bio.wikisort.org - Plant
This is a list of plant species that, when consumed by humans, are known or suspected to produce psychoactive effects: changes in nervous system function that alter perception, mood, consciousness, cognition or behavior. Many of these plants are used intentionally as psychoactive drugs, for medicinal, religious, and/or recreational purposes. Some have been used ritually as entheogens for millennia.[1][2]
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages)
|


The plants are listed according to the specific psychoactive chemical substances they contain; many contain multiple known psychoactive compounds.
Cannabinoids

Species of the genus Cannabis, known colloquially as marijuana, including Cannabis sativa and Cannabis indica, is a popular psychoactive plant that is often used medically and recreationally. The principal psychoactive substance in Cannabis, tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), contains no nitrogen, unlike many (but not all) other psychoactive substances[lower-alpha 1] and is not an indole, tryptamine, phenethylamine, anticholinergic (deliriant) or dissociative drug. THC is just one of more than 100 identified cannabinoid compounds in Cannabis, which also include cannabinol (CBN) and cannabidiol (CBD).
Cannabis plants vary widely, with different strains producing dynamic balances of cannabinoids (THC, CBD, etc.) and yielding markedly different effects. Popular strains are often hybrids of C. sativa and C. indica.
The medicinal effects of cannabis are widely studied, and are active topics of research both at universities and private research firms. Many jurisdictions have laws regulating or prohibiting the cultivation, sale and/or use of medical and recreational cannabis.[citation needed]
Tryptamines

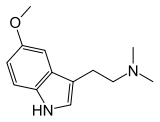



Many of the psychedelic plants contain dimethyltryptamine (DMT), or other tryptamines, which are either snorted (Virola, Yopo snuffs), vaporized, or drunk with MAOIs (Ayahuasca). It cannot simply be eaten as it is not orally active without an MAOI and it needs to be extremely concentrated to be vaporized.
Acanthaceae
Species, Alkaloid content, where given, refers to dried material
- Fittonia albivenis, a common ornamental plant from South America.
Aceraceae
- Acer saccharinum (Silver Maple Tree) was found to contain the indole alkaloid gramine (not active and extremely toxic) 0.05% in the leaves, so it is possible that other members of this plant family contain active compounds.[3]
Aizoaceae
- Delosperma acuminatum, DMT, 5-MeO-DMT[4][unreliable source?]
- Delosperma cooperi, DMT, 5-MeO-DMT[4]
- Delosperma ecklonis, DMT[4]
- Delosperma esterhuyseniae, DMT[4]
- Delosperma hallii, 5-MeO-DMT[4]
- Delosperma harazianum, DMT, 5-MeO-DMT[4]
- Delosperma harazianum
Shibam, DMT[4]
- Delosperma harazianum
- Delosperma hirtum, DMT[4]
- Delosperma hallii
aff. litorale
- Delosperma hallii
- Delosperma lydenbergense, DMT, 5-MeO-DMT[4]
- Delosperma nubigenum, 5-MeO-DMT[4]
- Delosperma pageanum, DMT, 5-MeO-DMT[4]
- Delosperma pergamentaceum, Traces of DMT[4]
- Delosperma tradescantioides, DMT[4]
Apocynaceae
- Prestonia amazonica: DMT[5]
- Voacanga africana: Iboga alkaloids
Erythroxylaceae
- Erythroxylum pungens: DMT[6]
Fabaceae (Leguminosae)















