bio.wikisort.org - Animal
Lagomorpha is an order of placental mammals, comprising the hares, rabbits, and pikas. Members of this order are called lagomorphs. It currently comprises 107 extant species, which are grouped into 12 genera. Lagomorphs live on every major landmass and in a variety of habitats, especially forests, grasslands, shrublands, and rocky areas. They are generally small in size and come in two main groupings of body plans, the larger rabbit group and smaller pika group, ranging overall from the 11 cm (4 in) long Gansu pika to the 76 cm (30 in) long desert hare. The domestic rabbit subspecies of the European rabbit has been domesticated, resulting in a worldwide distribution.


Lagomorpha is divided into two families: Leporidae, comprising the hares and rabbits; and Ochotonidae, or the pikas. The 73 extant species of Leporidae are divided into 11 genera, though the majority of the species are placed into Lepus (hares) and Sylvilagus (cottontail rabbits); the 34 extant species of Ochotonidae are grouped into a single genus, Ochotona. The exact organization of the species is not fixed, with many recent proposals made based on molecular phylogenetic analysis. No lagomorph species have recently gone extinct, though some species are endangered and the riverine rabbit is critically endangered.
Conventions
Range maps are provided wherever possible; if a range map is not available, a description of the collective range of species in that genera is provided. Ranges are based on the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species unless otherwise noted. All extinct genera or species listed alongside extant species went extinct after 1500 CE, and are indicated by a dagger symbol "![]() ".
".
Classification

The order Lagomorpha consists of 107 extant species belonging to 12 genera. This does not include hybrid species or extinct prehistoric species. Modern molecular studies indicate that the 12 genera can be grouped into 2 families.[1]
Family Leporidae
- Genus Brachylagus (pygmy rabbit): one species
- Genus Bunolagus (riverine rabbit): one species
- Genus Caprolagus (hispid hare): one species
- Genus Lepus (hares): 33 species
- Genus Nesolagus (striped rabbits): two species
- Genus Oryctolagus (European rabbit): one species
- Genus Pentalagus (Amami rabbit): one species
- Genus Poelagus (Bunyoro rabbit): one species
- Genus Pronolagus (red rock hares): four species
- Genus Romerolagus (volcano rabbit): one species
- Genus Sylvilagus (cottontail rabbits): 27 species
Family Ochotonidae
- Genus Ochotona (pikas): 34 species
|
Lagomorphs
The following classification is based on the taxonomy described by the reference work Mammal Species of the World (2005), with augmentation by generally accepted proposals made since using molecular phylogenetic analysis.[2]
Family Leporidae
Members of the Leporidae family are called leporids, or colloquially hares and rabbits. Leporidae comprises 73 extant species, divided into 11 genera.
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brachylagus | Miller, 1900
One species
|
Western America (introduced in red)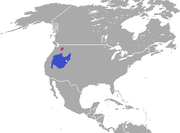 |
Size: 23–30 cm (9–12 in) long, plus 1–3 cm (0–1 in) tail[3]
Habitats: Shrubland and desert[4] Diet: Sagebrush, as well as grass and other plants[3] |
| Bunolagus | Thomas, 1929
One species
|
Southern South America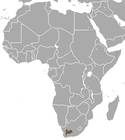 |
Size: 33–47 cm (13–19 in) long, plus 7–11 cm (3–4 in) tail[5]
Habitats: Shrubland[6] Diet: Shrubs as well as grass[6] |
| Caprolagus | Blyth, 1845
One species
|
Himalayas |
Size: 38–50 cm (15–20 in) long, plus 2–4 cm (1–2 in) tail[7]
Habitats: Grassland and inland wetlands[8] Diet: Grass as well as other plants[8] |
| Lepus (hare) |
Linnaeus, 1758
33 species
|
Africa, Asia, Europe, and North America | Size range: 28 cm (11 in) long, plus 5 cm (2 in) tail (Yarkand hare) to 76 cm (30 in) long (Desert hare)[9]
Habitats: Desert, coastal marine, inland wetlands, forest, shrubland, rocky areas, savanna, caves, and grassland[10] Diets: Wide variety of plants[10] |
| Nesolagus (striped rabbit) |
Major, 1899
Two species
|
Sumatra and the Annamite Range in Laos and Vietnam | Size range: 35 cm (14 in) long (Annamite striped rabbit) to 42 cm (17 in) long plus 17 cm (7 in) tail (Sumatran striped rabbit)[11]
Habitats: Forest[12] Diets: Various plants[12] |
| Oryctolagus | Lilljeborg, 1762
One species
|
Europe, southern South America, and Oceana (native in orange, introduced in purple) |
Size: 38–50 cm (15–20 in) long[13]
Habitats: Forest, savanna, shrubland, and grassland[14] Diet: Grass, leaves, buds, bark, and roots[13] |
| Pentalagus | Lyon, 1904
One species
|
Southern tip of Japan |
Size: 39–53 cm (15–21 in) long, plus 2–4 cm (1–2 in) tail[15]
Habitats: Forest, shrubland, and intertidal marine[16] Diet: Herbs, shrubs, and acorns[16] |
| Poelagus | St. Leger, 1932
One species
|
Central Africa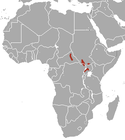 |
Size: 45–50 cm (18–20 in) long, plus 4–5 cm (2–2 in) tail[17]
Habitats: Forest, savanna, and rocky areas[18] Diet: Grass, shrubs, forbs, and tubers[17] |
| Pronolagus (red rock hare) |
Lyon, 1904
Four species
|
Southern Africa | Size range: 38 cm (15 in) long, plus 5 cm (2 in) tail (Hewitt's red rock hare) to 56 cm (22 in) long plus 11 cm (4 in) tail (Natal red rock hare)[19]
Habitats: Desert, grassland, shrubland, and rocky areas[20] Diets: Grass, herbs, and shrubs[20] |
| Romerolagus | Merriam, 1896
One species
|
Southern Mexico |
Size: 27–32 cm (11–13 in) long, plus 1–4 cm (0–2 in) tail[21]
Habitats: Forest and grassland[22] Diet: Grass[21] |
| Sylvilagus (cottontail rabbit) |
Gray, 1867
27 species
|
North America and South America | Size range: 21 cm (8 in) long, plus 1 cm (0 in) tail (Tres Marias cottontail) to 55 cm (22 in) long plus 8 cm (3 in) tail (Swamp rabbit)[23]
Habitats: Desert, inland wetlands, intertidal marine, forest, shrubland, rocky areas, savanna, and grassland[24] Diets: Wide variety of plants[24] |
Family Ochotonidae
Members of the Ochotonidae family are called ochotonids, or colloquially pikas. Ochotonidae comprises 34 extant species, which are all contained within a single genus.
| Name | Authority and species | Range | Size and ecology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ochotona (pika) |
Link, 1795
34 species
|
Asia and western North America | Size range: 11 cm (4 in) long (Gansu pika) to 29 cm (11 in) long (Northern pika)[25]
Habitats: Desert, forest, shrubland, rocky areas, and grassland[26] Diets: Wide variety of plants[26] |
References
- Matthee, C. A.; Van Vuuren, B. J.; Bell, D.; Robinson, T. J. (2004). "A Molecular Supermatrix of the Rabbits and Hares (Leporidae) Allows for the Identification of Five Intercontinental Exchanges During the Miocene". Systematic Biology. 53 (3): 433–477. doi:10.1080/10635150490445715.
- Wilson, pp. 185–211
- Rohde, Ashley (2006). "Brachylagus idahoensis". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Rachlow, J.; Becker, P. A.; Shipley, L. (2016). "Brachylagus idahoensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T2963A45176206. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T2963A45176206.en.
- Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 91
- Collins, K.; Bragg, C.; Birss, C. (2019). "Bunolagus monticularis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T3326A45176532. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T3326A45176532.en.
- Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 94
- Aryal, A.; Yadav, B. (2019). "Caprolagus hispidus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T3833A45176688. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T3833A45176688.en.
- Lepus sizes:
- Antelope jackrabbit: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 160
- Tamaulipas jackrabbit: Vargas, K.; Brown, D.; Wisely, E.; Culver, M. (May 27, 2019). "Reinstatement of the Tamaulipas white-sided jackrabbit, Lepus altamirae, based on DNA sequence data". Revista Mexicana de Biodiversidad. 90. doi:10.22201/ib.20078706e.2019.90.2520. ISSN 2007-8706. S2CID 191148222.
- Snowshoe hare: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 163
- Arctic hare: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 166
- Japanese hare: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 169
- Black-tailed jackrabbit: Ballenger, Liz (1999). "Lepus californicus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- White-sided jackrabbit: Dharmani, Aarti (2000). "Lepus callotis". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Cape hare: Begnoche, Dana (2002). "Lepus capensis". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved November 5, 2021.
- Broom hare: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 179
- Yunnan hare: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 222
- Korean hare: Faigle, Stacy (2014). "Lepus coreanus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Corsican hare: Cooper, Thomas (2015). "Lepus corsicanus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- European hare: Vu, Alan (2001). "Lepus europaeus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Ethiopian hare: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 190
- Tehuantepec jackrabbit: Warlin, Sierra (2013). "Lepus flavigularis". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Granada hare: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 193
- Abyssinian hare: Nickolai, Ashley (2014). "Lepus habessinicus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Hainan hare: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 197
- Black jackrabbit: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 198
- Manchurian hare: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 200
- Indian hare: Lundrigan, Barbara; Foote, Sarah (2003). "Lepus nigricollis". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Woolly hare: Ng, Jarita (2011). "Lepus oiostolus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Alaskan hare: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 204
- Burmese hare: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 205
- Scrub hare: Kushnereit, Aimee (2004). "Lepus saxatilis". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved November 5, 2021.
- Chinese hare: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 96
- Ethiopian highland hare: Kingdon, p. 310
- Desert hare: Sullivan, Shaunna (2013). "Lepus tibetanus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Mountain hare: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, pp. 212–213
- Tolai hare: Smith, Xie, et al., p. 291
- White-tailed jackrabbit: Verts, Carraway, p. 142
- African savanna hare: Riegler, Donald (2013). "Lepus microtis". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved November 5, 2021.
- Yarkand hare: Smith, Xie, et al., p. 292
- Lepus habitats and diets:
- Antelope jackrabbit: Lorenzo, C.; Brown, D. E. (2019). "Lepus alleni". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41272A45185265. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41272A45185265.en.
- Tamaulipas jackrabbit: Vargas, K.; Brown, D.; Wisely, E.; Culver, M. (May 27, 2019). "Reinstatement of the Tamaulipas white-sided jackrabbit, Lepus altamirae, based on DNA sequence data". Revista Mexicana de Biodiversidad. 90. doi:10.22201/ib.20078706e.2019.90.2520. ISSN 2007-8706. S2CID 191148222.
- Snowshoe hare: Mills, L.; Smith, A. T. (2019). "Lepus americanus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41273A45185466. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41273A45185466.en.
- Arctic hare: Smith, A. T.; Johnston, C. H. (2019). "Lepus arcticus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41274A45185887. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41274A45185887.en.
- Japanese hare: Yamada, F.; Smith, A. T. (2019). "Lepus brachyurus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41275A45186064. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41275A45186064.en.; Holmberg, Jennifer (2014). "Lepus brachyurus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved November 5, 2021.
- Black-tailed jackrabbit: Brown, D. E.; Lorenzo, C.; Álvarez-Castañeda, S. T. (2019). "Lepus californicus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41276A45186309. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41276A45186309.en.; Ballenger, Liz (1999). "Lepus californicus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- White-sided jackrabbit: Brown, D. E.; Smith, A. T. (2019). "Lepus callotis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T11792A45177499. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-2.RLTS.T11792A45177499.en.; Dharmani, Aarti (2000). "Lepus callotis". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Cape hare: Johnston, C. H.; Robinson, T. J.; Child, M. F.; Relton, C. (2019). "Lepus capensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41277A45186750. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41277A45186750.en.
- Broom hare: Ballesteros, F.; Smith, A. T. (2019). "Lepus castroviejoi". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T11797A503908. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-2.RLTS.T11797A503908.en.
- Yunnan hare: Smith, A. T.; Johnston, C. H. (2019). "Lepus comus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41278A45187160. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41278A45187160.en.; Smith, Xie, et al., p. 287
- Korean hare: Jo, Y.-S.; Smith, A. T. (2019) [errata version of 2019 assessment]. "Lepus coreanus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41279A161750768. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41279A161750768.en.; Faigle, Stacy (2014). "Lepus coreanus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Corsican hare: Randi, E.; Riga, F. (2019). "Lepus corsicanus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41305A2952954. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-2.RLTS.T41305A2952954.en.; Cooper, Thomas (2015). "Lepus corsicanus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- European hare: Hacklander, K.; Schai-Braun, S. (2019). "Lepus europaeus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41280A45187424. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41280A45187424.en.; Vu, Alan (2001). "Lepus europaeus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Ethiopian hare: Johnston, C. H.; Tolesa, Z. (2019). "Lepus fagani". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T11798A45178437. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T11798A45178437.en.
- Tehuantepec jackrabbit: Lorenzo, C.; Smith, A. T. (2019). "Lepus flavigularis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T11790A45176906. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-3.RLTS.T11790A45176906.en.; Warlin, Sierra (2013). "Lepus flavigularis". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Granada hare: Soriguer, R.; Carro, F. (2019). "Lepus granatensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41306A2953195. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41306A2953195.en.; Weaver, Derek (2013). "Lepus granatensis". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved November 5, 2021.
- Abyssinian hare: Johnston, C. H.; Tolesa, Z. (2019). "Lepus habessinicus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41289A45189637. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41289A45189637.en.; Nickolai, Ashley (2014). "Lepus habessinicus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Hainan hare: Smith, A. T.; Johnston, C. (2016). "Lepus hainanus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T11793A45177783. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T11793A45177783.en.; Lundberg, Annette (2013). "Lepus hainanus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved November 5, 2021.
- Black jackrabbit: Lorenzo, C.; Johnston, C. H. (2019). "Lepus insularis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T11794A45177986. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-3.RLTS.T11794A45177986.en.; Mejia, Joseph R. (1999). "Lepus insularis". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Manchurian hare: Smith, A. T.; Johnston, C. H. (2019). "Lepus mandshuricus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41281A45187882. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41281A45187882.en.; Smith, Xie, et al., p. 289
- Indian hare: Nameer, P. O.; Smith, A. T. (2019). "Lepus nigricollis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41282A45188041. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41282A45188041.en.; Lundrigan, Barbara; Foote, Sarah (2003). "Lepus nigricollis". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Woolly hare: Smith, A. T.; Johnston, C. H. (2019). "Lepus oiostolus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41283A45188432. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41283A45188432.en.; Ng, Jarita (2011). "Lepus oiostolus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Alaskan hare: Smith, A. T.; Johnston, C. H. (2019). "Lepus othus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T11795A45178124. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T11795A45178124.en.
- Burmese hare: Johnston, C. H.; Smith, A. T. (2019). "Lepus peguensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41284A45188632. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41284A45188632.en.
- Scrub hare: Robinson, T. J.; Child, M. F.; Relton, C.; Johnston, C. H. (2019). "Lepus saxatilis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41285A45188827. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41285A45188827.en.
- Chinese hare: Smith, A. T.; Johnston, C. H. (2019). "Lepus sinensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41286A45189035. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41286A45189035.en.
- Ethiopian highland hare: Johnston, C. H.; Tolesa, Z. (2019). "Lepus starcki". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41287A45189235. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41287A45189235.en.
- Desert hare: Smith, A. T.; Johnston, C. H. (2019). "Lepus tibetanus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41307A45193298. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41307A45193298.en.; Sullivan, Shaunna (2013). "Lepus tibetanus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Mountain hare: Smith, A. T.; Johnston, C. H. (2019). "Lepus timidus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T11791A45177198. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T11791A45177198.en.; Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, pp. 212–213
- Tolai hare: Smith, A. T.; Johnston, C. H. (2019). "Lepus tolai". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41308A45193447. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41308A45193447.en.
- White-tailed jackrabbit: Brown, D. E.; Smith, A. T. (2019). "Lepus townsendii". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41288A45189364. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41288A45189364.en.
- African savanna hare: Johnston, C. H.; Robinson, T. J.; Relton, C.; Child, M. F.; Smith, A. T. (2019). "Lepus victoriae". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41879A45194215. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41879A45194215.en.
- Yarkand hare: Smith, A. T.; Johnston, C. H. (2017) [errata version of 2016 assessment]. "Lepus yarkandensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T11796A115103994. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T11796A45178274.en.
- Nesolagus sizes:
- Sumatran striped rabbit: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 96
- Annamite striped rabbit: Hoedl, Amanda (2012). "Nesolagus timminsi". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Nesolagus habitats and diets:
- Sumatran striped rabbit: McCarthy, J.; Holden, J.; Martyr, D.; McCarthy, K. (2019). "Nesolagus netscheri". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T14662A45178557. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-2.RLTS.T14662A45178557.en.
- Annamite striped rabbit: Tilker, A.; Timmins, R. J.; Nguyen The Truong, A.; Coudrat, C. N. Z.; Gray, T.; Le Trong Trai, Willcox; D. H. A., Abramov; A. V., Wilkinson; N., Steinmetz; R. (2019). "Nesolagus timminsi". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41209A45181925. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41209A45181925.en.; Hoedl, Amanda (2012). "Nesolagus timminsi". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Tislerics, Ati (2000). "Oryctolagus cuniculus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Villafuerte, R.; Delibes-Mateos, M. (2020) [errata version of 2019 assessment]. "Oryctolagus cuniculus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41291A170619657. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-3.RLTS.T41291A170619657.en.
- Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 105
- Yamada, F. and Smith; A. T. (2016). "Pentalagus furnessi". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T16559A45180151. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T16559A45180151.en.
- Portman, Charles (2004). "Poelagus marjorita". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Johnston, C. H.; Smith, A. T. (2019). "Poelagus marjorita". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41292A45189965. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41292A45189965.en.
- Pronolagus sizes:
- Natal red rock hare: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 109
- Jameson's red rock hare: Bartel, Riley (2015). "Pronolagus randensis". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Smith's red rock hare: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 112
- Hewitt's red rock hare: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 113
- Pronolagus habitats and diets:
- Natal red rock hare: Child, M. F.; Matthee, C. M.; Robinson, T. J. (2019). "Pronolagus crassicaudatus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41293A45190100. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41293A45190100.en.; Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 109
- Jameson's red rock hare: Child, M. F.; Matthee, C. M.; Robinson, T. J. (2019). "Pronolagus randensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41294A45190258. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41294A45190258.en.; Bartel, Riley (2015). "Pronolagus randensis". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Smith's red rock hare: Child, M. F.; Matthee, C. M.; Robinson, T. J. (2019). "Pronolagus rupestris". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41295A45190415. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41295A45190415.en.; Sekine, Ryo (2000). "Pronolagus rupestris". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved November 8, 2021.
- Hewitt's red rock hare: Robinson, T. J.; Child, M. F.; Matthee, C. M. (2019). "Pronolagus saundersiae". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T136713A45194657. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T136713A45194657.en.; Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 113
- Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, pp. 114–115
- Velázquez, A.; Guerrero, J. A. (2019). "Romerolagus diazi". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T19742A45180356. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-2.RLTS.T19742A45180356.en.
- Sylvilagus sizes:
- Andean tapeti: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 127
- Bogota tapeti, Common tapeti, Ecuadorian tapeti, Fulvous tapeti, Central American tapeti, Northern tapeti, Nicefor's tapeti, Colombian tapeti, Santa Marta tapeti, Western tapeti: Ruedas, L. A.; Marques, S. S.; French, J. H.; Platt II, R. N.; Salazar-Bravo, J.; Mora, J. M.; Thompson, C. W. (October 22, 2019). "Taxonomy of the Sylvilagus brasiliensis complex in Central and South America (Lagomorpha: Leporidae)". Journal of Mammalogy. 100 (5): 1599–1630. doi:10.1093/jmammal/gyz126.
- Swamp rabbit: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 118
- Desert cottontail: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 120
- Brush rabbit: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 123
- Mexican cottontail: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 132
- Dice's cottontail: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 136
- Eastern cottontail: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 138
- Tres Marias cottontail: Viswanathan, Lata (2000). "Sylvilagus graysoni". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Robust cottontail: Diersing, V. E.; Wilson, D. E. (June 17, 2021). "Systematics of the mountain-inhabiting cottontails (Sylvilagus) from southwestern United States and northern Mexico (Mammalia: Lagomorpha: Leporidae)". Proceedings of the Biological Society of Washington. 134 (1): 42–79. doi:10.2988/006-324X-134.1.42.
- Omilteme cottontail: Lorenzo, C.; Brown, D. E.; Lanier, H. C. (2019). "Sylvilagus insonus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T21207A45180771. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-2.RLTS.T21207A45180771.en.
- Mountain cottontail: Feldhamer, Carlyle, Chapman, p. 104
- Appalachian cottontail: Kurta, p. 96
- Marsh rabbit: Thompson, Leah (2008). "Sylvilagus palustris". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Suriname tapeti: Ruedas, L. A. (May 2017). "A new species of cottontail rabbit (Lagomorpha: Leporidae: Sylvilagus) from Suriname, with comments on the taxonomy of allied taxa from northern South America". Journal of Mammalogy. doi:10.1093/jmammal/gyx048.
- Coastal tapeti: Ruedas, L. A.; Marques, S. S.; French, J. H.; Platt II, R. N.; Salazar-Bravo, J.; Mora, J. M.; Thompson, C. W. (February 9, 2017). "A Prolegomenon to the Systematics of South American Cottontail Rabbits (Mammalia, Lagomorpha Leporidae: Sylvilagus)". Miscellaneous Publications of the Museum of Zoology, University of Michigan. 205. ISSN 0076-8405.
- New England cottontail: Berenson, Tessa (2012). "Sylvilagus transitionalis". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Venezuelan lowland rabbit: Durant, P.; Guevara, M. A. (March 2001). "A new rabbit species (Sylvilagus, Mammalia: Leporidae) from the lowlands of Venezuela". Revista de Biología Tropical. 49 (1).
- Sylvilagus habitats and diets:
- Andean tapeti: Ruedas, L. A.; Smith, A. T. (2020) [errata version of 2019 assessment]. "Sylvilagus andinus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T142541491A165117323. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-2.RLTS.T142541491A165117323.en.
- Bogota tapeti, Ecuadorian tapeti, Fulvous tapeti, Northern tapeti, Nicefor's tapeti, Colombian tapeti, Santa Marta tapeti, Western tapeti: Ruedas, L. A.; Marques, S. S.; French, J. H.; Platt II, R. N.; Salazar-Bravo, J.; Mora, J. M.; Thompson, C. W. (October 22, 2019). "Taxonomy of the Sylvilagus brasiliensis complex in Central and South America (Lagomorpha: Leporidae)". Journal of Mammalogy. 100 (5): 1599–1630. doi:10.1093/jmammal/gyz126.
- Swamp rabbit: Lanier, H. C.; Nielsen, C. (2019). "Sylvilagus aquaticus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41296A45190578. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41296A45190578.en.; Roszko, Annamarie (2007). "Sylvilagus aquaticus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Desert cottontail: Smith, A. T.; Brown, D. E. (2019). "Sylvilagus audubonii". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41297A45190821. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41297A45190821.en.
- Brush rabbit: Kelly, P. A.; Lorenzo, C.; Alvarez-Castaneda, S. T. (2019). "Sylvilagus bachmani". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41302A45192710. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41302A45192710.en.
- Common tapeti: Ruedas, L. A.; Marques, S. S.; French, J. H.; Platt II, R. N.; Salazar-Bravo, J.; Mora, J. M.; Thompson, C. W. (October 22, 2019). "Taxonomy of the Sylvilagus brasiliensis complex in Central and South America (Lagomorpha: Leporidae)". Journal of Mammalogy. 100 (5): 1599–1630. doi:10.1093/jmammal/gyz126.; Ruedas, L.; Smith, A. T. (2019). "Sylvilagus brasiliensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T87491102A45191186. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-2.RLTS.T87491102A45191186.en.
- Mexican cottontail: Lorenzo, C.; Lanier, H. C. (2019). "Sylvilagus cunicularius". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T21211A45181292. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T21211A45181292.en.; Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 132
- Dice's cottontail: Mora, J. M.; Ruedas, L. and Smith; A. T. (2016). "Sylvilagus dicei". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T21209A45180947. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T21209A45180947.en.; Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 136
- Eastern cottontail: Nielsen, C.; Lanier, H. C. (2019). "Sylvilagus floridanus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41299A45191626. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41299A45191626.en.
- Central American tapeti: Ruedas, L. A.; Marques, S. S.; French, J. H.; Platt II, R. N.; Salazar-Bravo, J.; Mora, J. M.; Thompson, C. W. (October 22, 2019). "Taxonomy of the Sylvilagus brasiliensis complex in Central and South America (Lagomorpha: Leporidae)". Journal of Mammalogy. 100 (5): 1599–1630. doi:10.1093/jmammal/gyz126.; Ruedas, L.; Smith, A. T. (2019). "Sylvilagus gabbi". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T87491157A87491160. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T87491157A87491160.en.
- Tres Marias cottontail: Lorenzo, C.; Lanier, H. C. (2019). "Sylvilagus graysoni". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T21206A45180643. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-3.RLTS.T21206A45180643.en.; Viswanathan, Lata (2000). "Sylvilagus graysoni". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Robust cottontail: Diersing, V. E.; Wilson, D. E. (June 17, 2021). "Systematics of the mountain-inhabiting cottontails (Sylvilagus) from southwestern United States and northern Mexico (Mammalia: Lagomorpha: Leporidae)". Proceedings of the Biological Society of Washington. 134 (1): 42–79. doi:10.2988/006-324X-134.1.42.
- Omilteme cottontail: Lorenzo, C.; Brown, D. E.; Lanier, H. C. (2019). "Sylvilagus insonus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T21207A45180771. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-2.RLTS.T21207A45180771.en.
- Mountain cottontail: Smith, A. T.; Brown, D. E. (2019). "Sylvilagus nuttallii". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41300A45192243. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41300A45192243.en.; "Mountain Cottontail — Sylvilagus nuttallii". Montana Field Guide. Montana Department of Fish, Wildlife and Parks. Retrieved November 8, 2021.
- Appalachian cottontail: Barry, R.; Lanier, H. C. (2019). "Sylvilagus obscurus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41301A45192437. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-2.RLTS.T41301A45192437.en.
- Marsh rabbit: McCleery, R.; Lanier, H. C. (2019). "Sylvilagus palustris". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41303A45192995. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41303A45192995.en.; Thompson, Leah (2008). "Sylvilagus palustris". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Suriname tapeti: Ruedas, L. A. (May 2017). "A new species of cottontail rabbit (Lagomorpha: Leporidae: Sylvilagus) from Suriname, with comments on the taxonomy of allied taxa from northern South America". Journal of Mammalogy. doi:10.1093/jmammal/gyx048.
- Coastal tapeti: Ruedas, L. A.; Marques, S. S.; French, J. H.; Platt II, R. N.; Salazar-Bravo, J.; Mora, J. M.; Thompson, C. W. (February 9, 2017). "A Prolegomenon to the Systematics of South American Cottontail Rabbits (Mammalia, Lagomorpha Leporidae: Sylvilagus)". Miscellaneous Publications of the Museum of Zoology, University of Michigan. 205. ISSN 0076-8405.
- New England cottontail: Litvaitis, J.; Lanier, H. C. (2019). "Sylvilagus transitionalis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T21212A45181534. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-2.RLTS.T21212A45181534.en.; Berenson, Tessa (2012). "Sylvilagus transitionalis". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 22, 2021.
- Venezuelan lowland rabbit: Johnston, C. H.; Smith, A. T. (2019). "Sylvilagus varynaensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41311A45193972. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41311A45193972.en.
- Ochotona sizes:
- Alpine pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 31
- Helan Shan pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 33
- Gansu pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 35
- Collared pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 36
- Korean pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 40
- Plateau pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 40
- Daurian pika: Ciwko, Erin (2014). "Ochotona dauurica". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 17, 2021.
- Chinese red pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 46
- Flat-headed pika: Liu, S.; Jin, W.; Liao, R.; Sun, Z. (2017). "Phylogenetic study of Ochotona based on mitochondrial Cyt b and morphology with a description of one new subgenus and five new species". Acta Theriologica Sinica. doi:10.16829/j.slxb.201701001.
- Forrest's pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 47
- Glover's pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, pp. 48–49
- Hoffmann's pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 50
- Yellow pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 83; Liu, S.; Jin, W.; Liao, R.; Sun, Z. (2017). "Phylogenetic study of Ochotona based on mitochondrial Cyt b and morphology with a description of one new subgenus and five new species". Acta Theriologica Sinica. doi:10.16829/j.slxb.201701001.
- Northern pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, pp. 51–52
- Ili pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 54
- Koslov's pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 56
- Ladak pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, pp. 57–58
- Large-eared pika: Jordan, Dana (2005). "Ochotona macrotis". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 17, 2021.
- Manchurian pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, pp. 60–61
- Nubra pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 62
- Kazakh pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, pp. 63–64
- Pallas's pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 66
- American pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, pp. 68–70
- Steppe pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 73
- Qionglai pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 83; Liu, S.; Jin, W.; Liao, R.; Sun, Z. (2017). "Phylogenetic study of Ochotona based on mitochondrial Cyt b and morphology with a description of one new subgenus and five new species". Acta Theriologica Sinica. doi:10.16829/j.slxb.201701001.
- Royle's pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, pp. 75–76
- Afghan pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 77
- Turkestan red pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 80
- Sacred pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 83; Liu, S.; Jin, W.; Liao, R.; Sun, Z. (2017). "Phylogenetic study of Ochotona based on mitochondrial Cyt b and morphology with a description of one new subgenus and five new species". Acta Theriologica Sinica. doi:10.16829/j.slxb.201701001.
- Sikkim pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 83; Liu, S.; Jin, W.; Liao, R.; Sun, Z. (2017). "Phylogenetic study of Ochotona based on mitochondrial Cyt b and morphology with a description of one new subgenus and five new species". Acta Theriologica Sinica. doi:10.16829/j.slxb.201701001.
- Tsing-ling pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 82
- Moupin pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 83
- Thomas's pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 84
- Turuchan pika: Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 86
- Ochotona habitats and diets:
- Alpine pika: Smith, A. T.; Cook, J. (2016). "Ochotona alpina". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41255A45182115. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T41255A45182115.en.
- Helan Shan pika: Smith, A. T.; Li, W. (2016). "Ochotona argentata". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41986A45194521. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T41986A45194521.en.
- Gansu pika: Smith, A. T.; Liu, S. (2016). "Ochotona cansus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41256A45182335. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T41256A45182335.en.
- Collared pika: Lanier, H. and Hik; D. (2016). "Ochotona collaris". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41257A45182533. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T41257A45182533.en.
- Korean pika: Smith, A. T.; Jo, Y.-S. (2019) [errata version of 2016 assessment]. "Ochotona coreana". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T87948071A161750319. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T87948071A161750319.en.
- Plateau pika: Smith, A. T. and Liu; S. (2019) [amended version of 2016 assessment]. "Ochotona curzoniae". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41258A160699229. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-3.RLTS.T41258A160699229.en.
- Daurian pika: Smith, A. T.; Cook, J. (2016). "Ochotona dauurica". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41259A45182905. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T41259A45182905.en.; Ciwko, Erin (2014). "Ochotona dauurica". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 17, 2021.
- Chinese red pika: Smith, A. T.; Lissovsky, A. (2016). "Ochotona erythrotis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41260A45183115. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T41260A45183115.en.
- Flat-headed pika: Liu, S.; Jin, W.; Liao, R.; Sun, Z. (2017). "Phylogenetic study of Ochotona based on mitochondrial Cyt b and morphology with a description of one new subgenus and five new species". Acta Theriologica Sinica. doi:10.16829/j.slxb.201701001.
- Forrest's pika: Smith, A. T.; Liu, S. (2016). "Ochotona forresti". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T15048A45178927. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T15048A45178927.en.
- Glover's pika: Smith, A. T.; Liu, S. (2016). "Ochotona gloveri". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41261A45183256. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T41261A45183256.en.; Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, pp. 48–49
- Hoffmann's pika: Smith, A. T. and Lissovsky; A. (2016). "Ochotona hoffmanni". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T40800A45181807. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T40800A45181807.en.; Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 50
- Yellow pika: Smith, A. T.; Liu, S. (2016). "Ochotona thibetana". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41271A45185018. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T41271A45185018.en.
- Northern pika: Smith, A. T.; Lissovsky, A. (2016). "Ochotona hyperborea". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T87948061A45183490. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T87948061A45183490.en.; Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, pp. 51–52
- Ili pika: Li, W.; Smith, A. T. (2019). "Ochotona iliensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T15050A45179204. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T15050A45179204.en.; Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 54
- Koslov's pika: Li, W.; Smith, A. T. (2019). "Ochotona koslowi". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T15046A45178669. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T15046A45178669.en.
- Ladak pika: Smith, A. T.; Li, W. (2016). "Ochotona ladacensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41264A45183725. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T41264A45183725.en.; Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, pp. 57–58
- Large-eared pika: Smith, A. T.; Lissovsky, A. (2016). "Ochotona macrotis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41265A45183918. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T41265A45183918.en.; Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 59
- Manchurian pika: Smith, A. T.; Lissovsky, A. (2016). "Ochotona mantchurica". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T87948094A87948100. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T87948094A87948100.en.; Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, pp. 60–61
- Nubra pika: Smith, A. T.; Li, W. (2016). "Ochotona nubrica". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T15051A45179343. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T15051A45179343.en.; Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 62
- Kazakh pika: Smith, A. T.; Lissovsky, A. (2016). "Ochotona opaca". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T99892252A99892261. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T99892252A99892261.en.; Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, pp. 63–64
- Pallas's pika: Lissovsky, A.; Smith, A. T. (2016). "Ochotona pallasii". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T99890206A45184094. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T99890206A45184094.en.; DeMers, Anna (2007). "Ochotona pallasi". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Retrieved October 17, 2021.
- American pika: Smith, A. T. and Beever; E. (2016). "Ochotona princeps". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41267A45184315. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T41267A45184315.en.; Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, pp. 68–70
- Steppe pika: Smith, A. T.; Lissovsky, A. (2016). "Ochotona pusilla". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T15052A45179445. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T15052A45179445.en.; Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, p. 73
- Qionglai pika: Smith, A. T.; Liu, S. (2016). "Ochotona thibetana". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41271A45185018. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T41271A45185018.en.
- Royle's pika: Smith, A. T. and Bhattacharyya; S. (2016). "Ochotona roylei". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41268A45184591. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T41268A45184591.en.; Smith, Johnston, Alves, Hackländer, pp. 75–76
- Afghan pika: Smith, A. T.; Johnston, C. (2016). "Ochotona rufescens". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41269A45184750. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T41269A45184750.en.
- Turkestan red pika: Smith, A. T.; Lissovsky, A. (2016). "Ochotona rutila". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41270A45184897. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T41270A45184897.en.
- Sacred pika: Smith, A. T.; Liu, S. (2016). "Ochotona thibetana". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41271A45185018. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T41271A45185018.en.
- Sikkim pika: Smith, A. T.; Liu, S. (2016). "Ochotona thibetana". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41271A45185018. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T41271A45185018.en.
- Tsing-ling pika: Smith, A. T. and Lissovsky; A. (2016). "Ochotona syrinx". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T87948175A87948187. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T87948175A87948187.en.
- Moupin pika: Smith, A. T.; Liu, S. (2016). "Ochotona thibetana". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41271A45185018. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T41271A45185018.en.
- Thomas's pika: Smith, A. T.; Liu, S. (2019). "Ochotona thomasi". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T15053A45179577. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T15053A45179577.en.
- Turuchan pika: Smith, A. T. and Lissovsky; A. (2016). "Ochotona turuchanensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41503A45194115. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T41503A45194115.en.
Sources
- Feldhamer, George A.; Thompson, Bruce Carlyle; Chapman, Joseph A. (2003). Wild Mammals of North America. Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 978-0-8018-7416-1.
- Kingdon, Jonathan (2015). The Kingdon Field Guide to African Mammals (Second ed.). Bloomsbury Publishing. ISBN 978-1-4729-2531-2.
- Kurta, Allen (1995). Mammals of the Great Lakes Region. University of Michigan Press. ISBN 978-0-472-06497-7.
- Smith, Andrew T.; Johnston, Charlotte H.; Alves, Paolo C.; Hackländer, Klaus, eds. (2018). Lagomorphs: Pikas, Rabbits, and Hares of the World. Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 978-1-4214-2340-1.
- Smith, Andrew T.; Xie, Yan; Hoffmann, Robert S.; Lunde, Darrin; MacKinnon, John; Wilson, Don E.; Wozencraft, W. Chris, eds. (2010). A Guide to the Mammals of China. Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-1-4008-3411-2.
- Verts, B. J.; Carraway, Leslie N. (1998). Land Mammals of Oregon. University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-21199-5.
- Wilson, Don E., ed. (2005). Mammal Species of the World. Vol. 1 (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0.
Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии










