricata suricatta". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T41624A45209377. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-4.RLTS.T41624A45209377.en.
- "Fossilworks: Herpestidae". Paleobiology Database. University of Wisconsin–Madison. Retrieved December 17, 2021.
Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии


