- Acacia acuminata, Up to 1.5% alkaloids, mainly consisting of dimethyltryptamine in bark & leaf[7] Also, harman, tryptamine, NMT, other alkaloids in leaf.[citation needed]
- Acacia alpina, Active principles in leaf[8][unreliable source?]
- Acacia angustissima, β-methyl-phenethylamine,[9] NMT and DMT in leaf (1.1-10.2 ppm)[10]
- Acacia aroma, Tryptamine alkaloids.[11] Significant amount of tryptamine in the seeds.[12]
- Acacia auriculiformis, 5-MeO-DMT in stem bark[13]
- Acacia baileyana, 0.02% tryptamine and β-carbolines, in the leaf, Tetrahydroharman[14]
- Acacia beauverdiana, Psychoactive[15] Ash used in Pituri.[16]
- Acacia berlandieri, DMT, phenetylamine, mescaline, nicotine[17]
- Acacia catechu, DMT and other tryptamines in leaf, bark[citation needed]
- Acacia caven, Psychoactive[18]
- Acacia chundra, DMT and other tryptamines in leaf, bark
- Acacia colei, DMT[19]
- Acacia complanata, 0.3% alkaloids in leaf and stem, almost all N-methyl-tetrahydroharman, with traces of tetrahydroharman, some of tryptamine[20][21][22]
- Acacia confusa, DMT & NMT in leaf, stem & bark 0.04% NMT and 0.02% DMT in stem.[8] Also N,N-dimethyltryptamine N-oxide[23]
- Acacia cornigera, Psychoactive,[18] Tryptamines[24] DMT according to C. Rastch.
- Acacia cultriformis, Tryptamine, in the leaf, stem[8] and seeds.[12] Phenethylamine in leaf and seeds[12]
- Acacia cuthbertsonii, Psychoactive[15]
- Acacia decurrens, Psychoactive,[18] but less than 0.02% alkaloids[14]
- Acacia delibrata, Psychoactive[15]
- Acacia falcata, Psychoactive,[15] but less than 0.02% alkaloids[14] Psychoactive 0.2-0.3% alkaloids[citation needed]
- Acacia farnesiana, Traces of 5-MeO-DMT[25] in fruit. β-methyl-phenethylamine, flower.[26] Ether extracts about 2-6% of the dried leaf mass.[27] Alkaloids are present in the bark[28] and leaves.[29] Amphetamines and mescaline also found in tree.[24]
- Acacia flavescens, Strongly Psychoactive, Bark.
- Acacia floribunda, Tryptamine, phenethylamine,[30] in flowers[12] other tryptamines,[31] DMT,tryptamine,NMT 0.3-0.4% phyllodes.[32]
- Acacia georginae, Psychoactive,[18] plus deadly toxins
- Acacia horrida, Psychoactive[18]
- Acacia implexa, Psychoactive[33]
- Acacia jurema, DMT, NMT
- Acacia karroo, Psychoactive
- Acacia laeta, DMT, in the leaf[8]
- Acacia longifolia, 0.2% tryptamine in bark, leaves, some in flowers, phenylethylamine in flowers,[30] 0.2% DMT in plant.[34] Histamine alkaloids.[14]
- Acacia sophorae, Tryptamine in leaves, bark[12]
- Acacia macradenia, Tryptamine[12]
- Acacia maidenii, 0.6% NMT and DMT in about a 2:3 ratio in the stem bark, both present in leaves[8]
- Acacia mangium, Psychoactive[18]
- Acacia melanoxylon, DMT, in the bark and leaf,[35] but less than 0.02% total alkaloids[14]
- Acacia mellifera, DMT, in the leaf[8]
- Acacia nilotica, DMT, in the leaf[8]
- Acacia nilotica subsp. adstringens, Psychoactive, DMT in the leaf
- Acacia neurophylla DMT in bark, Harman in leaf.[36]
- Acacia obtusifolia, Tryptamine, DMT, NMT, other tryptamines,[37] 0.4-0.5% in dried bark,0.15-0.2% in leaf, 0.07% in branch tips.[38]
- Acacia oerfota, Less than 0.1% DMT in leaf,[39] NMT
- Acacia penninervis, Psychoactive[15]
- Acacia phlebophylla, 0.3% DMT in leaf, NMT[8]
- Acacia podalyriaefolia, Tryptamine in the leaf,[8] 0.5% to 2% DMT in fresh bark, phenethylamine, trace amounts.[30] Although this species is claimed to contain 0.5% to 2% DMT in fresh bark the reference for this is invalid as there is no reference to Acacia Podalyriffolia anywhere in the reference article. Additionally, well known and proven extraction techniques for DMT have failed to produce any DMT or alkaloids from fresh bark or the leaves on multiple sample taken at various seasons. Should DMT actually exist in this species of Acacia then it exists in extremely small amounts and have failed to produce any alkaloids with Acid/Base extraction techniques using HCl/Na(OH)2. On the same note, more academic research is definitely required into the DMT content of this and other Australian Acacia species with proper chemical analysis of sample.[citation needed]
- Acacia polyacantha, DMT in leaf[8] and other tryptamines in leaf, bark
- Acacia polyacantha ssp. campylacantha, Less than 0.2% DMT in leaf, NMT; DMT and other tryptamines in leaf, bark[40]
- Acacia rigidula, DMT, NMT, tryptamine, traces of amphetamines, mescaline, nicotine and others[41]
- Acacia sassa, Psychoactive[18]
- Acacia schaffneri, β-methyl-phenethylamine, Phenethylamine[42] Amphetamines and mescaline also found.[24]
- Acacia senegal, Less than 0.1% DMT in leaf,[8] NMT, other tryptamines. DMT in plant,[26] DMT in bark.[12]
- Acacia seyal, DMT, in the leaf.[8] Ether extracts about 1-7% of the dried leaf mass.[27]
- Acacia sieberiana, DMT, in the leaf[8]
- Acacia simplex, DMT and NMT, in the leaf, stem and trunk bark, 0.81% DMT in bark, MMT[8][43]
- Acacia tortilis, DMT, NMT, and other tryptamines[33]
- Acacia vestita, Tryptamine, in the leaf and stem,[8] but less than 0.02% total alkaloids[14]
- Acacia victoriae, tryptamines, 5-MeO-alkyltryptamine[12]
- List of acacia species having little or no alkaloids in the material sampled:[14]
(0% C 0.02%, Concentration of alkaloids) - Albizia inundata leaves contain DMT.[18]
- Anadenanthera colubrina, Bufotenin, Beans,[44][45] Bufotenin oxide, Beans,[44] N,N-Dimethyltryptamine, Beans,[44][45] pods,[44]
- Anadenanthera colubrina var. cebil - Bufotenin and Dimethyltryptamine have been isolated from the seeds and seed pods, 5-MeO-DMT from the bark of the stems.[46] The seeds were found to contain 12.4% bufotenine, 0.06% 5-MeO-DMT and 0.06% DMT.[47]
- Anadenanthera peregrina,
1,2,3,4-Tetrahydro-6-methoxy-2,9-dimethyl-beta-carboline, Plant,[48] 1,2,3,4-Tetrahydro-6-methoxy-2-methyl-beta-carboline, Plant,[45] 5-Methoxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine, Bark,[45] 5-Methoxy-N-methyltryptamine, Bark,[45] Bufotenin, plant,[45] beans,[44] Bufotenin N-oxide, Fruit,[45] beans,[44] N,N-Dimethyltryptamine-oxide, Fruit[45][49]
- Anadenanthera peregrina var. peregrina, Bufotenine is in the seeds.[50]
- Desmanthus illinoensis, 0–0.34% DMT in root bark, highly variable.[51] Also NMT, N-hydroxy-N-methyltryptamine, 2-hydroxy-N-methyltryptamine, and gramine (toxic).[52]
- Desmanthus leptolobus, 0.14% DMT in root bark, more reliable than D. illinoensis[51]
- Desmodium caudatum[53] (syn. Ohwia caudata), Roots: 0.087% DMT,
- Desmodium intortum, Bufotentine, DMT[54]
- Codariocalyx motorius(syn. Desmodium gyrans), DMT, 5-MeO-DMT, leaves, roots
- Desmodium racemosum, 5-MeO-DMT
- Desmodium triflorum, 0.0004% DMT-N-oxide, roots,[55] less in stems[55] and trace in leaves.[55]
- Lespedeza capitata,
- Lespedeza bicolor, DMT, 5-MeO-DMT in leaves and roots[56]
- Lespedeza bicolor var. japonica, DMT, 5-MeO-DMT in leaves and root bark
- Mimosa ophthalmocentra, Dried root: DMT 1.6%, NMT 0.0012% and hordenine 0.0065%[57]
- Mimosa scabrella, tryptamine, NMT, DMT and N-methyltetrahydrocarboline in bark[58]
- Mimosa somnians, tryptamines and MMT
- Mimosa tenuiflora (syn. "Mimosa hostilis"), 0.31-0.57% DMT (dry root bark).[59]
- Mimosa verrucosa, DMT[60] in root bark
- Mucuna pruriens, "The leaves, seeds, stems and roots contain L-Dopa, Serotonin, 5-HTP, and Nicotine, as well as N,N-DMT, Bufotenine, and 5-MeO-DMT."[61]
- Petalostylis casseoides, 0.4-0.5% tryptamine, DMT, etc. in leaves and stems[56]
- Petalostylis labicheoides var. casseoides, DMT in leaves and stems
- Phyllodium pulchellum(syn. Desmodium pulchellum), 0.2% 5-MeO-DMT, small quantities of DMT[56] DMT (dominates in seedlings and young plants), 5-MeO-DMT (dominates in mature plant), whole plant, roots, stems, leaves, flowers
- Erythrina flabelliformis, other Erythrina species, seeds contain the alkaloids erysodin and erysovin[62]
Subfamily Caesalpinioideae
- Petalostylis cassioides: 0.4-0.5% tryptamine, DMT, etc. in leaves and stems[63]
- Petalostylis labicheoides, Tryptamines in leaves and stems, MAO's up to 0.5%[64][unreliable source?]
Lauraceae
- Nectandra megapotamica, NMT[65][unreliable source?]
Malpighiaceae
- Diplopterys cabrerana: McKenna et al. (1984) assayed and found the leaves contain 0.17% DMT [66]
Myristicaceae
- Horsfieldia superba: 5-MeO-DMT[56] and beta-carbolines[63]
- Iryanthera macrophylla: 5-MeO-DMT in bark[56]
- Iryanthera ulei: 5-MeO-DMT in bark
- Osteophloem platyspermum: DMT, 5-MeO-DMT in bark
- Virola calophylla, Leaves 0.149% DMT, leaves 0.006% MMT 5-MeO-DMT in bark[67]
- Virola calophylloidea, DMT
- Virola carinata, DMT in leaves
- Virola cuspidata, DMT[64]
- Virola divergens, DMT in leaves
- Virola elongata(syn. Virola theiodora), DMT, 5-MeO-DMT in bark, roots, leaves and flowers
- Virola melinonii, DMT in bark
- Virola multinervia, DMT, 5-MeO-DMT in bark and roots
- Virola pavonis, DMT in leaves
- Virola peruviana, 5-MeO-DMT, traces of DMT and 5-MeO-tryptamine in bark
- Virola rufula, Alkaloids in bark and root, 95% of which is MeO-DMT[68] 0.190% 5-MeO-DMT in bark, 0.135% 5-MeO-DMT in root, 0.092% DMT in leaves.
- Virola sebifera, The bark contains 0.065% to 0.25% alkaloids, most of which are DMT and 5-MeO-DMT.[69]
- Virola venosa, DMT, 5-MeO-DMT in roots, leaves DMT
Ochnaceae
- Testulea gabonensis: 0.2% 5-MeO-DMT, small quantities of DMT,[56] DMT in bark and root bark, NMT
Pandanaceae
- Genus Pandanus (Screw Pine): DMT in nuts[56]
Poaceae (Gramineae)
Some Graminae (grass) species contain gramine, which can cause brain damage, other organ damage, central nervous system damage and death in sheep.[70]
- Arundo donax, 0.0057% DMT in dried rhizome, no stem, 0.026% bufotenine, 0.0023% 5-MeO-MMT[71]
- Phalaris aquatica, 0.0007-0.18% Total alkaloids,[72] 0.100% DMT,[73] 0.022% 5-MeO-DMT,[73] 0.005% 5-OH-DMT[73]
- Phalaris arundinacea, 0.0004-0.121% Total alkaloids[72]
- Phalaris brachystachys, aerial parts up to 3% total alkaloids, DMT present[citation needed]
- Phragmites australis, DMT in roots.
None of the above alkaloids are said to have been found in Phalaris californica, Phalaris canariensis, Phalaris minor and hybrids of P. arundinacea together with P. aquatica.[72]
Polygonaceae
- Eriogonum : DMT
Rubiaceae
- Psychotria carthagenensis, 0.2% average DMT in dried leaves
- Psychotria colorata, Presence of mu opioid receptor(MOR) agonist and NMDA antagonist: hodgkinsine, psychotridine. Also mentioned in The Encyclopedia of Psychoactive Plants: Ethnopharmacology and Its Applications.[74]
- Psychotria expansa, DMT[64]
- Psychotria forsteriana, DMT[64]
- Psychotria insularum, DMT[64]
- Psychotria poeppigiana,[75] DMT[64]
- Psychotria rostrata, DMT[64]
- Psychotria rufipilis, DMT[64]
- Psychotria viridis, DMT 0.1-0.61% dried mass.[76]
Rutaceae[77][78]
- Dictyoloma incanescens, 5-MeO-DMT in leaves,[68] 0.04% 5-MeO-DMT in bark[56]
- Dutaillyea drupacea, > 0.4% 5-MeO-DMT in leaves[33]
- Dutaillyea oreophila, 5-MeO-DMT in leaves
- Tetradium ruticarpum(syn. Evodia rutaecarpa), 5-MeO-DMT in leaves, fruit and roots
- Limonia acidissima, 5-MeO-DMT in stems
- Euodia leptococca (formerly Melicope), 0.2% total alkaloids, 0.07% 5-MeO-DMT; 5-MeO-DMT in leaves and stems, also "5-MeO-DMT-Oxide and a beta-carboline"[63]
- Pilocarpus organensis, DMT, 5-MeO-DMT in leaves[79] (Might also contain pilocarpine)
- Vepris ampody, Up to 0.2% DMT in leaves and branches[56]
- Zanthoxylum arborescens, DMT in leaves
- Zanthoxylum procerum, DMT in leaves
- Citrus limon, DMT, N-Methylated tryptamine derivative in leaves [80][81]
- Citrus sinesis,DMT, N-Methylated tryptamine derivative [80][81]
- Citrus bergamia,DMT, N-Methylated tryptamine derivative [80][81]
- Mandarin orange Traces of N-methylated tryptamine derivative in leaf.[82][81]
- Chinotto Tree, N-Methylated tryptamine derivative in leaf [82][81]
- Citrus medica, N-Methylated tryptamine derivative in leaf [82][81]
Phenethylamines



Species, Alkaloid Content (Fresh) - Alkaloid Content (Dried)
- Austrocylindropuntia cylindrica (syn. Opuntia cylindrica),[83] Mescaline[84]
- Coryphantha contains various phenethylamine alkaloids including macromerine, coryphanthine, O-methyl-candicine, corypalmine, and N-methyl-corypalmine.[85][86]
- Cylindropuntia echinocarpa (syn. Opuntia echinocarpa), Mescaline 0.01%, DMPEA 0.01%, 4-hydroxy-3-5-dimethoxyphenethylamine 0.01%[84]
- Cylindropuntia spinosior (syn. Opuntia spinosior),[87] Mescaline 0.00004%, 3-methoxytyramine 0.001%, tyramine 0.002%, 3-4-dimethoxyphenethylamine.[84]
- Echinopsis lageniformis (syn. Trichocereus bridgesii), Mescaline > 0.025%,[88] also DMPEA < 1%, 3-methoxytyramine < 1%, tyramine < 1%; Mescaline 2%[89]
- Echinopsis macrogona (syn. Trichocereus macrogonus), > 0.01-0.05% Mescaline[90]
- Echinopsis pachanoi (syn. Trichocereus pachanoi), Mescaline 0.006-0.12%, 0.05% Average;[91] Mescaline 0.01%-2.375%[91]
- Echinopsis peruviana (syn. Trichocereus peruvianus), Mescaline 0.0005%-0.12%;[91] Mescaline
- Echinopsis scopulicola (syn. Trichocereus scopulicola), Mescaline[92]Lycaeum
- Echinopsis spachiana (syn. Trichocereus spachianus), Mescaline;[84] Mescaline[84]
- Echinopsis tacaquirensis subsp. taquimbalensis (syn. Trichocereus taquimbalensis),[93] > 0.005-0.025% mescaline[90]
- Echinopsis terscheckii (syn. Trichocereus terscheckii, Trichocereus werdemannianus)[94] > 0.005-0.025% Mescaline;[90] mescaline 0.01%-2.375%[91]
- Echinopsis valida, 0.025% mescaline[92]
- Lophophora williamsii (Peyote), 0.4% Mescaline;[92] 3-6% Mescaline[84]
- Opuntia acanthocarpa Mescaline[95]
- Opuntia basilaris Mescaline 0.01%, plus 4-hydroxy-3-5-dimethoxyphenethylamine[84]
- Pelecyphora aselliformis, mescaline[92]
Beta-carbolines








Beta-carbolines are "reversible" MAO-A inhibitors. They are found in some plants used to make Ayahuasca. In high doses the harmala alkaloids are somewhat hallucinogenic on their own. β-carboline is a benzodiazepine receptor inverse agonist and can therefore have convulsive, anxiogenic and memory enhancing effects.[96]
Apocynaceae
- Amsonia tabernaemontana, Harmine
- Aspidosperma exalatum, Beta-carbolines[97]
- Aspidosperma polyneuron, Beta-carbolines[97]
- Apocynum cannabinum, Harmalol
- Ochrosia nakaiana, Harman
- Pleiocarpa mutica, Beta-carbolines[97]
Bignoniaceae
- Newbouldia laevis, Harman
Calycanthaceae
- Calycanthus occidentalis, Harmine
Chenopodiaceae
- Hammada leptoclada, Tetrahydroharman, etc.
- Kochia scoparia, Harmine, etc.
Combretaceae
- Guiera senegalensis, Harman, etc.
Cyperaceae
- Carex brevicollis, Harmine, etc.
- Carex parva, Beta-carbolines[97]
Elaeagnaceae
- Elaeagnus angustifolia, Harman, etc.
- Elaeagnus commutata, Beta-carbolines[97]
- Elaeagnus hortensis, Tetrahydroharman, etc.
- Elaeagnus orientalis, Tetrahydroharman
- Elaeagnus spinosa, Tetrahydroharman
- Hippophae rhamnoides, Harman, etc.
- Shepherdia argentea, Tetrahydroharmol
- Shepherdia canadensis, Tetrahydroharmol
Gramineae
- Arundo donax, Tetrahydroharman
- Festuca arundinacea, Harman, etc.
- Lolium perenne, (Perennial Ryegrass), Harman, etc.
- Phalaris aquatica, Beta-carbolines[97]
- Phalaris arundinacea, Beta-carbolines[97]
Lauraceae
- Nectandra megapotamica, Beta-carbolines[97]
Leguminosae
- Acacia baileyana, Tetrahydroharman
- Acacia complanata, Tetrahydroharman, etc.
- Burkea africana, Harman, etc.
- Desmodium gangeticum, Beta-carbolines[97]
- Desmodium gyrans, Beta-carbolines[97]
- Desmodium pulchellum, Harman, etc.
- Mucuna pruriens, 6-Methoxy-Harman
- Petalostylis labicheoides, Tetrahydroharman; MAO's up to 0.5%[64]
- Prosopis nigra, Harman, etc.
- Shepherdia pulchellum, Beta-carbolines[97]
Loganiaceae
Malpighiaceae
- Banisteriopsis argentia, 5-methoxytetrahydroharman, (−)-N(6)-methoxytetrahydroharman, dimethyltryptamine-N(6)-oxide[9]
- Banisteriopsis caapi, Harmine 0.31-0.84%,[98] tetrahydroharmine, telepathine, dihydroshihunine,[99] 5-MeO-DMT in bark[100]
- Banisteriopsis inebrians, Beta-carbolines[97]
- Banisteriopsis lutea, Harmine, telepathine[9]
- Banisteriopsis metallicolor, Harmine, telepathine[9]
- Banisteriopsis muricata Harmine up to 6%, harmaline up to 4%, plus DMT[101]
- Diplopterys cabrerana, Beta-carbolines[97]
- Cabi pratensis, Beta-carbolines[97]
- Callaeum antifebrile(syn. Cabi paraensis), Harmine
- Tetrapterys methystica(syn. Tetrapteris methystica), Harmine[102]
Myristicaceae
- Gymnacranthera paniculata, Beta-carbolines[97]
- Horsfieldia superba Beta-carbolines[63]
- Virola cuspidata, 6-Methoxy-Harman
- Virola rufula, Beta-carbolines[97]
- Virola theiodora, Beta-carbolines[97]
Ochnaceae
- Testulea gabonensis, Beta-carbolines[97]
Palmae
- Plectocomiopsis geminiflora, Beta-carbolines[97]
Papaveraceae
- Meconopsis horridula, Beta-carbolines[97]
- Meconopsis napaulensis, Beta-carbolines[97]
- Meconopsis paniculata, Beta-carbolines[97]
- Meconopsis robusta, Beta-carbolines[97]
- Meconopsis rudis, Beta-carbolines[97]
- Papaver rhoeas, Beta-carbolines[97]
Passifloraceae
- Passiflora actinia, Harman
- Passiflora alata, Harman
- Passiflora alba, Harman
- Passiflora bryonoides, Harman
- Passiflora caerulea, Harman
- Passiflora capsularis, Harman
- Passiflora decaisneana, Harman
- Passiflora edulis, Harman, 0-7001 ppm[26] in fruit
- Passiflora eichleriana, Harman

- Passiflora foetida, Harman
- Passiflora incarnata (with bee), Harmine, Harmaline, Harman, etc. 0.03%.[103] Alkaloids in rind of fruit 0.25%[103]
- Passiflora quadrangularis, Harman
- Passiflora ruberosa, Harman
- Passiflora subpeltata, Harman
- Passiflora warmingii, Harman
Polygonaceae
- Calligonum minimum, Beta-carbolines[97]
- Leptactinia densiflora, Leptaflorine, etc.
- Ophiorrhiza japonica, Harman
- Pauridiantha callicarpoides, Harman
- Pauridiantha dewevrei, Harman
- Pauridiantha lyalli, Harman
- Pauridiantha viridiflora, Harman
- Simira klugei, Harman
- Simira rubra, Harman
Rubiaceae
- Borreria verticillata, Beta-carbolines[97]
- Leptactinia densiflora, Beta-carbolines[97]
- Nauclea diderrichii, Beta-carbolines[97]
- Ophiorrhiza japonica, Beta-carbolines[97]
- Pauridiantha callicarpoides, Beta-carbolines[97]
- Pauridiantha dewevrei, Beta-carbolines[97]
- Pauridiantha yalli, Beta-carbolines[97]
- Pauridiantha viridiflora, Beta-carbolines[97]
- Pavetta lanceolata, Beta-carbolines[97]
- Psychotria carthagenensis, Beta-carbolines[97]
- Psychotria viridis, Beta-carbolines[97]
- Simira klugei, Beta-carbolines[97]
- Simira rubra, Beta-carbolines[97]
- Uncaria attenuata, Beta-carbolines[97]
- Uncaria canescens, Beta-carbolines[97]
- Uncaria orientalis, Beta-carbolines[97]
Rutaceae
- Tetradium (syn. Evodia) species: Some contain carbolines
- Euodia leptococca Beta-carboline[63]
- Araliopsis tabouensis, Beta-carbolines[97]
- Flindersia laevicarpa, Beta-carbolines[97]
- Xanthoxylum rhetsa, Beta-carbolines[97]
Sapotaceae
- Chrysophyllum lacourtianum, Norharman etc.
- Scutellaria???
- Scutellaria nana???
Simaroubaceae
- Ailanthus malabarica, Beta-carbolines.[97] See also Nag Champa.
- Perriera madagascariensis, Beta-carbolines[97]
- Picrasma ailanthoides, Beta-carbolines[97]
- Picrasma crenata, Beta-carbolines[97]
- Picrasma excelsa, Beta-carbolines[97]
- Picrasma javanica, Beta-carbolines[97]
Solanaceae
- Vestia foetida, (Syn V. lycioides) Beta-carbolines[97]
Symplocaceae
- Symplocos racemosa, Harman
Tiliaceae
- Grewia mollis, Beta-carbolines[97]
Zygophyllaceae
- Fagonia cretica, Harman
- Nitraria schoberi, Beta-carbolines[97]
- Peganum harmala, (Syrian Rue), The seeds contain about 2-6% alkaloids, most of which is harmaline.[104] Peganum harmala is also an abortifacient.
- Peganum nigellastrum, Harmine[105]
- Tribulus terrestris, Harman
- Zygophyllum fabago, Harman, harmine
Plants containing other psychoactive substances
This section needs additional citations for verification. (April 2022) |
| Substance(s) | Plant | Comments |
|---|---|---|
 Asarone |
 |
Toxic.[citation needed] |
 Yohimbine |
Alchornea floribunda | α2-adrenergic receptor antagonist.[citation needed] |
 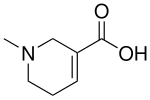 Arecoline, Arecaidine |
 |
GABA uptake inhibitor,[106][107] stimulant.[108] |
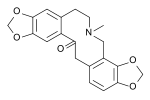 Protopine |

|
Used by Chinese residents of Mexico during the early 20th century as a legal substitute for opium and currently smoked as a marijuana substitute.[citation needed] |
 Ergine |

Argyreia nervosa (Hawaiian Baby Woodrose) |
Seeds contain ergine (also known as LSA), often 50-150X the amounts found in Ipomoea violacea. LSA is a hallucinogen.[109] |
 Thujone |
 |
Also called "wormwood". GABA receptor antagonist.[110] |
| Quinoline & Aporphine alkaloids |  Asimina triloba (Paw Paw) |
Identical alkaloid to morphine.[111] |
 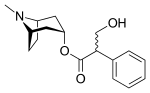  Tropane alkaloids (scopolamine, atropine, hyoscyamine) |
 |
Commonly known as 'deadly nightshade'. An anticholinergic deliriant.[112] |
   Tropane alkaloids (scopolamine, atropine, and hyoscyamine) |
 Brugmansia |
Commonly known as 'angel's trumpets'. An anticholinergic deliriant.[112] |
| Unknown | 
Calea zacatechichi |
Produces vivid dreams after smoking. It is also employed by the Chontal people as a medicinal herb against gastrointestinal disorders, and is used as an appetizer, cathartic anti-dysentery remedy, and as a fever-reducing agent. Its psychedelic properties do not become apparent until the user is asleep. Reports describe rituals that involve drinking it as a tea to induce divinatory or lucid dreams due to its properties as an oneirogen.[113] |
 Caffeine |
 |
Tea leaves, tea, native to Asia.[citation needed] |
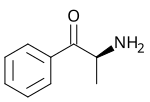 Cathinone |

Catha edulis |
Khat, commonly chewed, produces a stimulant effect.[114] |
 Vincristine |
 |
Catharanthus roseus is (perhaps unpleasantly) "hallucinogenic."[115] |
| Unknown |  |
Commonly referred to as 'night-blooming jasmine', 'lady of the night', and 'poisonberry'. It has an unknown mechanism of action.[citation needed] |
 Caffeine |
 |
Coffee beans, coffee, native to Africa.[116] |
 Caffeine |
 Cola |
Cola or kola nut, traditional additive to cola, native to Africa.[citation needed] |
| Salvinorin A | 
Coleus |
Unknown |

Bulbocapnine |

Corydalis solida, cava |
Bulbocapnine, Nantenine, Tetrahydropalmatine |
  Tropane alkaloids (Scopolamine, Atropine) |

Datura |
Also known as 'thorn apple', 'devil's trumpets', 'loco weed', and 'Jimson weed'. Scopolamine and Atropine are both anticholinergics[117][118] which produce hallucinogenic and deliriant effects. It has an extensive history of being used recreationally.[119] |
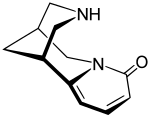 Cytisine |
 Dermatophyllum |
Nicotine-like effects. partial agonist of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs).[120] |
| Unknown |  Desfontainia spinosa |
Causes visions.[121] |
 Nicotine |
 |
Pituri |
| Unknown |  |
African dream herb.[citation needed] |
 Ephedrine |
 |
Ephedra |
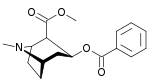 Cocaine |
 |
Coca. Widely used illegal stimulant, produces hallucination in overdose, native to South America.[citation needed] |
| Unknown |  |
Nerve or mosaic plant, said to produce vision of eyeballs |
 Himbacine |
Galbulimima belgraveana | Galbulimima belgraveana is rich in alkaloids and twenty-eight alkaloids have been isolated including himbacine.[citation needed] |
 Glaucine |

|
Hallucinogenic effects.[122] |
 Possibly Cryogenine[citation needed] |
Heimia myrtifolia | Auditory |
 Possibly Cryogenine[citation needed] |
 |
Auditory[123] |
  Lobeline, Nicotine |
 Hippobroma longiflora |
Star of Bethlehem |
 Hyperforin |
 |
Saint John's wort |
| Tropane alkaloids |  Hyoscyamus |
Henbane |
  Caffeine, Theobromine, Dimethylxanthines |
 |
Ilex guayusa is used as an additive to some versions of Ayahuasca. According to the Ecuadorian indigenous, it is also slightly hallucinogenic on its own, when drunk in high enough quantities.[citation needed] |
 Ergine |
 |
Ergine in seeds; up to 0.12% total[124] Produces psychedelic effects. |
| Unknown |  Justicia pectoralis |
Unknown |
| Lactucarium | 
|
Lactucarium |

Lagochilin |
 |
Lagochilin is thought to be responsible for the sedative, hypotensive and hemostatic effects of this plant.[citation needed] |
 Pukateine |

|
Pukateine |
| Unknown |  Rollinia mucosa |
Rollinia mucosa is said to be a narcotic.[111] |
 Leonurine |

|
Both leaves and flowers (where most concentrated) contain Leonurine. (Effects reminiscent of marijuana)[citation needed] |
 Nicotine[125] |
 Leucas aspera |
Nicotine |
 Leonurine |

|
Both leaves and flowers (where most concentrated) contain Leonurine. (Effects reminiscent of marijuana)[citation needed] |
 Lobeline |
 |
Indian tobacco |
| Unknown | 
|
[126] |
   Tropane alkaloids (scopolamine, atropine, and hyoscyamine) |
 |
Mandrake has deliriant and anticholinergic properties.[112] |
 Ergine |
 Some Mirabilis spp. |
Possibly contains ergine[citation needed], a hallucinogen. |
  Mitragynine, Mitragynine pseudoindoxyl |
 Mitragyna speciosa |
Usually referred to as kratom. Has opioid-like and stimulant properties.[127] |
 Myristicin |
 |
Nutmeg |
 Aporphine |
 |
Sacred lotus |
 Nepetalactone |
 Nepeta cataria |
Catnip |
 Nicotine |
 |
Tobacco. Can cause hallucinations in very large doses.[citation needed] |
 Aporphine, Apomorphine |

Nymphaea caerulea |
Blue lotus or lily. Recent studies have shown Nymphaea caerulea to have psychedelic properties, and may have been used as a sacrament in ancient Egypt and certain ancient South American cultures. Dosages of 5 to 10 grams of the flowers induces slight stimulation, a shift in thought processes, enhanced visual perception, and mild closed-eye visuals. Nymphaea caerulea is related to, and possesses similar activity as Nelumbo nucifera, the Sacred Lotus. Both Nymphaea caerulea and Nelumbo nucifera contain the alkaloids nuciferine and apomorphine, which have been recently isolated by independent labs.[citation needed]
These psychoactive effects make Nymphaea caerulea a likely candidate (among several) for the lotus plant eaten by the mythical Lotophagi in Homer's Odyssey. Used in aromatherapy, Nymphaea caerulea is purported to have a "divine" essence, bringing euphoria, heightened awareness and tranquility.[citation needed] Other sources cite anti-spasmodic and sedative, purifying and calming properties. |
 Ginsenosides |
 Panax |
Ginseng |
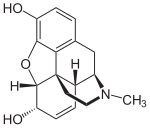 Morphine |
 |
Opium. Widely used analgesic, native to the Old World.[128] |
| Unknown |  |
Narcotic and toxic when the root is consumed.[111] |
 Yohimbine |
 Pausinystalia johimbe |
α2-adrenergic receptor antagonist.[citation needed] |
| Unknown |  |
Indian warrior |
 Kavalactones |

Piper methysticum |
An anxiolytic[129] and hypnotic.[130] Often advertised as a 'healthier' alternative to alcohol.[citation needed] |
 Ergine |
 Rivea corymbosa |
Seeds contain ergine, lysergol, and turbicoryn; lysergic acid alkaloids up to 0.03%[131] Has psychedelic properties. |
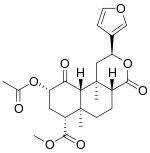 Salvinorin A |

|
Salvinorin A, 0.89-3.87 mg/g, also Salvinorin B and Salvinorin C[132] |
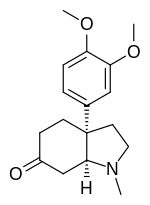 Mesembrine |
 |
Kanna |
 Baicalein |
 Scutellaria |
Known commonly as 'skullcaps'. Baicalein is a positive allosteric modulator of GABAA receptor.[133] |
| Unknown | 
Silene capensis |
Produces vivid dreams after smoking.[134] |
| Unknown | 
|
Anethole, Chavicol, Coumarin, Estragole, Isorhamnetin, Methyleugenol, Quercitin |
 Ibogaine |

Tabernanthe iboga |
Ibogaine in root bark. Produces psychedelic and a dissociative effects.[135][136] |
 Ibogaine |
Tabernanthe orientalis |
Ibogaine in root leaves. Produces psychedelic and a dissociative effects.[135][136] |
  Voacangine, Ibogaine |

|
Is a psychedelic and a dissociative.[136] |
 Ibogaine |
Tabernanthe pubescens |
Is a psychedelic and a dissociative. Contains ibogaine and similar alkaloids.[135][136] |
 Ibogaine |
 Tabernaemontana sp. |
Is a psychedelic and a dissociative.[135][136] |
 Theobromine |
 |
Cocoa or cacao bean, chocolate, native to the Americas |
 Ibogaine |

|
Exhibits psychedelic and dissociative effects. Contains ibogaine, coronaridine, voacangine, apparicine, conoflorine, and 19-epi-voacangarine.[137][138] |
 Valerenic acid |
 Valeriana officinalis |
Possible sedative and anxiolytic effects. Valerenic acid is GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulator,[139] and a 5-HT5A receptor partial agonist.[140] |
 Vincamine |
 |
Vincamine.[141] |
 Voacangine |
 Voacanga africana |
Voacangine is similar in structure to ibogaine. It inhibits AChE.[142][143] |
  Possibly Genistein and Apigenin |
 Zornia latifolia |
Zornia latifolia is sometimes combined with synthetic cannabis. It may produce similar effects to cannabis.[144][145] It is nicknamed Maconha brava because locals use it as a cannabis substitute.[citation needed] |
See also
- Aztec entheogenic complex
- Entheogenic drugs and the archaeological record
- God in a Pill?
- Hallucinogenic fish
- Hallucinogenic plants in Chinese herbals
- List of Acacia species known to contain psychoactive alkaloids
- List of entheogenic/hallucinogenic species
- List of plants used for smoking
- List of poisonous plants
- List of psychoactive plants, fungi, and animals
- Louisiana State Act 159
- N,N-Dimethyltryptamine
- Psilocybin mushrooms
- Psychoactive cactus
- Psychoactive plant
Notes
- Other psychoactive compounds without nitrogen atoms include kavalactones and salvinorins, known from kava and Salvia divinorum, respectively.
References
- Sayin, H. Umit (2016). "Psychoactive Plants Used during Religious Rituals". Neuropathology of Drug Addictions and Substance Misuse. Elsevier. pp. 17–28. doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-800634-4.00002-0. ISBN 9780128006344.
- Kohek, Maja; Sánchez Avilés, Constanza; Romaní, Oriol; Bouso, José Carlos (2021). "Ancient psychoactive plants in a global village: The ritual use of cannabis in a self-managed community in Catalonia". International Journal of Drug Policy. Elsevier BV. 98: 103390. doi:10.1016/j.drugpo.2021.103390. ISSN 0955-3959. PMID 34340169.
- "IJ PACHTER, DE ZACHARIAS, O RIBEIRO - The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 1959 -" (PDF). Pubs.acs.org. Retrieved 22 December 2017.
- "Trout's Notes on Some Other Succulents". Archived from the original on 2015-09-24. Retrieved 2015-01-14.
- "Profiles of Psychedelic Drugs". paranoia.lycaeum.org. Archived from the original on 2002-05-22. Retrieved 2008-04-19.
- Macedo Pereira G, Moreira LG, Neto TD, Moreira de Almeida WA, Almeida-Lima J, Rocha HA, Barbosa EG, Zuanazzi JA, de Almeida MV, Grazul RM, Navarro-Vázquez A, Hallwass F, Ferreira LS, Fernandes-Pedrosa MF, Giordani RB (November 2018). "Isolation, spectral characterization, molecular docking, and cytotoxic activity of alkaloids from Erythroxylum pungens O. E. Shulz". Phytochemistry. 155: 12–18. doi:10.1016/j.phytochem.2018.07.003. PMID 30056276. S2CID 51908961.
- "Lycaeum > Leda > Acacia acuminata". leda.lycaeum.org. Archived from the original on 2007-10-12. Retrieved 2008-02-23.
- "Plants & Seeds > A > Acacia spp". Shaman Australis Botanicals. Retrieved 14 January 2015.
- Glasby, John Stephen (1991). Dictionary of Plants Containing Secondary Metabolites. CRC Press. p. 2. ISBN 978-0-85066-423-2.
- Nutritive value assessment of the tropical shrub legume Acacia angustissima: anti-nutritional compounds and in vitro digestibility. Personal Authors: McSweeney, C. S., Krause, D. O., Palmer, B., Gough, J., Conlan, L. L., Hegarty, M. P.Author Affiliation: CSIRO Livestock Industries, Long Pocket Laboratories, 120 Meiers Road, Indooroopilly, Qld 4068, Australia. Document Title: Animal Feed Science and Technology, 2005 (Vol. 121) (No. 1/2) 175-190
- "Maya Ethnobotanicals - Ayahuasca, Rainforest Plants, Folklore, Incenses, Art & Visions". Archived from the original on 25 October 2008. Retrieved 14 January 2015.
- Black Panther. "Akacje". Herbarium.0-700.pl. Retrieved 14 January 2015.
- "Lycaeum > Leda > Acacia auriculiformis". Leda.lycaeum.org. Archived from the original on 7 December 2008. Retrieved 14 January 2015.
- Hegnauer, R. (1996-07-30). Caesalpinioideae und Mimosoideae. ISBN 9783764351656. Retrieved 14 January 2015 – via Books.google.com.
- Australian Bush Food and Native Medicine Forum members. "Australian Bushfood (Bushtucker) and Native Medicine Forum". Bushfood.net. Archived from the original on 4 August 2014. Retrieved 14 January 2015.
- "Entheology.org - Preserving Ancient Knowledge". Entheology.org. Retrieved 22 December 2017.
- "Ask Dr. Shulgin Online September 26, 2001". Cognitiveliberty.org. Retrieved 14 January 2015.
- Index of Rätsch, Christian. Enzyklopädie der psychoaktiven Pflanzen, Botanik, Ethnopharmakologie und Anwendungen, 7. Auflage. AT Verlag, 2004, 941 Seiten. ISBN 3-85502-570-3 at "Enzyklopädie der psychoaktiven Pflanzen". Archived from the original on 2007-10-10. Retrieved 2007-06-13. (in German)
- "Dr Karl's Q&A forum". Abc.net.au. Retrieved 14 January 2015.
- "comp phyto". Users.lycaeum.org. Archived from the original on 7 December 2008. Retrieved 14 January 2015.
- "acacias and entheogens". Users.lycaeum.org. Archived from the original on 7 December 2008. Retrieved 14 January 2015.
- "Lycaeum > Leda > Acacia complanata". Users.lycaeum.org. Archived from the original on 7 December 2008. Retrieved 14 January 2015.
- NMR spectral assignments of a new chlorotryptamine alkaloid and its analogues from Acacia confusa Malcolm S. Buchanan, Anthony R. Carroll, David Pass, Ronald J. Quinn Magnetic Resonance in Chemistry Volume 45, Issue 4, pp. 359–361. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
- "Naturheilpraxis - Fachforum - Die Heilkraft der Akazien – Ein einführender Überblick". 5 January 2010. Archived from the original on 5 January 2010. Retrieved 22 December 2017.
- "Lycaeum > Leda > Acacia cultriformis". Leda.lycaeum.org. Archived from the original on 7 December 2008. Retrieved 14 January 2015.
- "Plant Choices - Phytochemeco Databases". Ars-grin.gov. Archived from the original on 27 December 2014. Retrieved 14 January 2015.
- Vivid Interactive and Design. "Rural Industries Research and Development Corporation - Page Not Found" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 December 2008. Retrieved 14 January 2015.
{{cite web}}: Cite uses generic title (help) - "www.bpi.da.gov.ph" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on July 20, 2011.
- "Acacia farnesiana". Hort.purdue.edu. Retrieved 14 January 2015.
- Hegnauer, Robert (1994). Chemotaxonomie der Pflanzen. Springer. p. 500. ISBN 978-3-7643-2979-2.
- "Lycaeum > Leda > Acacia floribunda". leda.lycaeum.org. Archived from the original on 2007-10-12. Retrieved 2008-02-23.
- Voogelbreinder, S. "Garden Of Eden" 2009
- "Lista över hallucinogena växter, svampar och djur". Wiki.magiskamolekyler.org. Retrieved 14 January 2015.
- "Lycaeum > Leda > Acacia longifolia". leda.lycaeum.org. Archived from the original on 2007-04-18. Retrieved 2008-02-23.
- extentech.sheetster.com[permanent dead link]
- S. Voogelbreinder "Garden Of Eden" 2009
- "Lista över hallucinogena växter, svampar och djur - Magiska Molekylers Wiki". wiki.magiskamolekyler.org.
- "obtusifolia phyto". Users.lycaeum.org. Archived from the original on 3 December 2008. Retrieved 14 January 2015.
- Plants Containing DMT (German) Archived 2007-06-29 at the Wayback Machine
- "Acacia campylacantha - Hortipedia". www.hortipedia.org. Archived from the original on 2007-10-12. Retrieved 2008-02-23.
- "Acacia rigidula - Magiska Molekylers Wiki". wiki.magiskamolekyler.org. Retrieved 2008-02-23.
- "Chemistry of Acacias from South Texas" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on May 15, 2011.
- "Eins". Factorey.ch. Archived from the original on 12 August 2008. Retrieved 22 December 2017.
- Granier-Doyeux, Marcel (January 1, 1965). "Native hallucinogenic drugs piptadenias". United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime. Archived from the original on January 20, 2005. Retrieved February 28, 2019.
- Dr. Duke's Archived 2004-11-10 at the Wayback Machine Phytochemical and Ethnobotanical Databases
- "Cultivo de Curupay, Cebil colorado (Anadenanthera colubrina) y usos, herbotecnia". Herbotecnia.com.ar. Retrieved 14 January 2015.
- "Bufo alvarius - Jonathan Ott on Bufotenine". Erowid.org. Retrieved 2008-02-23.
- Dr. Duke's Archived 2013-02-19 at the Wayback Machine Phytochemical and Ethnobotanical Databases
- Stafford, Peter (2013-02-18). Psychedelics Encyclopedia. ISBN 9781579511692. Retrieved 14 January 2015 – via Books.google.com.
- Ott, J. (July–September 2001). "Pharmañopo-psychonautics: human intranasal, sublingual, intrarectal, pulmonary and oral pharmacology of bufotenine". Journal of Psychoactive Drugs. 33 (3): 273–81. doi:10.1080/02791072.2001.10400574. PMID 11718320. S2CID 5877023.
- "Erowid Online Books : "Ayahuasca: alkaloids, plants, and analogs" by Keeper of the Trout". Erowid.org. Retrieved 14 January 2015.
- Hegnauer, R. (1996-07-30). Google Book Search. ISBN 978-3-7643-5165-6. Retrieved 2008-05-08.
- "Desmodium caudatum". Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN). Agricultural Research Service (ARS), United States Department of Agriculture (USDA). Retrieved 2008-05-02.
- "Pharmaceutical, Nutraceutical and Industrial Potential of Temperate Legumes" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-04-17. Retrieved 2015-01-14.
- "Trout's Notes on Desmodium" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on August 31, 2005.
- "Erowid Psychoactive Vaults : Tryptamine FAQ". Erowid.org. Retrieved 14 January 2015.
- "Isolation and Identification of Putative Hallucinogenic Constituents from the Roots of Mimosa ophthalmocentra". Pharmaceutical Biology.
- Hegnauer, R. (1996-07-30). Google Book Search. ISBN 978-3-7643-5165-6. Retrieved 2008-05-07.
- "Ask Erowid : ID 75 : What is the DMT content of Mimosa hostilis rootbark?". Erowid.org. Retrieved 14 January 2015.
- "UNODC Bulletin on Narcotics 1969". Archived from the original on 2007-07-08.
- "Erowid Mucuna pruriens Vault". Erowid.org. Retrieved 14 January 2015.
- "Kalifornischer Korallenstrauch (Erythrina decora) im GIFTPFLANZEN.COMpendium - giftpflanzen.com". Giftpflanzen.com. Retrieved 2008-04-18.
- "tryptamines: fungi". Bluezoo.org. Retrieved 14 January 2015.
- [permanent dead link]
- "Plants Containing DMT List". Dmt-nexus.com. Retrieved 22 December 2017.[permanent dead link]
- Ott, Jonathan (1996). Pharmacotheon. p. 219. ISBN 9780961423483.
- "Species Information". sun.ars-grin.gov. Archived from the original on 2004-11-10. Retrieved 2008-04-11.
- "5-MeO-DMT". Tryptamines.com. Retrieved 14 January 2015.
- "Committee for veterinary medicinal products virola sebifera summary report" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on July 10, 2007.
- Peter R. Cheeke (1989). Toxicants of Plant Origin. CRC-Press. p. 169. ISBN 978-0-8493-6990-2. Retrieved 2008-04-20 – via books.google.com.
- "Erowid Arundo donax Vaults : Trout's Notes on Tryptamine Content of Arundo donax". Erowid.org. Retrieved 14 January 2015.
- "DMT, Life and the Universe". Nepenthes.lycaeum.org. Archived from the original on 2008-06-18. Retrieved 14 January 2015.
- "Erowid Phalaris Vault : FAQ 2.01". Erowid.org. Retrieved 14 January 2015.
- "Psychotria - The Most Important Genera and Species from A to Z - The Encyclopedia of Psychoactive Plants: Ethnopharmacology and Its Applications".
- "Psychotria poeppigiana - Uragoga tomentosa". Discover Life. Retrieved 2013-10-14.
- "Amazing Nature". Amazing-nature.com. Archived from the original on 27 September 2007. Retrieved 22 December 2017.
- Servillo, L; Giovane, A; Balestrieri, ML; Cautela, D; Castaldo, D (Sep 2012). "N-methylated tryptamine derivatives in citrus genus plants: identification of N,N,N-trimethyltryptamine in bergamot". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 60 (37): 9512–8. doi:10.1021/jf302767e. PMID 22957740.
- Servillo, L; Giovane, A; Balestrieri, ML; Casale, R; Cautela, D; Castaldo, D (May 2013). "Citrus genus plants contain N-methylated tryptamine derivatives and their 5-hydroxylated forms". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 61 (21): 5156–62. doi:10.1021/jf401448q. PMID 23682903.
- Santos, Ana Paula; Moreno, Paulo Roberto Hrihorowitsch (Jun 2004). "Pilocarpus spp.: A survey of its chemical constituents and biologicalactivities" (PDF). Brazilian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 40 (2): 116–137. doi:10.1590/S1516-93322004000200002. S2CID 34614172. Retrieved June 16, 2021.
- "Citrus Growers Manufacture Huge Amounts of DMT".
- "Citrus Genus Plants Contain N-Methylated Tryptamine Derivatives and Their 5-Hydroxylated Forms".
- "CitrusGenus Plants Contain N‑Methylated Tryptamine Derivativesand Their 5‑Hydroxylated Forms" (PDF).
- "Austrocylindropuntia cylindrica". Desert-tropicals.com. Retrieved 22 December 2017.
- "Descriptions of psychoactive Cacti". Users.lycaeum.org. Archived from the original on 15 July 2009. Retrieved 14 January 2015.
- Meyer, B. N.; Helfrich, J. S.; Nichols, D. E.; McLaughlin, J. L.; Davis, D. V.; Cooks, R. G. (1983). "Cactus Alkaloids. LIII. Coryphanthine and O-Methyl-Candicine, Two New Quaternary Alkaloids from Coryphantha greenwoodii". Journal of Natural Products. 46 (5): 688–693. doi:10.1021/np50029a017.
- N. Meyer, B; S. Helfrich, J; Nichols, David; L. McLaughlin, J; V. Davis, D; G. Cooks, R (1 July 2004). "Cactus Alkaloids. LIII. Coryphanthine and O-Methyl-Candicine, Two New Quaternary Alkaloids from Coryphantha greenwoodii". Journal of Natural Products. 46 (5): 688–693. doi:10.1021/np50029a017. Retrieved 22 December 2017 – via ResearchGate.
- "Cane Cholla (Cylindropuntia spinosior )". Desert-tropicals.com. Retrieved 14 January 2015.
- "Partial List of Alkaloids in Trichocereus Cacti". Thenook.org. Archived from the original on 2009-02-11. Retrieved 2013-10-14.
- a1b2c3.com. "Trichocereus spp. Information". A1b2c3.com. Retrieved 22 December 2017.
- "Partial List of Alkaloids in Trichocereus Cacti". Thennok.org. Archived from the original on 11 February 2009. Retrieved 22 December 2017.
- Forbidden Fruit Archives Archived 2005-11-28 at the Wayback Machine
- "Erowid Cacti Vaults : Visionary Cactus Guide - Mescaline from Sawdust". Erowid.org. Retrieved 14 January 2015.
- "Echinopsis tacaquirensis ssp. taquimbalensis". Desert-tropicals.com. Retrieved 14 January 2015.
- "Cardon Grande (Echinopsis terscheckii)". Desert-tropicals.com. Archived from the original on 5 April 2015. Retrieved 14 January 2015.
- "Archived copy". users.lycaeum.org. Archived from the original on 8 March 2001. Retrieved 17 January 2022.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - Venault P, Chapouthier G (2007). "From the behavioral pharmacology of beta-carbolines to seizures, anxiety, and memory". ScientificWorldJournal. 7: 204–23. doi:10.1100/tsw.2007.48. PMC 5901106. PMID 17334612.
- "Cornell University Department of Animal Science". Ansci.cornell.edu. Retrieved 14 January 2015.
- Callaway, JC; Brito, GS; Neves, ES (2005). "Phytochemical analyses of Banisteriopsis caapi and Psychotria viridis". Journal of Psychoactive Drugs. 37 (2): 145–150. doi:10.1080/02791072.2005.10399795. PMID 16149327. S2CID 30736017.
- Glasby, J. S. (2002-09-11). Directory Of Plants Containing Secondary Metabolites. ISBN 9780203489871. Retrieved 14 January 2015 – via Books.google.com.
- "Chemical Information". sun.ars-grin.gov. Archived from the original on 2004-11-21. Retrieved 2008-04-11.
- "Silbrige Ayahuasca-Liane (Banisteriopsis muricata) im GIFTPFLANZEN.COMpendium". Giftpflanzen.com. Retrieved 2008-04-18.
- "Erowid Online Books : "Ayahuasca: alkaloids, plants, and analogs" by Keeper of the Trout". Erowid.org. Retrieved 22 December 2017.
- "Passion Flower". Drugs.com. Retrieved 14 January 2015.
- "www.amazing-nature.com". Archived from the original on September 27, 2007.
- Ma, ZZ; Hano, Y; Nomura, T; Chen, YJ (April 2000). "Alkaloids and phenylpropanoids from Peganum nigellastrum". Phytochemistry. 53 (8): 1075–8. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(99)00440-9. PMID 10820833. Retrieved 2008-01-12.
- Voigt, V; Laug, L; Zebisch, K; Thondorf, I; Markwardt, F; Brandsch, M (2013). "Transport of the areca nut alkaloid arecaidine by the human proton-coupled amino acid transporter 1 (hPAT1)". The Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology. 65 (4): 582–90. doi:10.1111/jphp.12006. PMID 23488788. S2CID 27577546.
- Johnston, G. A. R.; Krogsgaard-Larsen, P.; Stephanson, A. (1975). "Betel nut constituents as inhibitors of γ-aminobutyric acid uptake". Nature. 258 (5536): 627–628. Bibcode:1975Natur.258..627J. doi:10.1038/258627a0. ISSN 0028-0836. PMID 1207742. S2CID 4147760.
- Ghelardini C, Galeotti N, Lelli C, Bartolini A (2001). "Arecoline M1 receptor activation is a requirement for arecoline analgesia". Il Farmaco. 56 (5–7): 383–5. doi:10.1016/S0014-827X(01)01091-6. hdl:2158/327019. PMID 11482763.
- Halpern, J.H. (2004). "Hallucinogens and dissociative agents naturally growing in the United States". Pharmacology & Therapeutics. 102 (2): 131–138. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2004.03.003. PMID 15163594. S2CID 30734515.
Although LSD does not occur in nature, a close analogue, lysergic acid amide (LSA, ‘‘ergine’’) is found in the seeds of Argyreia nervosa (Hawaiian baby woodrose)
- Olsen, Richard W. (2000-04-25). "Absinthe and γ-aminobutyric acid receptors". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 97 (9): 4417–4418. Bibcode:2000PNAS...97.4417O. doi:10.1073/pnas.97.9.4417. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 34311. PMID 10781032.
- Denise Otsuka, Rafaela; Otsuka, Rafaela Denise; Lago, Joao Henrique Ghilardi; Rossi, Lucia; Galduroz, Jose Carlos Fernandes; Rodrigues, Eliana (2010). "Psychoactive Plants Described in a Brazilian Literary Work and their Chemical Compounds". Central Nervous System Agents in Medicinal Chemistry. 10 (3): 218–237. doi:10.2174/1871524911006030218. PMID 20557283 – via www.academia.edu.
- Kennedy, David O. (2014). "The Deliriants - The Nightshade (Solanaceae) Family". Plants and the Human Brain. New York: Oxford University Press. pp. 131–137. ISBN 9780199914012. LCCN 2013031617.
- Sałaga, Maciej; Fichna, Jakub; Socała, Katarzyna; Nieoczym, Dorota; Pieróg, Mateusz; Zielińska, Marta; Kowalczuk, Anna; Wlaź, Piotr (2016). "Neuropharmacological characterization of the oneirogenic Mexican plant Calea zacatechichi aqueous extract in mice". Metabolic Brain Disease. 31 (3): 631–641. doi:10.1007/s11011-016-9794-1. ISSN 0885-7490. PMC 4863909. PMID 26821073.
- Al Zarouni, Yousif (2015). The Effects of Khat (Catha Edulis) (First ed.). London: Yousif Al Zarouni. p. 5. ISBN 978-1-326-24867-3.
- "Protected Blog". Sliceoftheday. Retrieved 14 January 2015.
- Silvarolla, Maria B.; Mazzafera, Paulo; Fazuoli, Luiz C. (2004). "Plant biochemistry: A naturally decaffeinated arabica coffee". Nature. 429 (6994): 826. Bibcode:2004Natur.429..826S. doi:10.1038/429826a. PMID 15215853. S2CID 4428420.
- "Atropine". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 2015-07-12. Retrieved Aug 13, 2015.
- Osbourn AE, Lanzotti V (2009). Plant-derived Natural Products: Synthesis, Function, and Application. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 5. ISBN 9780387854984. Archived from the original on 10 September 2017.
- Fatur, Karsten (7 January 2021). "Peculiar plants and fantastic fungi: An ethnobotanical study of the use of hallucinogenic plants and mushrooms in Slovenia". PLOS ONE. 16 (1): e0245022. Bibcode:2021PLoSO..1645022F. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0245022. PMC 7790546. PMID 33412556.
- Dallanoce C, Frigerio F, Martelli G, Grazioso G, Matera C, Pomè DY, et al. (2010). "Novel tricyclic Δ2-isoxazoline and 3-oxo-2-methyl-isoxazolidine derivatives: Synthesis and binding affinity at neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subtypes". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry. 18 (12): 4498–4508. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2010.04.065. ISSN 0968-0896. PMID 20478710.
- Schultes, Richard Evans, Iconography of New World Plant Hallucinogens. p. 101
- Rovinskiĭ VI (Sep 1989). "A case of hallucinogen-like action of glaucine. (Russian)". Klinicheskaia Meditsina (Mosk). 67 (9): 107–8. PMID 2586025.
- "Erowid Sinicuichi Vault : FAQ (heimia salicifolia Frequently Asked Questions)". Erowid.org. Retrieved 14 January 2015.
- "Trichterwinde (Ipomoea violacea) im GIFTPFLANZEN.COMpendium". Giftpflanzen.com. Retrieved 2008-04-18.
- Mangathayaru, K; Thirumurugan, D; Patel, PS; Pratap, DV.V; David, DJ; Karthikeyan, J (2006). "Isolation and identification of nicotine from leucas aspera (willd) link". Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 68 (1): 88. doi:10.4103/0250-474X.22972. ISSN 0250-474X. S2CID 54509667.
- Rätsch, Christian (25 April 2005). The Encyclopedia of Psychoactive Plants: Ethnopharmacology and Its Applications. Inner Traditions/Bear. ISBN 9781594776625. Retrieved 22 December 2017 – via Google Books.
- Eastlack, Steven C.; Cornett, Elyse M.; Kaye, Alan D. (2020). "Kratom—Pharmacology, Clinical Implications, and Outlook: A Comprehensive Review". Pain and Therapy. 9 (1): 55–69. doi:10.1007/s40122-020-00151-x. ISSN 2193-8237. PMC 7203303. PMID 31994019.
- "Opium definition". Drugs.com. Retrieved 28 April 2022.
- Pittler MH, Ernst E (2003). Pittler, Max H (ed.). "Kava extract for treating anxiety". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (1): CD003383. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003383. PMC 6999799. PMID 12535473.
- Baker, Jonathan D. (2011-06-01). "Tradition and toxicity: evidential cultures in the kava safety debate". Social Studies of Science. 41 (3): 361–384. doi:10.1177/0306312710395341. ISSN 0306-3127. PMID 21879526. S2CID 33364504.
- "Ololiuqui (Rivea corymbosa) im GIFTPFLANZEN.COMpendium". Giftpflanzen.com. Retrieved 2008-04-18.
- "Salvia divinorum Clones". Sagewisdom.org. Retrieved 14 January 2015.
- Hui KM, Wang XH, Xue H (2000). "Interaction of flavones from the roots of Scutellaria baicalensis with the benzodiazepine site". Planta Med. 66 (1): 91–3. doi:10.1055/s-0029-1243121. PMID 10705749.
- J. F. Sobiecki (2008). "A review of plants used in divination in southern Africa and their psychoactive effects". Southern African Humanities. 20: 333–351. S2CID 37305695.
- "Erowid Online Books : "TIHKAL" - #25 IBOGAINE". Erowid.org. Retrieved 14 January 2015.
- Krengel F, Herrera Santoyo J, Olivera Flores TJ, Chávez Ávila VM, Pérez Flores FJ, Reyes Chilpa R (December 2016). "Quantification of Anti-Addictive Alkaloids Ibogaine and Voacangine in In Vivo- and In Vitro-Grown Plants of Two Mexican Tabernaemontana Species". Chemistry & Biodiversity. 13 (12): 1730–1737. doi:10.1002/cbdv.201600146. PMID 27448833. S2CID 46046257.
- Dr. B. Bös. "Sternjasmin (Trachelospermum jasminoides) im GIFTPFLANZEN.COMpendium - giftpflanzen.com". Giftpflanzen.com. Retrieved 14 January 2015.
- "Indole Alkaloids from Trachelospermum jasminoides".
- Luger D, Poli G, Wieder M, Stadler M, Ke S, Ernst M, Hohaus A, Linder T, Seidel T, Langer T, Khom S, Hering S (2015). "Identification of the putative binding pocket of valerenic acid on GABAA receptors using docking studies and site-directed mutagenesis". Br. J. Pharmacol. 172 (22): 5403–13. doi:10.1111/bph.13329. PMC 4988470. PMID 26375408.
- Dietz, B.; Mahady, G.; Pauli, G.; Farnsworth, N. (2005). "Valerian extract and valerenic acid are partial agonists of the 5-HT receptor in vitro". Molecular Brain Research. 138 (2): 191–197. doi:10.1016/j.molbrainres.2005.04.009. PMC 5805132. PMID 15921820.
- Khanavi, M.; Pourmoslemi, S.; Farahanikia, B.; Hadjiakhoondi, A.; Ostad, S. N. (2010). "Cytotoxicity ofVinca minor". Pharmaceutical Biology. 48 (1): 96–100. doi:10.3109/13880200903046187. PMID 20645762. S2CID 42993549.
- VIEIRA I, MEDEIROS W, MONNERAT C, SOUZA J, MATHIAS L, BRAZ-FILHO R, PINTO A, SOUSA P, REZENDE C, EPIFANIO R (2008). "Two fast screening methods (GC-MS and TLC-ChEI assay) for rapid evaluation of potential anticholinesterasic indole alkaloids in complex mixtures" (PDF). Annals of the Brazilian Academy of Sciences. 80 (3): 419–426. doi:10.1590/s0001-37652008000300003. ISSN 0001-3765. PMID 18797794. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2020-02-19.
- Andrade MT, Lima JA, Pinto AC, Rezende CM, Carvalho MP, Epifanio RA (June 2005). "Indole alkaloids from Tabernaemontana australis (Muell. Arg) Miers that inhibit acetylcholinesterase enzyme". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry. 13 (12): 4092–5. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2005.03.045. PMID 15911323.
- Cornara, L.; Fortuna-Perez, A. P.; Bruni, I.; Salis, A.; Damonte, G.; Borghesi, B.; Clericuzio, M. (2018-09-01). "Zornia latifolia: a smart drug being adulterated by Stylosanthes guianensis". International Journal of Legal Medicine. 132 (5): 1321–1331. doi:10.1007/s00414-018-1774-z. hdl:11449/164509. ISSN 1437-1596. PMID 29362872. S2CID 12630518.
- Fattore, Liana; Fratta, Walter (2011). "Beyond THC: The New Generation of Cannabinoid Designer Drugs". Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience. 5: 60. doi:10.3389/fnbeh.2011.00060. ISSN 1662-5153. PMC 3187647. PMID 22007163.
Bibliography
- Al Zarouni, Yousif (2015). The Effects of Khat (Catha Edulis). London: Yousif Al Zarouni.
External links
- Descriptions of psychoactive Cacti. Lycaeum Visionary Cactus Guide
- Erowid Tryptamine FAQ – More Plants Containing Tryptamines
- John Stephen Glasby, Dictionary of Plants Containing Secondary Metabolites, Published by CRC Press
- Golden Guide to Hallucinogenic Plants
- Hallucinogens on the Internet: A Vast New Source of Underground Drug Information John H. Halpern, M.D. and Harrison G. Pope, Jr., M.D.
- Chemical Investigations of the Alkaloids from the Plants of the Family Elaeocarpaceae – Peter L. Katavic, Chemical Investigations of the Alkaloids From the Plants Of The Family Elaeocarpaceae, School of Science/Natural Product Discovery (NPD), Faculty of Science, Griffith University
- Alexander T. Shulgin, Psychotomimetic Drugs: Structure-Activity Relationships
- UNODC The plant kingdom and hallucinogens (part II)
- UNODC The plant kingdom and hallucinogens (part III)
- Virola – Dried Herbarium Specimens
- Virola Species Pictures – USGS
- Desmanthus illinoensis – USDA
- Psychedelic Reader (Google Books)
Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии
