bio.wikisort.org - Plant
This glossary of botanical terms is a list of definitions of terms and concepts relevant to botany and plants in general. Terms of plant morphology are included here as well as at the more specific Glossary of plant morphology and Glossary of leaf morphology. For other related terms, see Glossary of phytopathology and List of Latin and Greek words commonly used in systematic names.
A
- ab-
- A prefix meaning "from, away from, or outside".
- abaxial
- The surface of an organ facing away from the organ's axis, e.g. the lower surface of a lateral organ such as a leaf or petal.[1] Contrast adaxial.
- abort
- To abandon development of a structure or organ.
- abscission
- The shedding of an organ that is mature or aged, as of a ripe fruit or an old leaf.
- abscission zone
- A specialised layer of tissue that allows an organ to be shed by abscission when it is ripe or senescent. Such tissue is commonly formed, for example, at the base of a petiole or pedicel.
- acaulescent
- Having no apparent stem, or at least none visible above the ground surface.[1] Examples include some species of Agave, Oxalis, and Attalea.[2] Antonym of caulescent (possessing stem)
- accrescent
- Increasing in size with age, such as a calyx that continues to grow after the corolla has fallen,[1] e.g. in Physalis peruviana.
- accumbent
- Lying against another part of the plant; when applied to a cotyledon, it means that one edge of the cotyledon lies along the radicle.
- -aceae
- A suffix added to the stem of a generic name to form the name of a taxonomic family; for example, Rosaceae is the rose family, of which the type genus is Rosa.
- achene
- A dry, one-seeded indehiscent fruit[3] in which the true fruit is not the so-called "berry", but the achenes, which are the so-called "seeds" on the infructescence, e.g. in the genus Fragaria.
- acicular
- Slender or needle-shaped.[3]
- acropetal
- Moving from roots to leaves, e.g. of molecular signals in plants.
- acrophyll
- The regular leaves of a mature plant, produced above the base, as opposed to bathyphyll.
- acrostichoid
- (describing a type of sorus) Covering the entire abaxial surface of a frond, usually densely so, as in Elaphoglossum and Acrostichum.
- actino-
- A prefix that indicates a radial pattern, form, or morphology.
- actinodromous
- (leaf venation) Palmate or radially arranged venation with three or more primary veins arising at or near the base of the leaf and reaching the margin in most species, but not all.
- actinomorphic
- Regular or radially symmetrical;[4] may be bisected into similar halves in at least two planes. Applies e.g. to steles and flowers in which the perianth segments within each whorl are alike in size and shape. Compare regular; contrast asymmetrical, irregular, and zygomorphic.
- aculeate
- Armed with prickles,[5] e.g. the stem of a rose.
- acuminate
- Tapering gradually to a point, with concave sides approaching the point.[5] Contrast acute and mucronate.
- acute
- 1. Sharply pointed, but not drawn out, with straight sides approaching the point.[5] Contrast acuminate.
- 2. Converging at an angle of less than 90°. Contrast obtuse.
- ad-
- A prefix meaning "near or toward"; also meaning "added to".[5]
- adaxial
- The surface of an organ facing toward the organ's axis,[5] e.g. the upper surface of a lateral organ such as a leaf or petal. Contrast abaxial.
- adelphia
- Plural: adelphiae. A bundle or structure of stamens forming one unit in an adelphous flower; for example, the stamen tube around the pistil of Hibiscus.
- adelphous
- Having organs, particularly filaments such as stamens, connected into one or more adelphiae, whether in the form of bunches or tubes, such as is commonly seen in families such as Malvaceae. Usage of the term is not consistent; some authors include closely bunched filaments, while others include only adelphiae in which filaments are connected at their bases at least. See for example, Sims: "...the filaments are so closely pressed that they have the appearance of being monadelphous...".[6] Compare derived terms such as monadelphous, having stamens growing in a single bunch or tube, for example in Hibiscus, and diadelphous growing in two bunches.
- adherent
- Slightly united to an organ of another kind,[5] usually to a part of another whorl, e.g. a sepal connected to a petal. Contrast adnate.
- adnate
- Grown from or closely fused to an organ of a different kind,[5] especially along a margin, e.g. a stamen fused to a petal. Adnate anthers have their halves attached to the filament through most of their length. (Contrast connate.)
- adventitious
- Produced in an unpredictable or unusual position,[5] e.g. an adventitious bud produced from a stem rather than from the more typical axil of a leaf. Adventitious roots may develop from nodes of prostrate stems of some plant species, or from the hypocotyl rather than from the radicle of a germinating monocotyledon.
- adventive
- Introduced accidentally[5] (usually referring to a weed).
- aerial
- Of the air; growing or borne above the surface of the ground or water.[7]
- aestivation
- The arrangement of sepals and petals or their lobes in an unexpanded flower bud. Contrast vernation.
- aff. (affinis)
- With affinity to others, akin to; often used for a provisionally recognized but unnamed taxon considered close to that name, perhaps a hybrid or extreme variant.
- aggregate fruit
- A cluster of fruits formed from the free carpels of a single flower, e.g. a blackberry. Compare multiple fruit.
- agochoric
- Plants that are spread through accidental transport.
- agricultural weed
- See weed.
- agriophyte
- Plant species that have invaded native vegetation and could survive there without human intervention. They are established there in natural habitats, remaining part of natural vegetation even after human influence has ceased, and are independent of humans in their continued existence.[8]
- agrophic
- a comb-like series of veins forking from a single side of a primary or secondary vein
- alate
- Having a wing or wings.
- albumen
- An older name for the endosperm of flowering plants. Except for being a storage tissue for nutrients, it is not at all like the albumen (egg white) of animal embryos.
- albuminous
- (of seeds) Containing endosperm.
- -ales
- A suffix added to the stem of a generic name or descriptive name to form the name of a taxonomic order.
- alien
- Any plant introduced to an area outside its natural range. Often used interchangeably or in combination with foreign, exotic, non-native, and non-indigenous.
- alkaloid
- Any of a loosely defined class of organic compounds found in the tissues of many species of plants. Alkaloid molecules have one or more alkaline-reacting nitrogen atoms in their carbon structures. Many alkaloids are commercially important as drugs or poisons, e.g. caffeine, morphine, quinine, and strychnine, each of which occurs naturally in certain plants.
- allelopathy
- Secretion of biochemicals by a plant which influence the growth and reproduction of nearby plants.
- allopatric
- Having separate ranges of distribution.[9] Contrast sympatric.
- alternate
- 1. (adj.) (of leaves or flowers) Borne singly at different levels along a stem, including spiralled parts. Contrast opposite.
- 2. (prep.) Occurring between something else, e.g. stamens alternating with petals.
- alternipetalous
- A configuration where parts of the flower, e.g. stamens, alternate in position with the petals.[10]
- ament
- A synonym of catkin.
- amphitropous
- (Of an ovule) Bent so that both ends are near each other. Contrast anatropous, campylotropous, and orthotropous.
- amplexicaul
- With the base dilated and clasping the stem, usually of leaves.
- amylum star
- a vegetative propagative body filled with starch (amylum) and located around the lower nodes of certain stoneworts.
- anastomose
- Branching and then rejoining, as with leaf venation.
- anastomosis
- A connection or fusion of two or more veins that are normally diverging or branching, thereby forming a network.
- anatropous
- (of an ovule) Inverted so that the micropyle faces the placenta (this is the most common ovule orientation in flowering plants). Contrast amphitropous, campylotropous, and orthotropous.
- ancipital
- Flat, with two edges (versus round).[11]
- androdioecious
- Having bisexual flowers and male flowers on separate individuals. Contrast andromonoecious, polygamodioecious, polygamomonoecious, and polygamous.
- androecium
- A collective name for the male reproductive parts of a flower; the stamens of a flower considered collectively. Contrast gynoecium. Abbreviated A; e.g. A 3+3 indicates six stamens in two whorls.
- androgynophore
- A stalk bearing both the androecium and gynoecium of a flower above the level of insertion of the perianth.
- androgynous
- Having male and female flowers in the same inflorescence.
- androphore
- The stalk or column supporting the stamens in certain flowers.
- andromonoecious
- Having bisexual flowers and male flowers on the same individual plant. Contrast androdioecious, gynomonoecious, polygamodioecious, polygamomonoecious, and polygamous.
- anemophilous
- Adapted to pollination by wind.
- anemophily
- Adaptation to pollination by wind.
- angiosperm
- A flowering plant; a plant with developing seeds enclosed in an ovary.
- anisomery
- The condition of having a floral whorl with a different (usually smaller) number of parts from the other floral whorls.
- anisotomic
- Branching, with branches having unequal diameters, such as a trunk and its branch. Contrast isotomic.
- annual
- A plant that completes its life cycle (i.e. germinates, reproduces, and dies) within a single year or growing season.
- annulus
- 1. A ring-like structure; in the form of a ring. Pappus bristles are sometimes attached to a ring called an annulus or disk at the top of the achene beak. In some pollen grains, the exine around the apertures is either thicker or thinner. In pores, this border is termed an annulus. Certain flowers have ring-like constrictions at the mouth of the flower, e.g. in Huernia and Aristolochia.
- 2. A ring of specialized cells on the sporangium.
- anterior
- Positioned in front of, toward the apex. Compare distal.
- anthemoid
- In the Compositae, a style with a brush-like tuft of sweeping hairs at the tip of each style branch.
- anther
- The pollen-bearing part of a stamen.
- antheridium
- in bryophytes, a specialised gametophytic organ that produces the male gametes
- antheridiophore
- In liverworts of the order Marchantiales, a male gametophore, a specialised, stalked structure that bears the antheridia
- antherode
- A sterile anther of a staminode.
- anthesis
- 1. (of a flower) The period during which pollen is presented and/or the stigma is receptive.
- 2. (of a flowering plant) The period during which flowers in anthesis are present. Not defined for some cases, such as when pollen is released in the bud.
- anthocarp
- A type of fruit in which some part of the flower persists attached to the pericarp, e.g. in Nyctaginaceae.
- anthophore
- A stalk-like structure, internode located between the calyx and the other parts of the flower.
- anticlinal
- Pointing up, away from, or perpendicular to a surface. Contrast periclinal.
- antrorse
- Directed foward or upward, e.g. of hairs on a stem. Contrast retrorse.
- apetalous
- Lacking petals.
- apex
The tip; the point furthest from the point of attachment.
- aphananthous
- (of flowers) Inconspicuous or unshowy, as opposed to phaneranthous or showy.
- aphlebia
Imperfect or irregular leaf endings commonly found on ferns and fossils of ferns from the Carboniferous Period.
- aphyllous
- Leafless; having no leaves.[12]
- apical
- At or on the apex of a structure, usually a shoot, a stem, or the trunk of a tree, e.g. an apical meristem or an apical bud.
- apiculate
- especially of leaves, ending in a short triangular point.
- apiphily
- A form of pollination whereby pollen is distributed by honey bees.
- apo-
- A prefix meaning "away from, separate, without".
- apocarpous
- (of a gynoecium) Consisting of one or more carpels which are free from one another (or almost so), e.g. in members of the Ranunculaceae and Dilleniaceae.
- apomixis
A type of asexual reproduction whereby viable seeds or spores are produced asexually, without fertilization, such that the genetic material they contain is a clone of the parent's genetic material. A plant produced in this way is called an apomict.
- apomorphy
- In cladistics, a "different form" from the form of an ancestor (i.e., an innovation) of use in determining membership in a clade.
- apopetalous
- Having separate petals, not fused (sympetalous).
- apophyllous
- perianth or other segments free, not united. Compare symphyllous, gamophyllous, polyphyllous.
- apophysis
- 1. The external part of a cone scale.
- 2. An outgrowth of an organ or an enlargement of a stem.
- appendage
- A secondary part attached to a main structure; an external growth that seldom has any obvious function, hence appendiculate.
- appendiculate
- Having the nature of or bearing appendages.
- appressed
- Pressed closely but not fused, e.g. leaves against a stem.
- aquatic plant
- A plant whose natural habitat is water, living in or on water for all or a substantial part of its lifespan; generally restricted to fresh or inland waters.
- arachnoid
- Cobwebby, from being covered with fine white hairs.
- arborescent
- Tree-like in growth or general appearance.
- arboretum
A taxonomically arranged collection of trees.
- archaeophyte
- A non-native plant that has nonetheless been present in a particular geographic area for some time. Contrast neophyte.
- archegonium
- A multicellular structure or organ of the gametophyte phase of certain plants, producing and containing the ovum or female gamete. The corresponding male organ is called the antheridium.
- archegoniophore
- In liverworts of the order Marchantiales, a female gametophore, specialised, stalked structure that bears the archegonia and the sporophytes
- arctotoid
- In the Compositae, a style with a ring of sweeping hairs borne on the shaft of the style proximal to the style branches.
- areolate
- Having or being composed of areoles, as an areolate crustose lichen.
- areole
- 1. A space between the threads of a net, e.g. that part of a leaf surface defined by each of the elements of a vein network; as with cacti, the area between the veinlets of a leaf.
- 2. A structure on the stem node of a cactus; the region of a cactus upon which spines and flowers are borne.
- 3. In lichenology, a polygonal piece of a thallus surface where a crustose lichen is broken up like old dried and cracked paint, or like the polygonal "islands" of dried mud in a dry lake bed.
- aril
- A membranous or fleshy appendage formed by expansion of the funicle which partly or wholly covers a seed, e.g. the fleshy outer layer of lychee fruit, or that found in members of the Sapindaceae.
- aristate
- With a stiff, bristle-like awn or tip.
- article
- A segment of a jointed stem or of a fruit with constrictions between the seeds; an organ part that separates easily from the rest of the organ at a joint or articulation.
- articulate
- Jointed; separating freely, leaving a clean scar; e.g. the fronds of certain ferns where they join the rhizome.
- ascending
- 1. (of a stem) Spreading horizontally, then directed upward; an ascending stem is more or less prostrate near its base, then erect.
- 2. (of an ovule) Attached somewhat above the base.
- ascidiate
- Shaped like a pitcher, as with the leaves of pitcher plants, e.g. species of Nepenthes and Sarracenia.[13]
- asexual reproduction
- Reproduction that does not involve gametes. Often used interchangeably with vegetative reproduction.
- asperulous
- Having a rough, sandpapery texture, e.g. some leaf surfaces.
- asymmetrical
- Irregular or unequal; lacking any plane of symmetry; e.g. flowers of Canna.
- attenuate
- Narrowing gradually.
- auricle
- An ear-shaped lobe, particularly a small, roundish, lateral appendage of a leaf or leaf-like organ.
- autogamous
- Self-pollinating, self-fertilizing – in flowering plants
- awn
- 1. Any long, bristle-like appendage.
- 2. In the Poaceae, an appendage terminating or on the back of glumes and/or lemmas of some grass spikelets.
- 3. In the Geraniaceae, the part of the style that remains attached to the carpel that separates from the carpophore (column).
- 4. A generally straight, stiff pappus element, varying from stiffly bristle-like to hard and needle-like. In Strophanthus, the awn is the beak of the seed, stipe of the coma hairs.
- axil
- The upper angle between one part of a plant and another, e.g. the stem and a leaf.
- axile
- On an axis; of a placenta, on the central axis of the ovary.
- axillary
- Borne in or arising from the axil, usually referring to the axil of a leaf.
- axis
- The main stem of a whole plant or inflorescence; also, the line along which this stem extends.


Viburnum abscission

Welwitschia mirabilis presents an example of an acaulescent growth habit unusual in so large a plant species.

Schematic diagrams of the accumbent arrangement of the cotyledons and radicle in a seed of Erysimum
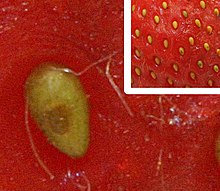
Achenes on the surface of the stem of the infructescence of a strawberry

Geranium incanum flowers are actinomorphic, having five axes of symmetry, as opposed to the two axes of symmetry of the zygomorphic flowers of most species of the related genus Pelargonium.

Fern frond with acuminate leaflets

Adelphous stamens in flower of Gossypium tomentosum

Watsonia flower slit open and with one stamen bent upward to show its adnate attachment to the petal.


Rothmannia leaf with extensively anastomose venation

Androgynous flower of Sandersonia aurantiaca cut open longitudinally to show the androecium, which comprises the anthers surrounding the green central pistil.



Aphananthous flowers of oaks such as Quercus robur, being anemophilous, have no need of being conspicuous to pollinating animals.

Apical bud of a poplar shoot

The apparently separate nuts of Ochrosia borbonica actually are apocarpous carpels, two from each flower.

Apophyses on the tips of the cone scales of Araucaria cunninghamii amount to spikes.




Blighia, Akee seeds, one whole, one in longitudinal section, showing the pale aril



Axillary buds in leaf
B
- baccate
- Fruit appearing like a berry that may or may not be a true berry.[14]
- baculiform
- Rod-like; longer than wide. Compare cylindrical.
- barb
- A rear-facing point, as in a fish hook.
- barbed
- Having barbs pointing in one direction.
- barbellate
- Having barbed hairs (barbellae).
- bark
- The protective external layer of tissue on the stems and roots of woody trees and shrubs; includes all of the living and non-living tissue external to the cambium.
- basal
- Situated or attached at the base.
- basifixed
- Something attached by its base, e.g. an anther attached to the filament. Compare dorsifixed.
- basipetal
- Developing sequentially from the apex toward the base (i.e. with the youngest toward the base), e.g. of flowers in an inflorescence. Also, moving from leaves to roots, e.g. of molecular signals in plants.
- bathyphyll
- A specialized leaf produced at the base of a plant, usually when the plant is immature, and which serves to anchor the plant to a substrate; especially notable in the fern Teratophyllum. Contrast acrophyll.
- beak
- A prominent, pointed terminal projection, especially of a carpel or fruit.
- berry
- A type of indehiscent fruit with the seeds immersed in the pulp, e.g. a tomato.
- bi-
- A prefix meaning "two"; e.g. bisulcate, having two sulci or grooves.
- biennial
- A plant which completes its life cycle (i.e. germinates, reproduces, and dies) within two years or growing seasons. Biennial plants usually form a basal rosette of leaves in the first year and then flower and fruit in the second year.
- bifid
- Forked; cut in two for about half its length. Compare trifid.
- bifoliate
- (of a compound leaf) Having precisely two leaflets, usually in a symmetrical pair, e.g. a leaf of Colophospermum mopane. Compare jugate lobed leaf, e.g. most species of Bauhinia.
- bifusiform
- Fusiform with a pinch in the middle.
- bilabiate
- Having two lips, e.g. the form of the petals in many irregular flowers.
- bilateral
- 1. Having two distinguishable sides, such as the two faces of a dorsiventral leaf.
- 2. Arranged on opposite sides, e.g. leaves on a stem; cf. distichous and opposite.
- 3. Bilaterally symmetrical, as in a leaf with a symmetrical outline.
- biloculate
- Having two loculi, e.g. in anthers or ovaries.
- binomial
- Making use of names consisting of two words to form the scientific name (or combination) in a Latin form. For example, where the first is the name of the genus to which the species belongs, and the second is the specific epithet given to that species to distinguish it from others in the same genus.
- binomial nomenclature
- The system of nomenclature in which the scientific name of a species (and not of a taxon at any other rank) is a combination of two names, the first name being the generic name. The second name is referred to botanically as the specific epithet. Note that the two names together (not just the second name) constitute the species name.
- bipinnate
- Doubly pinnate; e.g. a compound leaf with individual leaflets pinnately divided.
- bipinnatisect
- A pinnatisect leaf with deeply dissected segments.
- bisexual
- Bearing both male and female reproductive organs; usually, flowers with both stamens and carpels; synonymous with hermaphrodite, synoecious, and monoclinous. Bisexual flowers occur only on monoecious plants. See also androgynous, monoicous, and plant reproductive morphology.
- bitegmic
- (of an ovule) Covered by two integuments. Contrast unitegmic.
- biternate
- Ternate, with each division divided into three.
- bivalve
- Having two valves or hinged parts. Contrast trivalve.
- blade
- The lamina or flattened part of a leaf, excluding the stalk or petiole.
- bloom
- A fine white or bluish waxy powder occurring on plant parts, usually stems, leaves, and fruits. It is easily removed by rubbing.
- bole
- The trunk of a tree, usually the portion below the lowest branch. Compare canopy.
- bostrychoid
- Arranged on a conical surface (like a snail shell); used to describe inflorescences in which the buds are arranged in an almost helical manner on the outside of a long, tapering, conical rachis.
- bract
- A modified leaf associated with a flower or inflorescence and differing in shape, size, or colour from other leaves (and without an axillary bud).
- bracteate
- Possessing bracts.
- bracteole
- A small bract borne singly or in pairs on the pedicel or calyx; synonymous with bractlet.
- bracteolate
- Possessing bracteoles (bractlets).
- bracteose
- Having many or showy bracts.[15]
- bractlet
- See bracteole.
- branchlet
- A small branch.
- brevideciduous
- A plant that loses all of its leaves only briefly before growing new ones, so that it is leafless for only a short time, e.g. approximately two weeks.
- bristle
- A straight, stiff hair (smooth or with minute teeth); the upper part of an awn (when the latter is bent and has a lower, stouter, and usually twisted part, called the column).
- brochidodromous
- Pinnate leaf venation in which the secondary veins do not terminate at the leaf margin, but are joined in a succession of prominent arcs.
- brochus
Width of one lumen of a pollen grain reticulum and half of the width of the surrounding muri (walls), hence heterobrochate and homobrochate, where the lumina are of different or similar sizes, respectively.
- bryophyte
- Informally, any plant that is a moss, hornwort, or liverwort. Formally, these plants are placed in three separate divisions: hornworts (Anthocerophyta), liverworts (Marchantiophyta), and mosses (Bryophyta).
- bulb
- A thick storage organ, usually underground, consisting of a stem and leaf bases (the inner ones fleshy).
- bulbel
- A bulb arising from another bulb. See bulblet.
- bulbil
- A small, deciduous bulb or tuber formed in the axil of a leaf or pinna; a means of vegetative propagation.
- bulblet
- A bulb arising from another bulb; a bulbel.
- bullate
- Having rounded or globular blisters on the surface.
- burl
- A deformation or knot in the branches or trunk of a tree, sometimes sought after in woodworking.[16]
- burr
- 1. A prickly fruit.
- 2. A rough or prickly propagule consisting of a seed or fruit and associated floral parts or bracts.
- buttress root
- A root growing from an above-ground stem or trunk, and providing support, e.g. commonly of Ficus macrophylla.
- byssoid
- A growth form of a lichen thallus that is whispy, like teased wool.


Barbs occur on the spines of some species of cactus, as shown here enlarged.

Berries of Olinia ventosa, including a cross-section showing hard seeds in the pulp

The bifoliate compound leaves of the Mopane tree, Colophospermum mopane, suggested the common name "butterfly tree".

Cross-section of a silique of Arabidopsis thaliana, showing it to be biloculate, formed of two carpels, morphologically a silique and not a pod

Bipinnate leaf of Gymnocladus dioicus


This African Baobab tree, Adansonia digitata, has an enormous bole beneath a relatively modest canopy that is typical of this species.

The large, colourful bracts of Bougainvillea are commonly mistaken for its petals.

Burrs, fruits of Arctium species

C
- C, C−, C+
- In lichenology, "C" is an abbreviation for the test result of placing 5% solution of calcium hypochlorite or sodium hypochlorite (e.g. household bleach without additives) on the cortex or medulla of a lichen, to note the change in color, with no reaction noted as "C−", and production of a bright colour noted as "C+".
- caducous
- Falling off early, e.g. the sepals of poppies, which fall off when the petals begin to open. Compare persistent and fugacious.
- caespitose
- Tufted or turf-like, e.g. the growth form of some grasses.
- calcarate
- possessing a spur.
- calcareous
- A soil type or a lichen substrate rock type that is rich in or largely composed of calcium carbonate.
- calceolate
- Shaped like a slipper.[17]
- calcicole
- A plant which thrives in calcareous soil. Also calciphile, calciphyte. Antonym: calcifuge. [17]
- callose
- Hardened; thickened; callous.
- callus
1. A protruding mass of tissue
- 2. Undifferentiated tissue growth formed in response to wounding; may be grown in vitro.
- 3. In orchids, fleshy outgrowths from the labellum which can be variously shaped from papillae to plates.
- 4. In grasses, a hardened extension from the base of a floret (formed from the rachilla joint and/or the base of the lemma) which may or may not elongate and is often covered in hairs or bristles.
- calyciflorous
- Having petals and stamens attached to the calyx.
- calycophyll
- A leaf-like structure formed from a sepal or calyx lobe which enlarges, usually many-fold, before or after anthesis, especially when most of the other sepals or calyx lobes retain their original size. More extreme than an accrescent calyx, calycophylls are found in Rubiaceae. Compare semaphyll and pterophyll.
- calyculate
- Having an epicalyx.
- calyculus
- 1. A cup-shaped structure formed from bracts resembling an outer calyx.
- 2. In some Asteraceae, a circle of bracts below the involucre.
- calyptra
- A hood or lid. See operculum.
- calyx
A collective term for the sepals of one flower; the outer whorl of a flower, usually green. Compare corolla.
- calyx tube
- A tube formed by the fusion of the sepals (calyx), at least at the base.
- cambium
- A tissue layer that provides partially undifferentiated cells for plant growth.
- campanulate
- Bell-shaped.
- camptodromous
- Pinnate venation in which the secondary veins curve toward the margins, in some cases becoming nearly parallel with them, and not reconnecting with other veins to form loops.
- campylotropous
- When the ovule is oriented transversely (i.e. with its axis at right angles to its stalk) and with a curved embryo sac. Compare amphitropus, anatropous, and orthotropous.
- canaliculate
- Channelled; having a longitudinal groove.
- canescent
- Approaching white in color, as in a leaf covered with white down or wool.
- canopy
- The branches and foliage of a tree; the crown. Also refers to the protective upper layer of a forest. Compare trunk.
- capillary
- 1. A tube, pore or passage with a narrow, internal cross-section.
- 2. Slender; hair-like.
- capitate
- 1. (of an inflorescence) Having a knob-like head, with the flowers unstalked and aggregated into a dense cluster.
- 2. (of a stigma) Like the head of a pin.
- capitulum
- A dense cluster of sessile or subsessile flowers or florets, e.g. a flower head in the daisy family, Asteraceae. See pseudanthium.
- capsule
- A dry fruit formed from two of more united carpels and dehiscing when ripe (usually by splitting into pieces or opening at summit by teeth or pores).
- carduoid
- In the Asteraceae, having a style with a ring of sweeping hairs borne on the shaft of the style below the style branches.
- carina
- See keel.
- carinal canal
- A longitudinal cavity in the stems of Equisetum and extinct Equisetopsida, coinciding with a ridge in the stem surface.
- carneous
- Flesh-coloured, especially as applied to some flowers.
- carnose, carnous
- Fleshy or pulpy in texture, especially as applied to some tissues or organs. Contrast coriaceous and corneous.
- Caropodium
- Genus of flowering plants in the family Apiaceae. Native range: Turkey to Iran. Not to be confused with Carpopodium
- carpel
- The basic female reproductive organ in angiosperms, either consisting of a single sporophyll or a single locule of a compound ovary, with a style and a stigma. The gynoecium is the collective term for all of the carpels of a single flower.
- carpellary
- Referring to carpels or to associated structures or outgrowths of carpels, for example staminodes attached to carpels in Nymphaeaceae, were frequently referred to as carpellary attachments. The current and past usage of the terms "carpellary attachments", paracarpels, and staminodes is confused and varies among authors.
- carpopodium
- On achenes (Cypselae), an elongation of the base of the gynoecium which looks distinct; the abscission zone, where the achene is separated from the receptacle.
- 2. Genus Carpopodium in the family Brassicaceae; not to be confused with Caropodium
- cartilaginous
- Hard and tough; gristly. Compare corneous and coriaceous.
- caruncle
- A small piece of flesh-like tissue, typically lumpy or warty, growing on the testa near the hilum. Contrast aril.
- caryopsis
- A dry, indehiscent, one-seeded fruit in which the seed coat is closely fused to the fruit wall, e.g. in most grasses.
- Casparian strip
- A continuous band of suberin in the radial primary cell walls of the endodermis in vascular plant stems and roots that forms a permeability barrier to the passive diffusion of external water and solutes into the vascular tissue.
- cassideous
- Hood-, helmet- or bonnet-shaped; generally referring to floral anatomy, e.g. in the flowers of Aconitum, Satyrium, etc.
- castaneous
- Chestnut-coloured, reddish-brown.[18]
- casual alien
- An exotic plant that appears with no apparent human assistance but does not develop a sustained population(s), or one that persists only by repeated new introductions. Compare alien.
- cataphyll
- Any plant structure which is morphologically a leaf but which has at most an incidental or transient photosynthetic function. They are either shed when their main function has been completed, or are incorporated into structures where, when dead, they serve a protective or supportive purpose.
- catenulate
- In the shape of a chain; formed of parts or cells connected as if chained together, e.g. some diatoms, algae, and cyanobacteria such as Anabaena. See also concatenate.
- catkin
- A spike, usually pendulous, in which the mostly small flowers are unisexual and without a conspicuous perianth, e.g. in willows, poplars, oaks, and casuarinas. The individual flowers often have scaly bracts and are generally wind-pollinated. Catkins are usually shed as a unit.
- caudate
- Having a narrow, tail-like appendage or tip, e.g. a drip tip. Contrast acuminate, cuspidate, and mucronate.
- caudex
The stem of a plant, especially a woody one; also used to mean a rootstock, or particularly a basal stem structure or storage organ from which new growth arises. Compare lignotuber.
- caudiciform
- Stem-like or caudex-like; sometimes used to mean "pachycaul", meaning "thick-stemmed".
- caulescent
- possessing a well-developed stem above ground, similar to cauline. Antonym of acaulescent (lacking an apparent stem)
- cauliflory
Having flowers or fruits growing directly from a tree's branches or trunk.[19]
- cauline
- Borne on an aerial stem or caulis, as with leaves, flowers, or fruits (when applied to the latter two organs, usually referring to older stems.
- caulirosulate
- Borne at the end of the stem or caulis, as with leaves or bracts.
- cell
- 1. The basic, microscopic unit of plant structure, generally consisting of compartments in a viscous fluid surrounded by a cell wall.
- 2. A cavity of an anther or ovary.
- cenanthous
- (of a perianth) Lacking both stamens and pistil, i.e. a flower with neither androecium nor gynoecium.
- centrifixed
- Of a two-branched organ attached by its centre, e.g. a hair or anther.
- ceraceous
- Having a waxy appearance, colour, or texture, e.g. flowers of many species of Ceropegia, and the waxy fruit of some species of Myrica.
- cernuous
- Nodding, falling headlong or face down; inclined, stooping, or bowing forward. Applied to many species with a nodding, stooping habit, such as many Narcissus and Dierama species. Many plant species bear the specific epithet "cernua".
- cespitose
- An alternative spelling of caespitose, meaning Tufted or turf-like, e.g. the growth form of some grasses.
- chamber
- A cavity of an ovary.
- channelled
- Sunken below the surface, resulting in a rounded channel.
- chartaceous
- Having a papery texture.
- chasmogamous
- Of flowers that are pollinated when the perianth is open. Compare cleistogamous.
- chasmophyte
- A plant adapted to growing in crevices or hollows, such as in cliff faces. Compare cremnophyte.[20][21]
- chimera
- An individual composed of two or more genetically distinct tissues, most commonly as a result of a graft and sometimes by mutations that occur during cell division or cellular transfers during seed development.
- chiropterophilous
- Pollinated by bats.
- chlorophyll
- Any of a variety of different chemical pigments in chloroplasts that are essential for photosynthesis.
- chloroplast
- An organelle present in plant cells which contains chlorophyll.
- chlorosis
- An abnormal lack or paleness of color in a normally green organ.
- cilia
Very small hairs or hair-like protrusions more or less confined to the margins of an organ, as with eyelashes; in motile cells, minute, hair-like protrusions which aid motility.
- circinate
- Spirally coiled with the tip innermost, e.g. circinate vernation of the developing fronds of most ferns.
- cirrhose
- (of a leaf) Ending in a tendril at the apex.
- cladode
- A photosynthetic branch or stem, often leaf-like and usually with foliage leaves either absent or much reduced. Compare phyllode.
- class
- The principal category for taxa ranking between division and order.
- clathrate
- Shaped like a net or lattice; pierced with apertures, as with a cage.
- clavate
- Club-shaped.
- clavuncula
- In the Apocynaceae, an enlarged, drum-shaped stigma of which the sides and lower surface are the receptive zones. Coherent with the anthers or not.
- claw
- 1. A narrow, stalk-like, basal portion of a petal, sepal, or bract.
- 2. In Melaleuca, the united portion of a stamen bundle.
- cleistogamous
- Having flowers which self-pollinate and never open fully, or which self-pollinate before opening. Compare chasmogamous.
- climber
- A plant growing more or less erect by leaning on or twining around another structure for support, or by clinging with tendrils.
- cline
A continuous morphological variation in form within a species or sometimes between two species.
- clone
- A plant derived from the asexual vegetative reproduction of a parent plant, with both plants having identical genetic compositions.
- coalescent
- Having plant parts fused or grown together to form a single unit.
- cochleariform
- Concave and spoon-shaped.
- cochleate
- Coiled like a snail's shell.
- coenobium
- An arranged colony of algae that acts like a single organism.
- coenocyte
- A single cell with multiple nuclei, formed when nuclear division was not followed by cytokinesis.
- coleoptile
- One type of sheath in the structure of monocotyledonous seeds. The coleoptile is a protective sheath or cap (pileus), generally more or less pointed, that covers the monocotyledonous plumule as it emerges from the soil. It generally turns green and contributes to photosynthesis until its function is superseded by the main growth of the seedling. Contrast this with the coleorhiza, which remains underground until it is superseded as the roots emerge.
- coleorhiza
- One type of sheath in the structure of monocotyledonous seeds. The coleorhiza connects the coleoptile to the radicle and protects the monocotyledonous radicle during germination. Unlike the coleoptile, the coleorhiza is associated with the root and does not emerge from the soil during germination. Contrast coleoptile.
- collenchyma
- A specialized tissue consisting of living cells with unevenly thickened cellulose and pectin cell walls that performs a support function in organs such as leaves and young stems that are composed of primary plant tissues.
- colleter
- A multicellular, glandular hair that usually produces a mucilaginous substance and is located on sepals, stipules, or petioles, or on nearby parts of stems; commonly found on plants in the order Gentianales.
- columella
- In flowering plants, the central axis of the cone or fruit, e.g. in Callitris.
- column
- 1. A structure extending above the ovary and incorporating the style and stamens also known as the gynostegium, e.g. in orchids and milkweeds.
- 2. In grasses, the lower, stouter, and usually twisted part of an awn, distinct from the slender upper part or bristle.
- columnar
- Shaped like a column.
- coma
- 1. A tuft of hairs from testa or funiculus at one or both ends of some seeds, e.g. in Strophanthus, Asclepias, or Alstonia.
- 2. Sterile bracts, e.g. in Curcuma, Ananas, or Eucomis.
- 3. Sterile flowers, e.g. in Muscari and Leopoldia, at the apex of some inflorescences.
- 4. A tuft of hairs at the base of some flowers, e.g. in Pfaffia gnaphalioides.
- 5. A tuft of hairs at the apex or base of some spikelets.
- 6. An axil tuft of hairs in inflorescences in some Poaceae, e.g. in Eragrostis comata.
- commercial name
- A name often of no botanical standing and not governed by the ICNCP. The term generally applies to names such as Trademark Names, names covered by Plant Breeders Rights, Patents and Promotional Names, which are often used to enhance the sale of a plant.
- commissure
- The seam or face at which two carpels adhere. See also fissure and suture.
- community
- An ecological assemblage of plants that characteristically occur together.
- compound
- Composed of several parts, e.g. a leaf composed of multiple leaflets, a gynoecium composed of multiple carpels, or an inflorescence made up of multiple smaller inflorescences.
- compound palmate
- Having leaflets that radiate from a central point (usually at the top of a petiole), like spread-out fingers radiating from the palm of a hand. Compare palmate.
- compressed
- Flattened lengthwise, either laterally (from side to side) or dorsally (from front to back).
- concatenate
- Joined together in a chain-like form. See also concatenate and catenate.
- concolorous
- Having the same colour throughout; uniformly coloured.
- conduplicate
- Arranged such that two sides of a flat surface are folded along the midline to face each other. See also ptyxis, aestivation, and vernation.
- cone
- A type of fruit, usually woody, ovoid to globular, including scales, bracts, or bracteoles arranged around a central axis, e.g. in gymnosperms, especially conifers and Casuarina.
- conflorescence
- A rarely used term describing substantial differences between the overall structure of an inflorescence and that of its individual branches, e.g. the bottlebrush multiple-flower head of members of the genus Callistemon.
- connate
- Fused to another organ (or organs) of the same kind, e.g. petals in a gamopetalous corolla tube. Compare adnate.
- connective
- The part of an anther that connects the anther cells.
- connivent
- Coming into contact or converging.
- conspecific
- Belonging to the same species.
- contiguous
- Adjoining, touching, but not united.
- contort
- (of sepals or petals) A type of imbricate aestivation in which one side of each segment overlaps one of the adjacent segments and the other side is overlapped by the other adjacent segment. See convolute.
- contorted
- Twisted out of the normal shape.
- convolute
- 1. Referring to the arrangement of floral or foliar organs in a bud when each organ or segment has one edge overlapping the adjacent organ or segment; a form of imbricate arrangement. See contort.
- 2. (of leaves) A type of vernation in which one leaf is rolled up inside another.
- 3. A type of vernation of two leaves at a node, in which one half of each leaf is exposed and the other half is wrapped inside the other leaf.
- corcle
- A plant embryo, plumule, or plumule plus radicle.
- cordate
- Heart-shaped, with the notch lowermost; of the base of a leaf, like the notched part of a heart. Contrast obcordate.
- coriaceous
- Leathery; stiff and tough, but flexible. Compare corneous.
- corm
A fleshy, swollen stem base, usually underground and functioning in the storage of food reserves, with buds naked or covered by very thin scales; a type of rootstock.
- cormel
- A small corm (or cormlet), forming at the base of a growing larger corm.[22]
- corneous
- Horny in texture; stiff and hard, but somewhat tough. Compare coriaceous.
- corolla
- A collective term for the petals of a flower. Compare calyx.
- corona
- 1. In flowering plants, a ring of structures that may be united in a tube, arising from the corolla or perianth of a flower and standing between the perianth lobes and the stamens. The trumpet of a daffodil is a corona.
- 2. In grasses, a hardened ring of tissue surmounting the lemma in some species.
- cortex
In lichens, the "skin" or outer layer of thallus tissue that covers the medulla. Fruticose lichens have one cortex encircling the branches, even flattened, leaf-like forms; foliose lichens have different upper and lower cortices; crustose, placodioid, and squamulose lichens have an upper cortex but no lower cortex; and leprose lichens lack any cortex.
- corticolous
- Growing on bark or on wood with the bark stripped off. Compare lignicolous.
- corymb
An inflorescence with branches arising at different points but reaching about the same height, giving the flower cluster a flat-topped appearance.
- costa
- A rib.
- costapalmate
- Having a definite costa (midrib), unlike the typical palmate or fan leaf, but with the leaflets arranged radially as in a palmate leaf.
- cotyledon
- The primary leaf or leaves of a plant embryo which upon germination develops into the seed-leaf or the first set of leaves.
- craspedodromous
- Pinnate venation in which the secondary veins terminate at the margins, often as teeth.
- crateriform
- In the shape of a saucer or shallow cup; hemispherical or more shallow.
- cremnophyte
- A plant adapted to growing on, especially hanging from, cliff faces or crevices. Compare chasmophyte.[20][21]
- crenate
- Having blunt or rounded teeth; scalloped.
- crenulate
- Minutely scalloped.
- crisped
- Finely curled, as with the edges of leaves and petals.
- cristarque cell
- A sclereid which contains a druse and has the lignin deposited excentrically on the cell wall to form a cup shape, or in cross-section, a ∪-shape.
- crown
- See canopy.
- cross
- To make something interbreed; the act of hybridization.
- cruciform
- Cross-shaped.
- crustaceous
- Hard, thin and brittle.
- crustose
- Forming a closely applied surface layer or crust.
- cryptogam
- Any of the "lower plants" which produce spores and do not have stamens, ovaries, or seeds; literally, plants whose sexual reproductive organs are not conspicuous. This group typically includes the ferns, bryophytes, and algae, and sometimes fungi (including lichenized fungi). Compare phanerogam.
- cucullate
- Hood-like or hooded, commonly referring to the shape of leaves or petals, e.g. Pelargonium cucullatum. Similarly derived terms include cuculliform and cuccularis.
- culm
- In grasses, sedges, rushes, and some other monocotyledons, an aerial stem bearing the inflorescence, extending strictly from the base of the plant to the lowest involucral bract (or base of the inflorescence).
- cultigen
- A plant whose origin or selection is primarily due to intentional human activity.
- cultivar
- A term derived from "cultivated variety" denoting an assemblage of cultivated plants clearly distinguished by one or more characters (morphological, physiological, cytological, chemical, or other). When reproduced (either sexually or asexually), the assemblage retains its distinguishing characters. A cultivar may arise in cultivation or be introduced from the wild. It is a variant that is of horticultural interest or value. Cultivar names are written with single quotation marks around them, e.g. 'Blue Carpet' or 'Alba'. All new names established after 1 January 1959 must be in common language (that is, not in Latin), but names established in Latin prior to this date are retained in Latin form.
- cultivar epithet
- The defining part of a name that denominates a cultivar. Cultivars are designated by fancy (q.v.) epithets appended either to the scientific name or to the common name of the taxon to which they belong; they are not italicized but placed in single quotation marks, e.g. Rubus nitidoides 'Merton Early'. 'Merton Early' is the cultivar epithet.
- cuneate
- Wedge-shaped, with straight sides converging at a base.
- cupule
- A cup-shaped structure composed of coalescent bracts, such as the cup of an acorn. See calybium.
- cupular
- Shaped like a cupule.
- cupulate
- Bearing cupules.
- cupuliform
- Nearly hemispherical, shaped like a cupola or dome.
- cusp
- A hard, pointed tip, stiffer and more formidable than a mucro, hence cuspidate.
- cuspidate
- Tipped with a cusp, as with some leaves.
- cuticle
- A waterproofing layer covering the epidermis of aerial plant surfaces and composed of the polymers cutin, and/or cutan and waxes.
- cutting
- An apical tip of shoot structure, root, or leaf which is cut from a plant and used for asexual vegetative propagation.
- cyathium
An inflorescence of unisexual flowers surrounded by involucral bracts, especially the flowers of Euphorbia.
- cyathophyll
- In Euphorbia, the bract-like structure on which the involucre sits, usually but not always occurring in twos. They may sometimes be brightly colored and confused with petals.
- cylindrical
- Rod-like and two to three times as long as wide. Compare baculiform.
- cynaroid
- See carduoid.
- cyme
A type of inflorescence in which the main axis and all lateral branches end in a flower (each lateral may be repeatedly branched).
- cymose
- Having a cyme or cymes.
- cypsela
- A type of dry, one-seeded, indehiscent fruit formed from an inferior ovary.



Structure of flower of an orchid in genus Praecoxanthus, with the callus labelled

Bearded callus of a floret of the grass species Chrysopogon filipes



Male catkins of Betula pendula

The caudex of Dioscorea elephantipes grows largely above the soil surface. Many species that form caudices grow them underground.

Flowers growing from a branch of Syzygium moorei, an example of cauliflory.

Some members of the Espeletia genus exhibit a growth habit that is caulirosulate.

Moehringia growing as a chasmophyte on an overhanging cliff

Chloroplasts within the cells of the leaves of the moss Bryum capillare

Not all chloroplasts are simple in shape. Chloroplasts of Spirogyra are helical within the tubular cells of their algal filaments.



Colony of cells forming a coenobium, of an alga in the genus Pediastrum





The conical compound inflorescence of Aeonium arboreum is a compound panicle composed of minor panicles, some of which are compound in their turn.

California buckeye (Aesculus californica) has a compound palmate leaf, the leaflets radiating from a central point.

The lobes of the gamopetalous corolla of Nicotiana flowers are conduplicate in the bud.

Casuarina equisetifolia male and female flowers and cones



The corona of this Passiflora flower is a ring of purple filaments between the petals and the stamens.

Cotyledons of seedlings of Koelreuteria. One plant shows the first new leaves above its cotyledons; the rest show various younger stages of emerging cotyledons.

Crassula rupestris frequently grows as a cremnophyte on cliff faces in fynbos.

Nymphoides crenata has crenate leaf margins.


Mimetes cucullatus, so named for the hooded, cucullate shape of its white flowers

Murraya paniculata has leaves with cuneate (wedge-shaped) bases.

Examples of cupules of Fagaceae:
A: Quercus rubra B: Quercus trojana
C: Fagus sylvatica D: Castanea sativa
A: Quercus rubra B: Quercus trojana
C: Fagus sylvatica D: Castanea sativa

Cuspidate leaves of Diplacus bigelovii var. cuspidatus

D
- deciduous
- Dehiscing and falling seasonally, as with bark, leaves, or petals. Contrast persistent.
- declinate
- Curving downward, and then upward at the tip. Often qualified, e.g. declinate-ascendant.
- decompound
- Divided to more than one level, e.g. in bipinnate leaves, in which the leaflets of what would otherwise be a pinnate leaf are themselves pinnately divided.
- decorticate
- 1. (intr. v.) To shed the outer bark of a tree, usually seasonally as part of the natural growth cycle.
- 2. (tr. v.) To strip the peel, crust, bark, or other surface tissues from a plant or from harvested material, such as in extracting fibre from harvested Agave leaves.
- decumbent
- Having branches growing horizontally along the ground but which are turned up at the ends.
- decurrent
- Extending downward beyond the point of insertion, e.g. when the base of a leaf or a fungal gill is prolonged downward along the stem in a raised line or narrow wing.
- decussant
- A synonym of decussate; the usage decussant is questionable and occurs rarely, probably as an error. The formally correct usage is decussate.
- decussate
- Opposite with successive pairs borne at right angles to the last; generally applied to the arrangement of leaves.
- definite
- Of a constant number, e.g. twice as many stamens as petals or sepals (or less), or an inflorescence ending in a flower or an aborted floral bud, typically a cymose inflorescence. Contrast indefinite.
- deflexed
- Bent downward. Contrast inflexed.
- dehiscent
- Breaking open at maturity to release contents; refers e.g. to the opening of fruits to release seeds, of anthers to release pollen, and of sporangia to release spores. Contrast indehiscent.
- deltoid
- Shaped like the uppercase Greek letter Δ, i.e. like a more or less equilateral triangle.
- dendroid
- Tree-like; branching like a tree.
- dentate
- Toothed, especially in reference to leaf margins.
- denticulate
- Finely toothed; a diminutive form of dentate.
- deserticolous
- Inhabiting a desert.
- determinate
- Limited, usually in growth. Contrast indeterminate.
- diadelphous
- Referring to a class of adelphous structure in which the stamens or similar organs are connected in two adelphiae instead of just one.
- diaspore
- Any reproductive part of a plant adapted for dispersal and for establishing new plants; may be a disseminule such as a seed, or other parts such as specialised buds, branches, inflorescences, or fruits.
- dichasium
- A cymose inflorescence with all branches below the terminal flower in regular opposite pairs. Compare monochasium and pleiochasium.
- dichlamydeous
- Having a perianth which is divided into a separate calyx and corolla. Compare homochlamydeous.
- dichotomous
- Forking into two equal branches. This may result from an equal division of the growing tip, or may be sympodial, in which the growing tip is aborted and replaced. Typically refers to mode of branch growth, as in Aloidendron dichotomum, but also to other organs, such as the venation patterns on leaves, the thorns of various species of Carissa (which morphologically are branches), and the thalli or hyphae of various algae and fungi.
- dicotyledon
A flowering plant whose embryo has two or more cotyledons (seed leaves). Contrast monocotyledon.
- digitate
- With segments spreading from a common centre, like the fingers of a hand. See also palmate and palmatisect.
- digitiform
- shaped like a finger.
- dimorphic
- Occurring in two different forms (with respect to shape and/or size), e.g. of stamens, fronds, or leaves. See also monomorphic (having a single form) and polymorphic (having many forms).
- dioecious
- (of vascular plants) Having male and female reproductive structures which develop only on different individuals and never on the same individual. Contrast monoecious.
- dioicous
- (of a bryophyte gametophyte) Having male and female reproductive structures which develop only on different individuals and never on the same individual. Contrast monoicous.
- diploid
- Having two complete sets of chromosomes in the nucleus of a sporophyte cell, i.e. one set from each of the parental gametes. This is often expressed symbolically as 2n, where n = the number of chromosomes in the haploid gamete.
- diplostemonous
- Having stamens arranged in two whorls, with the outer whorl alternating with the petals while the inner whorl is opposite the petals. Compare obdiplostemonous and haplostemonous.
- disc
A plate or ring of structures derived from the receptacle, and occurring between whorls of floral parts. In some groups, especially Sapindales, the nectary is in the form of a prominent disk. In daisies, the central part of the capitulum is a disk, hence flowers borne there are called disk flowers or florets.
- discoid
- Resembling a disc or plate, having both thickness and parallel faces and with a rounded margin. Also used to describe the flower head of Asteraceae where there are no ray florets but only disc florets.
- discolorous
- (of leaves) Having upper and lower surfaces of different colours.
- disjunct
- Occurring in widely separated geographic areas, distinctly separate; applies to a discontinuous range in which one or more populations are separated from other potentially interbreeding populations with sufficient distance so as to preclude gene flow between them.
- disk floret
- A floret occurring most typically in the disk of the capitulum of flowers in the family Asteraceae, and to some extent in other plants that bear a flowering head with a disk, such as Scabiosa.
- dissected
- Deeply divided; cut into many segments.
- dissepiment
- A partition or septum in a plant part, usually referring to septa between the loculi of capsules or of other fruits with multiple partitions.
- distal
- Remote from the point of origin or attachment; the free end. Contrast proximal.
- distichous
- Arranged in two opposite rows (and hence in the same plane).
- distinct
- Separate or free; not united.
- distyly
- The condition in which the flowers of a species occur in two forms that differ only by the length of the style and stamens, and flowers of only one of these forms appear on any one plant. Compare heterostyly.
- diurnal
- Of the day; occurring or opening in the daytime.
- divaricate
- Wide-spreading.
- divergent
- Spreading in different directions, generally upward.
- division
- A taxonomic rank below kingdom in the standard taxonomic hierarchy. "Division" is generally used only for plants, and is the approximate botanical equivalent of the term phylum, which is used for animals and other kingdoms.
- domatia
Any hollow structure formed by a plant that is inhabited by animals such as ants or mites.
- dorsal
- From Latin dorsum, a ridge or the back of an animal. Partly because the term originally referred to animals rather than plants, usage in botany is arbitrary according to context and source. In general "dorsal" refers to "the rear or back or upper surface", but in botanical usage such concepts are not always clearly defined and may be contradictory. For example:
- facing away from the axis (abaxial) in a lateral organ of an erect plant
- facing away from the substrate in any part of an erect plant, for example the upper surface of a more or less horizontal leaf (adaxial) or the upper part of the crown of the plant
- facing away from the substrate in a prostrate or climbing plant or floating leaves such as those of Nymphaea.
- dorsifixed
- Attached at or by the back, e.g. anthers on a filament.
- dorsiventral
- Having structurally and visibly different upper and lower surfaces, e.g. some leaves. Compare bilateral and isobilateral.
- drip tip
- A long, narrow, acuminate, caudate, or cuspidate extension at the tip of a leaf or leaflet. Commonly an adaptation to rainy conditions, as it promotes shedding of water by its dripping from the narrow tip. The term "drip tip" is not anatomically descriptive in the way that say, acuminate or cuspidate, are; rather it is a description of the functional shape that aids dripping, irrespective of the specific geometry of the shape itself.
- drupe
- A type of succulent fruit formed from one carpel; the single seed is enclosed by a stony layer of the fruit wall, e.g. in peaches and olives. Also called a kernel.
- drupelet
- A small drupe formed from one of the carpels in an apocarpous flower. Drupelets usually form a compound fruit, as in Rubus, but they may become widely separated, as in Ochna.
- druse
- A globular mass of calcium oxalate crystals, usually with the crystals radiating from an organic core.

Seasonal, healthy decortication of Eucalyptus grandis outer bark

A decorticating machine collecting fibre from leaves

Decussate phyllotaxis of Crassula rupestris

Dentate leaf of elm

Denticulate leaves of Ziziphus mauritiana

Astragalus austriacus is regarded as diadelphous because it has one stamen unattached to the main adelphia (bunch).

The paired cotyledons of a castor bean seedling (Ricinus communis) are typical of a dicotyledon.

Discolorous leaves of Brachylaena discolor differ in colour between their upper and lower surfaces.

Disk florets opening in a capitulum of a cultivated Helianthus. They open progressively from the edge to the centre of the disk.


Boophone disticha has conspicuously distichous leaves.

Domatia at the bases of the thorns of Acacia drepanolobium, the "Whistling Thorn". Note the access holes.


E
- -eae
- A suffix added to the stem of a generic name to form the name of a tribe, e.g. Aster → Astereae.
- ebracteate
- Lacking bracts; synonymous with ebracteolate.
- ecological amplitude
- The range of environmental conditions in which an organism can survive.
- edaphic
- Of or influenced by the soil.
- elaiosome
- An external structure attached to the seed of many species of plants. Elaiosomes generally look fleshy and in some species they are rich in oils or other nutritious materials. Their functions vary and are not always obvious; commonly they attract ants or other animals that aid in dispersal, but they may also repel other animals from eating the seed.[23]
- elephophily
- A form of pollination whereby pollen or spores are distributed by the feet of elephants, as in Rafflesia arnoldii.
- ellipsoid
- A three-dimensional shape that is elliptical in all sections through the long axis.
- elliptical
Planar, shaped like a flattened circle, symmetrical about both the long and the short axis, tapering equally both to the tip and the base; oval.
- emarginate
- Typically in reference to leaf margins: notched or recessed at some part of the edge, such as the apex; the recess usually is broad and shallow. The location of a leaf's emargination(s) might be one or more of apical, lateral or basal
- embryo
- The young plant contained by a seed prior to germination.
- emergent
- A plant taller than the surrounding vegetation or, among aquatic plant species, one that bears flowers and commonly leaves above the surface of the water. Aquatic examples include water lilies, reeds, and papyrus. Some pondweeds such as Stuckenia are not emergent until they flower, at which time only their flowers appear above the water surface.
- enation
- Leaf-like outgrowth from a surface.[24]
- enantiostyly
- The condition in which the gynoecium protrudes laterally, to the right (dextrostyly) or to the left (sinistrostyly) of the androecium, e.g. Senna.
- endemic
- Having a natural distribution restricted to a particular geographic region. Compare native.
- endocarp
- The innermost layer of the wall of a fruit; in a drupe, the stony layer surrounding the seed.
- endodermis
- The innermost layer of the cortex of vascular plant roots, also present in the stems of pteridophytes. The radial walls are impregnated with suberin to form a permeability barrier known as the Casparian strip.
- endophloeodal
- See endophloic.
- endophloic
(of crustose lichens) Having the thallus growing within rather than upon the bark of trees.[25]: 159 Compare epiphloedal and corticolous (growing on the surface of wood or bark) and endolithic (growing within rock).
- endosperm
- 1. (angiosperms) A nutritive tissue surrounding the embryo of the seed, usually triploid, originating from the fusion of both polar nuclei with one gamete after the fertilization of the egg.
- 2. (gymnosperms) The prothallus within the embryo sac.
- endospory
- The production of spores that germinate into a reduced multicellular gametophyte contained within the spore wall. Contrast exospory.
- ensiform
- Shaped like the blade of a sword.
- entire
- 1. Not divided.
- 2. (of a margin) Smooth and not lobed or toothed (though possibly wavy or scalloped).
- entomophily
- A form of pollination whereby pollen or spores are distributed by insects.
- epecophyte
- Species of recent appearance, usually numerous and constant in the country, but confined to artificial habitats, such as meadows and ruderal vegetation and are dependent on humans for existence.[26]
- ephemeral
- Short-lived. See also caducous.
- epicalyx
- An involucre resembling an outer calyx, e.g. as in Hibiscus.
- epicarp
- The outer layer of the wall of a fruit, i.e. the "skin".
- epicormic
- Used to refer to buds, shoots, or flowers developing from the old wood of trees, especially after injury or fire.
- epicotyl
- The part of the plant axis or stem between the cotyledonary node and the first foliage leaves.
- epicuticular wax
- A layer of crystalline or amorphous wax deposited on the surface of the cuticle.
- epidermis
- An organ's outermost layer of cells, usually only one cell thick.
- epigynous
- Borne on the ovary; describes floral parts when attached above the level of the ovary and arising from tissue fused to the ovary wall. Compare hypogynous and perigynous.
- epilithic
- Growing on stone. Compare lithophytic, a plant growing on stone.
- epinecral
- Dead (necral) tissue above the surface of the cortex of a lichen.
- epipetalous
- Of stamens that are attached to the petals.
- epipetric
- Growing on rock or stone, lithophytic, epilithic.
- epiphloedal
- Growing on the surface of bark. Contrast endophloedal (growing inside, not on, the bark) and epilithic (growing on rock, not bark).
- epiphyte
- A plant, alga or fungus that grows on another plant without deriving nourishment from it but using it for support.
- epiphytic
- Of an epiphyte; living on the surface of a plant. Compare epilithic, lithophytic.
- episepalous
- Of stamens that are attached to the sepals.
- epitepalous
- Of stamens that are attached to the tepals.
- epithet
- The adjectival component in a binomial scientific name, usually more specifically called a specific epithet; the final word or combination of words in a name of more than one word (other than a term denoting rank) that denominates an individual taxon. The simplest and commonest example is the second word in a two-word name of a species, such as "mirabilis" in Welwitschia mirabilis.
- epizoochory
- A type of seed dispersal that occurs when seeds or fruits physically adhere to the outside of vertebrate animal bodies.
- epruinose
- Not pruinose.
- equitant
- (of a leaf) Folded lengthwise and clasping another leaf.
- erect
- Upright, more or less perpendicular to the ground or point of attachment. Compare patent (spreading) and erecto-patent, between erect and patent.
- ericoid
- Having leaves like those of the European heaths (Erica); small and sharply pointed.
- erose
- (of a margin) Irregular as though nibbled or worn away.
- ethelochoric
- Deliberate introduction by seedlings, seeds or plants in a new habitat by humans.
- etiolation
- Weak growth due to lack of light, resulting in elongated stems and yellowish colour.[27]
- even-pinnate
- Having an even number of leaflets in a compound leaf; synonymous with paripinnate.
- evergreen
- Not deciduous; having leaves all year.
- ex
- In nomenclature, indicating that the preceding author proposed the name but did not legitimately publish it, and that the succeeding author referred to the first author when legitimately publishing the name. See Author citation (botany).
- exalbuminous
- In seeds of a given species, having no endosperm, i.e. no albumen, e.g. in Fabaceae and Combretaceae.
- exocarp
- The outer layer of the pericarp, often the skin of fleshy fruits.
- exospory
- The production of spores that germinate into free-living multicellular gametophytes. Contrast endospory.
- exotesta
- The outer layer of the testa (seed coat). It is derived from the outer integument of the ovule.
- exotic
- Not native; introduced from another region or country.
- exserted
- Projected beyond, e.g. stamens beyond the corolla tube.
- exstipulate
- Lacking stipules.
- extrastaminal
- Outside the stamens or androecium, usually referring to the location of a nectary disk.
- extrorse
- (of anther locules) Opening toward the outside of the flower. Contrast introrse and latrorse.
![Plants of the genus Corydalis bear seeds with attached elaiosomes, which have various functions, commonly attracting ants. On some Corydalis species, elaiosomes that attract ants also repel mice.[23]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/9/92/Corydalis_cheilanthifolia_pod.jpg/220px-Corydalis_cheilanthifolia_pod.jpg)
Plants of the genus Corydalis bear seeds with attached elaiosomes, which have various functions, commonly attracting ants. On some Corydalis species, elaiosomes that attract ants also repel mice.[23]


Petals of Heracleum sphondylium are variously emarginate at their tips—flowers in the middle of the inflorescence have slightly emarginate petals, whereas flowers at the periphery are so deeply emarginate as to be almost cleft in two.


Water lilies and reeds represent two ecological categories of emergent aquatic vegetation.

Iris pseudacorus has clearly ensiform leaves: narrow, straight-edged, sword-shaped.



An epilithic lichen

Tillandsia recurvata growing as a harmless, non-parasitic epiphloedal epiphyte on a tree trunk that is also infested with an epiphloedal foliose lichen



Sections of exalbuminous seeds

Aloe marlothii flowers with stamens and stigmata of mature flowers exserted from the mouths of the floral tubes
F
- F1 hybrid
- A single cross; a plant breeding term for the result of a repeatable cross between two pure bred lines.
- F2 hybrid
- A plant breeding term for the result of a plant arising from a cross between two F1 hybrids; may also refer to self-pollination in a population of F1 hybrids.
- fabiform
- Shaped like a kidney bean.
- facultative
- Of parasites, optional. Compare obligate.
- falcate
- Curved like the blade of a scythe.
- family
- A taxonomic group of one or more genera with features and/or ancestry in common; the term for the principal rank between order and genus.
- farina
- powdery, pale yellow crystalline secretion consisting of flavonoids in Primula and other species
- farinaceous
- Powderiness that is mealy
- fascicle
A cluster, e.g. a tuft of leaves all arising from the same node.
- fasciculate
- Branching in clusters like a bundle of sticks or needles; having fascicles.
- faveolate
- Honeycombed; having regular, angled pits. Compare foveolate.
- faucal
- Pertaining to the fauces; located in the throat of a calyx or corolla.
- fauces
- The throat of a calyx or corolla; the conspicuously widened portion between the mouth and the apex of the tube. In Boraginaceae, the site of distinctive appendages.
- felted
- Covered with very dense, interlocked and matted hairs with the appearance or texture of felt or woollen cloth.
- female flower
- See pistillate flower.
- fenestrate
- Having translucent areas. See also perforate, with holes.
- ferruginous
- Ruddy or rust-colored.
- fertile
- Capable of producing fruit; of flowers when they produce seed or of anthers containing pollen.
- fertilization
- The union of male and female gametes during sexual reproduction.
- fiber
- 1. A fiber cell.
- 2. Any flexible, strong, stringy, and very elongate structure.
- fiber cell
- a type of cell that is found in sclerenchyma, it is much elongated and dies soon after an extensive modification of its cell wall. The cell wall is usually thickly lignified, but is sometimes gelatinous.
- filament
- 1. The stalk of a stamen.
- 2. Any very narrow, thread-like structure that is one or a few cells thick.
- filamentous
- consisting of filaments or fibres, hairlike.
- filiform.
- thread-like. e.g. stamen filaments, or leaf shapes.
- fimbria
- slender hair-like process (plural: fimbriae)
- fimbriate.
- Fringed.
- fissure
- A split or crack, often referring to fissured bark; a line or opening of dehiscence.
- fistule
- A tube-shaped cavity.
- fistulose
- Hollow; usually applied to a tube-shaped cavity, as in a reed.
- flabellate
- Fan-shaped.
- flaccid
- Limp; tending to wilt. Compare turgid.
- flexistyly
- Depending on the degree of maturation of the stamens, the style moves up or down (cataflexistyle or (ana-)hyperflexisyle).
- flexuous
- flexuose
- Bent alternately in different directions; zig-zag.
- floccose
- Having a soft and woolly covering of hairs.
- flora
- 1. all the plants growing in a certain region or country.
- 2. an enumeration of them, generally with a guide to their identification (e.g. the present volume, the Flora of Victoria, the Flora of New South Wales and so on). In this case 'flora' is written with a capital F.
- floral envelope
- See perianth.
- floral leaves
- The upper leaves at the base of the flowering branches.
- floral diagram
- A graphical means to describe flower structure, usually a schematic cross-section through a young flower.
- floral formula
- A description of flower structure using numbers, letters and various symbols.
- floral tube
- An imprecise term sometimes used as a synonym of hypanthium or of corolla tube or of calyx tube.
- floret
- A small flower, usually referring to the individual true flowers clustered within an inflorescence, particularly those of the grasses and the pseudanthia of daisies.
- flower
- The sexual reproductive structure of the angiosperms, typically with a gynoecium, androecium, perianth and an axis.
- foliate
- Preceded by a number: having a certain number of leaflets; for example, 3-foliate, "having three leaflets"
- foliicolous
- A growth habit of certain lichens, algae, and fungi that prefer to grow on the leaves of vascular plants.
- follicle
- A dry fruit formed from one carpel, splitting along a single suture, to which the seeds are attached. Compare pod (of legume).
- foliole
- A small leaf-like appendage on the front or back.
- foliose
- Leaf-like; flattened like a leaf.
- forb
- Any non-woody flowering plant that is not a grass, sedge, or rush.
- forest
- Vegetation dominated by trees with single trunks (including closely arranged trees with or without an understory of shrubs and herbs).
- forma (in common usage, form)
- A taxonomic category subordinate to species and within the taxonomic hierarchy, below variety (varietas), and usually differentiated by a minor character.
- foveolate
- Having regular tiny pits. Compare faveolate.
- free
- Not united with other organs of the same type; not attached at one end.
- free central
- Of placentation, ovules attached to a free-standing column in the centre of a unilocular ovary.
- frond
- A leaf of a fern, cycad, or palm.
- frutescent
- Shrub-like (fruticose) or becoming shrub-like.
- fruticose
- Shrubby; having the branching character of a shrub.
- fruit
- A seed-bearing structure present in all angiosperms, formed from the mature ovary and sometimes associated floral parts upon fertilization.
- fugacious
- Disappearing, falling off, or withering. Compare persistent and caducous.
- funicle (funiculus)
- The stalk of an ovule.
- funnelform
- Having a form gradually widening from the base to apex; funnel-shaped.
- furcate
- Forked, usually applied to a terminal division; with two long lobes.
- fused
- Joined together.
- fusiform
- Rod-shaped and narrowing gradually from the middle toward each end; spindle-shaped.

Astragalus falcatus has conspicuously falcate pods; not many falcate anatomical structures are so markedly curved.

Rhigozum obovatum bears its leaves in well-defined fascicles.

Favolaschia calocera, the orange pore fungus, has conspicuously faveolate fruiting bodies.

Emerging leaves of Oldenburgia grandis are heavily felted.

Fenestrate leaves of Darlingtonia californica

Digitalis ferruginea owes its specific name to its ferruginous (rust-coloured) flowers.

Calochortus fimbriatus has fimbriate flowers.


The pseudanthium of Zinnia elegans is typical of many Asteraceae in that it includes two types of florets, ray florets and disk florets.

The foliose thallus of the lichen Parmotrema tinctorum is leafy.

Medicago sativa (alfalfa or lucerne) is an agriculturally important forb, grown in large volumes for forage, soil improvement, and other purposes.

Foveolate seeds of Physochlaina physaloides

G
- galbulus
- In gymnosperms, a fleshy cone (megastrobilus); chiefly relates to cones borne by junipers and cypresses, which are often mistakenly called berries.
- galea
- An overhanging, helmet-shaped, structure that protects the reproductive parts from precipitation, wind or unwanted visitors.
- gall
- Abnormal outgrowth on external plant tissues, caused by various parasites, from viruses, fungi and bacteria, to other plants, insects and mites.
- gamete
- A cell or nucleus that fuses with another of the opposite sex during sexual reproduction.
- gametophore
- Specialized structures on the gametophytes of some bryophyte species, for example many species in the order Marchantiales; in such species the gametes are produced on the gametophores, which amount to sex organs.
- gametophyte
- The haploid multicellular phase in the alternation of generations of plants and algae that bears gametes. In bryophytes the gametophyte is the dominant vegetative phase; in ferns and their allies it is a small free-living plant known as the prothallus; in gymnosperms and angiosperms the gametophytes are reduced to microscopic structures dependent on the sporophyte, male gametophytes contained in pollen grains and females contained within the ovules.
- gamopetalous
- with joined or fused petals
- gamophyllous
- a single perianth-whorl of united segments. Compare symphyllous (synonym), apophyllous, polyphyllous
- gemma
- an asexual reproductive structure found in liverworts and mosses.
- gene pool
- The complete range of genetic variation found within a population.
- genus
A group of one or more species with features or ancestry (or both) in common. Genus is the principal category of taxa intermediate in rank between family and species in the standard nomenclatural hierarchy.
- generic name
- The name of a taxonomic genus, such as Acacia and Eucalyptus.
- genotype
- The genetic make-up of an individual.
- geophilous
- Growing or rooting in the ground.
- germination
- 1. of seeds, describing the complex sequence of physiological and structural changes that occur from resting to growth stage.
- 2. of a pollen grain; production of a pollen tube when contacting a stigma receptive to it.
- 3. of a spore of fungi/bacterium; change of state – from resting to vegetative.
- gibbous (gibbose)
- (of part of an organ) Swollen, usually with a pouch-like enlargement at the base.
- glabrescent
- Becoming glabrous, almost glabrous; glabrate.
- glabrous
- 1. Lacking surface ornamentation such as hairs, scales or bristles; smooth.
- 2. In lichenology, having no indumentum.
- gland
- A secretory structure within or on the surface of a plant.
- glandular hair
- A hair tipped with a gland.
- glaucous
- Describes the external surface of a plant part that has a whitish covering, in some cases with a blueish cast. Often applied to plants with a woolly or arachnoid surface, but properly referring to pruinose surfaces, meaning those with a waxy bloom. The surface of the young leaves of many eucalypts provide good examples, and so do some xerophytes.
- globose
Roughly spherical. See also subglobose.
- globulose
- Approximately spherical.
- glochid
- A tiny barbed hair or bristle, e.g. the fine defensive hairs in cactus species such as Opuntia.
- glumes
- bracts subtending the floret(s) of a sedge, or similar plant; in grasses forming the lowermost organs of a spikelet (there are usually 2 but 1 is sometimes reduced; or rarely, both are absent).
- glutinous
- Sticky.
- graft
- 1. The artificial union of plant parts.
- 2. A plant shoot suitable for grafting; loosely, a scion, sucker, or branch.
- graft chimaera (sometimes graft hybrid)
- A taxon whose members consist of tissue from two or more different plants in intimate association originated by grafting. The addition sign "+" is used to indicate a graft-chimaera either as a part of a formula (e.g. Crataegus monogyna + Mespilus germanica) or in front of an abbreviated name (e.g. +Crataegomespilus 'Dardari'). The nomenclature of graft hybrids is governed by the International Code of Nomenclature for Cultivated Plants.
- graminoid
- granular
- (of a surface) Covered with small rounded protuberances.
- grass
- A plant of the family Poaceae.
- grassland
- Low vegetation dominated by grasses.
- groundcover
- 1. Dense vegetation that covers the ground.
- 2. A term applied to describe a plant that covers the soil surface so densely that it smothers all beneath it.
- group
- A formal category equivalent to or below the rank of genus which distinguishes:
- an assemblage of two or more cultivars within a species or hybrid;
- plants derived from a hybrid in which one or more of the parent species is not known or is of uncertain origin;
- a range of cultivated plants of a species or hybrid which may exhibit variation but share one or more characters, which makes it worth distinguishing them as a unit.
- guard cell
- Each of two cells surrounding the stoma which control gas exchange between the apoplast of the plant and the external environment.
- guttate
- Having droplet-shaped spots. Compare punctate and maculate.
- guttation
- The secretion of liquid water from uninjured plant parts. See hydathode.
- guttulate
- Having or appearing to be spotted with oil droplets; of spores, having oil droplets inside.
- gymnosperm
- A seed-bearing plant with unenclosed ovules borne on the surface of a sporophyll. Gymnosperms are among the oldest clades of vascular plants, and today are represented by approximately 1,000 extant species worldwide, including, among others, conifers, Ginkgo, Gnetum and cycads. Compare angiosperm.
- gynaecium
- Alternative term for gynoecium, but with partly different etymology.
- gynobasic
- Of a style, arising near the base of the gynoecium, e.g. between the lobes of the ovary.
- gynodioecious
- Of a species, with some plants bearing only bisexual flowers and others bearing only female flowers.
- gynomonoecious
- Of a species, with bisexual flowers and female flowers on the same plant.
- gynoecium
- The collective term for the female reproductive parts of a flower or for the carpels of a flower, whether united or free. Contrast androecium. Abbreviation: G. For instance, G indicates a superior ovary; G(5) indicates having five fused carpels.
- gynophore
- A stalk supporting the gynoecium and situated above the level of insertion of the other floral parts.
- gynostegium
- A compound organ in milkweeds (Asclepiadaceae) and orchids formed by fusion of the filaments of the stamens with the style. Also known as the column.

Galbulus (berry-like, fleshy) cones on the coniferous tree Podocarpus elatus

Gametophores (red male antheridia and brown female archegonia) borne on a gametophyte of a Chara species of green algae

Longitudinal section of immature male pine cone, showing male gametophytes (pollen grains) developing between the cone scales

Glandular hairs on the stem of Geranium dissectum

The leaves, buds, and young stalks of Eucalyptus macrocarpa are glaucous, covered with a thick waxy pruinosity.


Glumes of a grass species with a fairly large inflorescence

Scanning electron micrograph of a stoma on the leaf of Haemanthus. The two lip-shaped cells on either side of the pore are the guard cells.


Examples of gymnosperms
LEFT1-Welwitschia mirabilis
2-Cycas revoluta
3-Taxus baccata
4-Ginkgo biloba
RIGHT
1-Cupressus sempervirens
2-Sequoiadendron giganteum
3-Agathis dammara
4-Araucaria heterophylla }}
H
- habit
- The general external appearance of a plant, including size, shape, texture, and orientation.
- habitat
- The place where a plant lives; the environmental conditions of its home.
- hafter
- A flat attachment that forms when the thallus of a fruticose or foliose lichens comes in contact with a substrate, different from rhizines and hapters.
- hair
- A single elongated cell or row of cells borne on the surface of an organ.
- half-inferior ovary
- An ovary partly below and partly above the level of attachment of the other floral parts. Compare inferior ovary, superior ovary.
- halonate
- Having a transparent coating, or being of a spore's outer layer.
- halophyte
- A plant adapted to living in highly saline habitats; a plant that accumulates high concentrations of salt in its tissues.
- hand-pollination
- The controlled act of pollination that excludes the possibility of open-pollination.
- haploid
- Having one set of chromosomes, e.g. the complement of chromosomes in each of the cells of the gametophyte, the nucleus of a gamete and the spores. This is expressed symbolically as n, where n = the gametic number of chromosomes. Compare diploid, triploid, and tetraploid.
- haplostemonous
- Having a single series of stamens equal in number to the proper number of petals, and alternating with them. Compare diplostemonous, obdiplostemonous.
- hapter
- An attachment that may form when a foliose lichen thallus comes in contact with a substrate.
- harmomegathy
- process by which pollen grains in arid environments close off their apertures to avoid losing water
- hastate
- Triangular in outline, the basal lobes pointing outward, so that the base appears truncate; may refer only to the base of a leaf with such lobes. Compare sagittate which refers to basal lobes pointing backward.
- haustorium
- In parasitic plants, a structure developed for penetrating the host's tissues.
- head
- See capitulum, a pseudanthium.
- heathland
- Vegetation dominated by small shrubs which usually have ericoid leaves.
- helicoid
- Coiled; of a cymose inflorescence, when the branching is repeatedly on the same side (the apex is often recurved). Compare scorpioid.
- hemerochory
- A plant that has been transported voluntarily or involuntarily by humans in a territory which it could not have colonized by its own natural mechanisms of dissemination, or at least much more slowly.[28]
- hemi-legume
- A legume fruit in which the seed or seeds and one valve of the pod are dispersed as a unit. The valve catches the wind and blows away with the seeds, as in Acacia tenuifolia and Peltogyne paniculata.
- herb
- Any vascular plant that does not develop a woody stem at any point during its life cycle, e.g. a daffodil.
- herbaceous
- Not woody; usually green and soft in texture.
- herbarium
A collection of preserved, usually pressed and dried, plant material used for identification and comparison; also a building in which such collections are stored.
- hermaphrodite
- A synonym of bisexual.
- hesperidium
- A form of berry that occurs most familiarly in the genus Citrus. The fruit tends to be large for a berry, ranging from not much more than a centimetre in small fruited genera such as Murraya, to 15 cm or more in some varieties of Citrus. The outer rind typically is thick and tough with many oil glands, while the carpels within are packed with juicy fibres.
- heteroblastic
- Having parts, especially leaves, that are distinctly different between the juvenile and adult stages.
- heteromorphic
- Having two or more distinct morphologies (e.g. of different size and shape). Compare isomorphic.
- heterospory
- The production of spores of two different sizes (small and large) by the sporophytes of land plants. Compare homospory.
- heterostyly
- The condition of a species having flowers with different style and stamen lengths, but with all the flowers of any one plant being identical. see:distyly.
- hilum
- The scar on a seed coat where it separates from its stalk (funicle).
- hip
- The fruit of a rose plant.
- hippocrepiform
- Horseshoe-shaped.
- hirsute
- Bearing coarse, rough, longish hairs. See indumentum.
- hispid
- Bearing long, erect, rigid hairs or bristles, harsh to touch.
- hoary
- Covered with a greyish to whitish layer of very short, closely interwoven hairs, giving a frosted appearance.
- holotype
- A type chosen by the author of a name. Compare lectotype.
- homochlamydeous
- Having a perianth which is not divided into a separate calyx and corolla. Contrast dichlamydeous.
- homospory
- The production of spores of only one size by the sporophytes of land plants. Compare heterospory.
- hort.
1. as a name misapplied by gardeners
- 2. as an invalid name derived from horticultural writings of confused authorship.
- husk
- The protective outer covering of certain seeds, for example, the leafy outer covering of an ear of maize (corn), the leathery covering of the walnut or the spiky covering of the chestnut.
- hyaline
- Translucent; usually delicately membranous and colourless.
- hybrid
- A plant produced by the crossing of parents belonging to two different named groups, e.g. genera, species, varieties, subspecies, forma and so on; i.e. the progeny resulting within and between two different plants. An F1 hybrid is the primary product of such a cross. An F2 hybrid is a plant arising from a cross between two F1 hybrids (or from the self-pollination of an F1 hybrid).
- hybrid formula
- The names of the parents of a hybrid joined by a multiplication sign, e.g. Cytisus ardonoi × C. purgans.
- hydrophily
- A form of pollination whereby pollen is distributed by the flow of waters.
- hypanthium
- A tube or cup-like structure in a flower that includes the bases of sepals, petals, and stamens, and may or may not be connected (adnate) to the ovary.
- hyper-resupinate
- In botany, describing leaves or flowers that are in the usual position, but are borne on a petiole or pedicel, respectively, that is twisted 360 degrees. The term is used to describe organs, such as orchid flowers, that are usually resupinate. Compare resupinate.
- hypocarpium
- An enlarged fleshy structure that forms below the fruit, from the receptacle or hypanthium.
- hypocotyl
- Of an embryo or seedling, the part of the plant axis below the cotyledon and node, but above the root. It marks the transition from root to stem development.
- hypocrateriform
- Salver shaped - synonym of salverform. From Greek kratḗrion - a vessel
- hypogynous
- Borne below the ovary; used to describe floral parts inserted below the ovary's level of insertion. Compare epigynous, perigynous.
- hypothallus
- The hypothallus is the outgrowth of hyphae from under the margin of the thallus of a crustose lichens, connecting the island-like areoles into a single lichen.
- hysteranthous
- A type of growth in which new leaves appear after flowering. Also spelled histeranthous. Compare proteranthous and synanthous.

Epidermal hairs on plant leaves

Multicellular hairs on the edge of a sepal of Veronica sublobata


Markedly hastate leaf of Salvia canariensis

The swollen haustorium of Viscum capense renders the end of the branch stunted compared to the lower part of the branch.


Heteroblastic growth is common in Eucalyptus species with leaves that are isobilateral in the mature tree; they generally start life with dorsiventral leaves. Some of these saplings are in the transient stage in which they have both forms of leaves, dorsiventral on lower branches, and isobilateral above.


A hypocarpium forms below the fruits of Sassafras albidum.

Flowers, fruit and propagule of a Rhizophora "mangle" or mangrove. The apparent root of the propagule is in fact meristematic tissue developing from the hypocotyl. The new plant develops largely from this tissue, especially if it has successfully penetrated into mud in which the new plant can establish itself.
I
- idioblast
- A cell, especially of a leaf, differing markedly from surrounding cells. They often synthesise specialised products such as crystals.
- illegitimate name (nomen illeg.)
- A name not abiding by the rules of the botanical Codes, e.g. later homonyms, cultivars that have been Latinised after 1 Jan 1959; cultivar names with more than 10 syllables or 30 letters; cultivar names that use confusing names of other plants, e.g. Camellia 'Rose'.
- imbricate
- From the Latin for "tiled". Overlapping each other; of perianth parts, edges overlapping in the bud (the convoluted arrangement is a special form of imbrication). Dormant buds of many deciduous species are imbricately covered with protective cataphylls called bud scales. Compare with subimbricates meaning lightly overlapping
- imparipinnate
- A pinnate leaf with an odd number of pinnae (terminated by a single leaflet). Compare paripinnate.
- in
- In nomenclature, where the preceding author published the name in an article or book, authored or edited by the succeeding author.
- -inae
- The suffix added to the stem of a generic name to form the name of a subtribe: for instance, Corydalinae from Corydalis + -inae.
- inbreeding
- The production of offspring between closely related parents leading to a high degree of similarity; self-fertilization is the most intense form of inbreeding.
- incertae sedis
- Of unknown taxonomic affinity; relationships obscure.
- incised
- Cut deeply and (usually) unevenly (a condition intermediate between toothed and lobed).
- included
- Enclosed, not protruding, e.g. stamens within the corolla.
- incomplete flower
- A flower which lacks one or more of its usual parts, such as carpels, sepals, petals, pistils, or stamens.
- incurved
- Bent or curved inward; of leaf margins, when curved toward the adaxial side.
- ined.
- An abbreviation of Latin inedita, an unpublished work. Used to indicate that a botanical name appeared only in a manuscript that was not published, so the name is invalid.
- indefinite
- variable in number, and as a rule numerous, e.g. more than twice as many stamens as petals or sepals, but no particular standard number of stamens. In another usage it is a synonym for the preferable term indeterminate, meaning the condition in which an inflorescence is not terminated by a flower, but continues growing until limited by physiological factors. Compare numerous. Contrast definite.
- indehiscent
- Not opening in any definite manner at maturity; usually referring to fruit. Contrast dehiscent.
- indeterminate
- usually referring to a stem or inflorescence in which there is no particular terminal bud or meristem that stops growth and ends the extension of the stem, which continues until physiological factors stop the growth. Racemes of some Xanthorrhoeaceae, such as many Aloes, and of many Iridaceae, such as Watsonias, are indeterminate. Contrast determinate.
- indigenous
- native to the area, not introduced, and not necessarily confined to the region discussed or present throughout it (hardly distinct from ‘native’ but usually applied to a smaller area). For example, the Cootamundra Wattle is native to Australia but indigenous to the Cootamundra region of southern New South Wales. Compare endemic.
- indumentum
- a collective term for a surface covering of any kind of trichomes, e.g. hairs, scales.
- induplicate
- folded upward, or folded with the two adaxial surfaces together.
- indusiumbiternateindusium
- 1. a membrane covering the sporangia of some ferns.
- 2. a cup enclosing the stigma in Goodeniaceae.
- inferior ovary
- An ovary at least partly below the level of attachment of other floral parts. Compare superior ovary, half-inferior ovary.
- inflated
- swollen, like a bladder.
- inflexed
- bent sharply upward or forward. Compare deflexed.
- inflorescence
- several flowers closely grouped together to form an efficient structured unit; the grouping or arrangement of flowers on a plant.
- infraspecific
- denotes taxonomic ranks below species level, for example subspecies.
- infrageneric
- denoting taxonomic ranks below the genus level, for example, subgenera, sections, and series.
- infructescence
- the grouping or arrangement of fruits on a plant.
- infundibular (infundibuliform)
- funnel-shaped, for example in the corolla of a flower.
- inrolled
- rolled inward.
- insectivorous
- catching, and drawing nutriment from, insects.
- insertion, point of
- The point at which one organ or structure (such as a leaf) is joined to the structure which bears it (such as a stem).
- inserted
- growing out from
- integument
- in general, any covering, but especially the covering of an ovule.
- intercalary
- (e.g. of growth) occurring between the apex and the base of an organ
- intercalary meristem
- a meristem located between the apex and the base of an organ
- interjugary glands
- in pinnate leaves, glands occurring along the leaf rachis between the pinnae (occurring below the single, and often slightly larger, gland at or just below the insertion of the pinnae). Compare jugary.
- internode
- The portion of a stem between two nodes.
- interpetiolar
- (of stipules) Between the petioles of opposite leaves, e.g in Rubiaceae.
- intramarginal
- inside but close to the margin, for example a vein in a leaf.
- intrastaminal
- inside the stamens or androecium, usually referring to the location of a nectary disk.
- introrse
- of anther locules, with opening toward the centre of flower (at least in bud). Compare extrorse, latrorse.
- invalid
- Use of names not validly published according to the Code, i.e. they are not strictly 'names' in the sense of the International Code of Botanical Nomenclature.
- involucre
- A structure surrounding or supporting, usually a head of flowers. In Asteraceae, it is the group of phyllaries (bracts) surrounding the inflorescence before opening, then supporting the cup-like receptacle on which the head of flowers sits. In Euphorbiaceae it is the cuplike structure that holds the nectar glands, nectar, and head of flowers, and sits above the bract-like cyathophyll structure. Involucres occur in Marchantiophyta, Cycads, fungi, and many other groups.
- involute
- Rolled inward, for example when the margins of a leaf are rolled toward the adaxial (usually upper) surface. Compare revolute.
- iridescent
- Having a reflective coloured sheen produced by structural coloration, as in the speculum of the mirror orchid Ophrys speculum.
- irregular
- Not able to be divided into two equal halves through any vertical plane. See also asymmetrical. Compare zygomorphic, actinomorphic, and regular.
- isidium
A warty of club-like structure in some lichens that breaks off and forms new lichens without sexual reproduction. Isidia are dispersed by mechanical means, compared to soredia, which are dispersed by wind.
- isobifacial
- (of flat structures, especially leaves) Having both surfaces similar, usually referring to cell types or to the number and distribution of stomata.
- isomerous
- Having an equal number of parts in the whorls.
- isomorphic
- with all features morphologically similar, i.e. of similar size and shape. Compare heteromorphic.
- isotomic
- Having branches of equal diameter. Compare anisotomic.


Petals of Mespilus germanica are imbricate before the flower opens.

Doubly imparipinnate compound leaf of Melia azedarach

Deeply incised leaves of Pelargonium graveolens

Indefinite stamens of Hypericum

Indehiscent pods of Libidibia ferrea; unlike most Fabaceae species, the plant depends on the pods being crushed by large ungulates to disperse the seeds.

![The leaves of Syagrus palms are 'induplicately] folded, in contrast to many other palm genera with reduplicate leaves.](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/2/2b/Starr_080117-1868_Syagrus_romanzoffiana.jpg/220px-Starr_080117-1868_Syagrus_romanzoffiana.jpg)
The leaves of Syagrus palms are 'induplicately] folded, in contrast to many other palm genera with reduplicate leaves.

Stamens of Calotropis gigantea are inserted at the base of the corolla.

The intramarginal veins near the margins of this leaf are outlined in white.

Two of these three green Asteraceae involucres encase unopened flower heads, and the third supports the open colourful head of emerging flowers. The imbricate phyllaries around the heads of this Malacothrix coulteri suggest the keeled scales of a snake, giving the plant its common name: "snake's head".

This Begonia leaf shows unusual iridescence for a plant.
J
- joint
- A node or junction of two parts; articulation.
- jugary
- associated with a jugum or something yoke-like; see for example jugary gland.
- jugary gland
- A gland occurring on the rachis of a pinnate or bipinnate leaf on a jugum, the junction or attachment of pairs of pinnae or pinnules, as in some Acacia species. Compare interjugary.
- jugate
- yoke-like; describing a structure of paired items joined together as in a jugum or something yoke-like, such as some leaves and fruit.
- jugum
- applied to various yoke-like organs, usually in the sense of their being paired, such as a pair of pinnae on a rachis.
- juvenile leaves
- Leaves formed on a young plant, typically differing from the adult leaves in form.

A. Rachilla
B. Pinnule
C. Jugary glands
D. Juga (plural of jugum)
E. Base of petiole
F. Petiolary gland
G. Rachis

Jugate leaf of Bauhinia glabra

Jugate fruit of Tabernaemontana elegans

K
- K, K+, K-
- In lichenology, "K" is the abbreviation for the outcome of a test in which a 10% solution of potassium hydroxide (KOH — hence "K") is placed on lichen tissues. Color change is noted by "K-" for none, and K+ for a yellow to red or purple color.
- keel
A prominent longitudinal ridge like the keel of a boat, e.g. the structure of the corolla formed by the fusion of the lower edge of the two abaxial anterior petals of flowers in the Fabaceae.
- kernel
- See drupe.
- kettle trap
- another term for the kettle-like pitchers of any of the carnivorous pitcher plants, in which they trap their prey.
- key innovation
- A novel phenotypic trait that allows subsequent evolutionary radiation and success of a taxonomic group.
- kidney shape
- fanciful term for a reniform object such as a bean or a leaf; more formally, oblately cordate, or crescent-shaped with the ends rounded.
- kingdom
- the highest generally employed category of the taxonomic hierarchy, above that of division (phylum). The Plant Kingdom includes vascular plants, bryophytes and green algae and is also known as the clade Viridiplantae.
- Klausenfrucht
- Klausen or Klausenfrucht (german) is a special type of fruits in Lamiaceae and Boraginaceae. A dry, dehiscent fruit formed from a superior ovary with axil or basal placentation, with an adherent calyx, from more than one carpel and usually breaking apart into 1-seeded units by separating each carpel by false septa. One unit is a half carpel, mostly there are four units, seeds. English terms are eremocarp, schizocarp, mericarp or nutlets.
- knee
- abrupt bend in a root or stem, commonly at a node; a cypress knee, or pneumatophore, is a type of bend or knob in the root of some plants, especially conifers such as some of the Taxodioideae, that shows as a projection of the root above ground level or mud level.

One form of the kettle traps of a pitcher plant

Kidney-shaped leaf of Cucurbita maxima

Typical knee at a node in a grass stem

Unusually dense stand of cypress knees around the parent tree
L
- labellum
- lip; one of three or five petals which is (usually) different from the others, e.g. in Orchidaceae, Zingiberaceae, Cannaceae and Stylidiaceae.
- labiate
- lipped; where a corolla is divided into two parts, called an upper and lower lip, the two resembling an open mouth with lips.
- lacerate
- jagged, as if torn.
- lacinia
- In foliose lichens, a linear to elongate lobe, usually arising from or at the end of a larger lobe
- laciniate
- Of lobes – with ends irregularly divided into deeply divided, narrow, pointed segments; Of margins – deeply divided into pointed segments in an irregular manner.
- lacuna
- An empty space, hole, cavity, pit, depression, or discontinuity.
- lamella
- a thin, plate-like layer. (plural lamellae; adjective lamellate – composed of an assemblage of many layers)
- lamina
- the blade of a leaf or the expanded upper part of a petal, sepal or bract.
- laminal
- of, or pertaining to, the upper surface, such as the cortex of a lichen.
- lanate
- covered in or composed of woolly hairs.
- lanceolate
- longer than broad, narrowly ovate, broadest in the lower half and tapering to the tip, like a lance or spear head; (sometimes, and incorrectly, used to mean narrowly elliptic).
- lateral
- attached to the side of an organ, e.g. leaves or branches on a stem. For more detail see dorsal.
- latex
- a milky fluid that exudes from such plants such as spurges, figs and dandelions.
- laticiferous
- latex-bearing, producing a milky juice.
- latrorse
- a type of anther dehiscence in which the anthers open laterally toward adjacent anthers. cf. introrse, extrorse.
- lauroid
- resembling Laurus, the laurel genus, particularly its leaves.
- lax
- loose, not compact. Of bundles of hyphae in lichens – not stiff and not adglutinate.
- leaf
- an outgrowth of a stem, usually flat and green; its main function is food manufacture by photosynthesis. Abbreviation: lvs.
- leaf gap
- a parenchymatous area in the stele above (distal to) a leaf trace.
- leaf scar
- A healing layer forming on a stem where a leaf has fallen off.
- leaf trace
- A vascular bundle connecting the stele to a leaf.
- leaflets
- The ultimate segments of a compound leaf.
- lecanorine
- of lichens, having apothecia with rims of tissue similar to the tissue of the thallus, as in the genus Lecanora[29]
- legume
- 1. a fruit characteristic of the family Fabaceae, formed from one carpel and either dehiscent along both sides, or indehiscent.
- 2. a crop species in the family Fabaceae.
- 3. a plant of the family Fabaceae.
- lemma
- the lower of 2 bracts enclosing a grass flower.
- lenticel
- Typically lenticular (lens-shaped) porous tissue in bark with large intercellular spaces that allows direct exchange of gases between the internal tissues and atmosphere through the bark.
- lenticular
- 1. lens-shaped.
- 2. covered in lenticels.
- lepidote
- covered with small scales.
- leprose
- powdery
- liana
- a woody climbing plant, rooted in the ground (liane is also used).
- liane
- a woody climbing plant, rooted in the ground. See also liana.
- lichenicolous
- growing on or in lichens, often but not necessarily as parasites
- ligneous
- having hard lignified tissues or woody parts, woody
- lignum
- Dead wood, typically in the context of a substrate for lichens.
- lignicolous
- Growing on wood tissue after bark as fallen or been stripped off (compare to corticolous).
- lignotuber
- a woody swelling of the stem below or just above the ground; contains adventitious buds from which new shoots can develop, e.g. after fire.
- ligulate
- 1. bearing a ligule.
- 2. strap-shaped.
- ligule
- 1. A small membranous appendage on the top of the sheath of grass leaves.
- 2. A minute adaxial appendage near the base of a leaf, e.g. in Selaginella.
- 3. An extended, strap-like corolla in some daisy florets.
- linea, line, British line, Paris line
- Various pre-metric units somewhat larger than 2 mm, used in botany into the 20th century. See Line (unit) and Paris line.
- linear
- Very narrow in relation to its length, with the sides mostly parallel. See Leaf shape.
- lingulate
- tongue-shaped.
- lip
- A labellum.
- lithophytic
- A plant growing on rocks; an epilithic plant.
- lobe
- Part of a leaf (or other organ), often rounded and formed by incisions to about halfway to the midrib.
- loculicidal
- (of a fruit) Dehiscing through the centres of loculi. Compare septicidal.
- locule
- A chamber or cavity containing seeds within an ovary, pollen within an anther or spores in a sporangium.
- lodicule
- One of two or three minute organs at the base of the ovary of a grass flower, representing parts of a strongly reduced perianth.
- lomentum or loment
- A pod-like indehiscent fruit that develops constrictions between the segments and at maturity breaks into one-seeded segments instead of splitting open.
- longicidal
- (of anthers) Opening lengthwise by longitudinal slits. Compare poricidal.
- lunate
- Crescent-shaped.
- lumen
- The cavity bounded by a plant cell wall.
- lyrate
- Lyre-shaped; deeply lobed, with a large terminal lobe and smaller lateral ones.

Labiate flowers of Prunella vulgaris

Laciniate, deeply incised, leaves of Pelargonium crispum

Most Euphorbias are laticiferous and instantly exude latex when even mildly punctured.

A leaf scar on Juglans regia, showing the layer of corky protective tissue that remained after the leaf separated along the abscission zone. It also shows the leaf traces of the vascular bundles that broke off when the abscission zone failed. The axillary bud associated with the leaf shows just above the scar.


The dark horizontal lines on silver birch bark are lenticels.

Lignotubers of Lambertia formosa growing sprouts after a bush fire

Ligule between the leaf sheath and leaf of a grass

Loculicidal dehiscence of a fruit capsule. The locule walls split at the back, and the valves separate, bearing the septa on their centres.

The loment (or lomentum) of Hedysarum occidentale splits into single-seeded segments along the visible lines of weakness when ripe.
M
- maculate
- Spotted; marked with spots.
- male flower
- See staminate flower.
- mallee
- A growth habit in which several woody stems arise separately from a lignotuber; a plant with such a growth habit, e.g. many Eucalyptus species; vegetation characterized by such plants.
- mangrove
- Any shrub or small tree growing in salt or brackish water, usually characterized by pneumatophores; any tropical coastal vegetation characterized by such species.
- margin
- The edge of a structure, as in the edge of a leaf blade.
- marginal
- Occurring at or very close to a margin.
- marsh
- A waterlogged area or swamp.
- mast
- Edible fruit and nuts produced by woody species of plants (e.g. acorns and beechmast) which is consumed on the ground by wildlife species and some domestic animals.
- mealy
- Covered with coarse, floury powder.
- medulla
- 1. In a lichen, the typically undifferentiated tissue underneath the cortex of the thallus, or between the upper and lower cortex if both are present. The medulla is analogous to the tissues underneath the epidermis (skin) of a leaf. The uppermost region commonly contains most of the photobionts.
- 2. pith. See also medullary rays in wood.
- megasporangium
- the larger of two kinds of sporangium produced by heterosporous plants, producing large spores that contain the female gametophytes. Compare microsporangium.
- megaspore
- the larger of two kinds of spores produced by a heterosporous plant, giving rise to the female gametophyte. Compare microspore.
- megasporophyll
- in hetersoporous plants, a modified leaf bearing one or more megasporangia. Compare microsporophyll.
- megastrobilus
- the larger of two kinds of cones or strobili produced by gymnosperms, being female and producing the seeds. Compare microstrobilus.
- membranous
- thin, translucent and flexible, seldom green.
- mericarp
- one segment of a fruit (a schizocarp) that splits at maturity into units derived from the individual carpels, or a carpel, usually 1-seeded, released by the break-up at maturity of a fruit formed from 2 or more joined carpels.
- meristem
- Any actively dividing plant tissue.
- mesic
- Moist, avoiding both extremes of drought and wet; pertaining to conditions of moderate moisture or water supply; applied to organisms (vegetation) occupying moist habitats.
- mesocarp
- The fleshy portion of the wall of a succulent fruit inside the skin and outside the stony layer (if any), surrounding the seed(s); sarcocarp.
- mesomorphic
- Soft and with little fibrous tissue, but not succulent.
- mesophyll
- 1. The parenchyma tissues between the upper and lower epidermis. They vary in function, but usually include the photosynthetic tissue of a leaf.
- 2. In ecology, the blade of a leaf or leaflet that has a surface area 4500–18225 mm2; a plant, or vegetation, that has mesophyll (sized) leaves.
- mesophyllous
- (of vegetation) Of moist habitats and having mostly large and soft leaves.
- mesophyte
- A plant thriving under intermediate environmental conditions of moderate moisture and temperature, without major seasonal fluctuations.
- micropyle
- Opening at apex of ovule.
- microsporangium
- The smaller of two kinds of sporangium produced by a heterosporous plant, producing microspores that contain the male gametophyte. Compare megasporangium.
- microspore
- The smaller of two kinds of spores produced by a heterosporous plant. Compare megaspore.
- microsporophyll
- In heterosporous plants, a modified leaf bearing one or more microsporangia. Compare megasporophyll.
- microstrobilus
- The smaller of two kinds of cones or strobilus produced by gymnosperms, being male and producing the pollen. Compare megastrobilus.
- midrib
The central and usually most prominent vein of a leaf or leaf-like organ.
- midvein
- See midrib.
- monad
- A single individual that is free from other individuals, not united with them into a group. The term is usually used for pollen to distinguish single grains from tetrads or polyads.
- moniliform
- Resembling a string of beads.
- monocarpic
- Flowering and setting seed only once before dying. See also semelparous.
- monochasium
- A cymose inflorescence with the branches arising singly. Compare dichasium, pleiochasium.
- monocot
- An abbreviation of monocotyledon.
- monocotyledon
- A flowering plant whose embryo contains one cotyledon (seed-leaf). Compare dicotyledon.
- monoecious
- (of vascular plants) Hermaphroditic, with all flowers bisexual, or with male and female reproductive structures in separate flowers but on the same plant, or of an inflorescence that has unisexual flowers of both sexes. Contrast dioecious.
- monoicous
- (of bryophyte gametophytes) Hermaphroditic or bisexual, where both male and female reproductive structures develop on the same individual. Contrast dioicous.
- monograph
- Of a group of plants, a comprehensive treatise presenting an analysis and synthesis of taxonomic knowledge of that taxon; the fullest account possible (at the time) of a family, tribe or genus. It is generally worldwide in scope and evaluates all taxonomic treatments of that taxon including studies of its evolutionary relationships with other related taxa, and cytological, genetic, morphological, palaeobotanical and ecological studies. The term is often incorrectly applied to any systematic work devoted to a single taxon. Compare revision.
- monomorphic
- Of one type, rather than several. See also dimorphic (two types) and polymorphic (many types).
- monophyllous
- Having a single leaf.
- monopodial
- A mode of stem growth and branching in which the main axis is formed by a single dominant meristem. Contrast sympodial.
- monostromatic
- Being a single cell thick, as in the alga Monostroma.
- monothecous
- having a sole compartment or cell. Compare Dithecous
- monotypic
- Containing only one taxon of the next lower rank, e.g. a family with only one genus, or a genus that includes only a single species.
- morphology
- The shape or form of an organism or part thereof.
- mucro
A sharp, short point, generally at the tip of a leaf or the tip of the midrib of a compound leaf.[20]
- mucronate
- Terminating in a mucro.
- multiple fruit
- A cluster of fruits produced from more than one flower and appearing as a single fruit, often on a swollen axis, as with many species of the family Moraceae. Compare aggregate fruit.
- muricate
- Covered with short hard protuberances.
- mutation
- In times before the nature of genetic encoding was understood, mutation was regarded as an abrupt, and sometimes heritable, variation from the norm of a population; for example a plant might unexpectedly produce "double" flowers, a novel colour, or a habit of growth uncharacteristic of the species or variety. Advances in genetics and molecular biology in the mid-twentieth century, showed that biological mutations comprise and reflect changes in the nucleic acid molecules that encode the genome of an organism or virus. The nucleic acid affected could be DNA in the chromosomes, or it could be extrachromosomal DNA (typically DNA in the mitochondria or chloroplasts). In RNA viruses a mutation would be a change to the genetic information that the RNA encodes.
- mycelium
- The "vegetative" (nonreproductive) part of a fungus, mostly composed of aggregations of hyphae. It functions in substrate decomposition and absorption of nutrients.
- mycobiont
- The fungal component of a lichen. Compare photobiont.
- mycorrhiza
One of several types of symbiotic association between a fungus and the roots of a plant.
- mycotroph
A plant that obtains most or all of its carbon, water, and nutrients by associating with a fungus.

Maculate leaves

Eucalyptus socialis, showing its mallee habit, a single tree with several trunks growing from an underground lignotuber

Mast from beeches on the forest floor

Geranium incanum schizocarp and mericarp
Apical meristem in root tip:
1: Meristem2: Columella
showing statocytes with statoliths
3: Lateral part of the tip
4: Dead cells
5: Elongation zone

Mesophyll as seen in the cross section of a dicotyledonous leaf
A-Lower epidermisB-Lower palisade mesophyll
C-Upper epidermis
D-Upper palisade mesophyll
E- Spongy mesophyll
F-Leaf vein

Longitudinal section of Pinus ovule
A=GametophyteB=Egg cell
C=Micropyle
D=Integument
E=Megasporangium

Strobilus of a Selaginella
A-MegasporeB-Microsporangium
C-Megasporangium
D-Microspore
E-Sporophyll

Moniliform pods on Vachellia nilotica

A germinating date palm, Phoenix dactylifera, a monocotyledon, showing its single cotyledon


Fungal mycelium grown in culture dish

N
- native
- Naturally occurring in an area, but not necessarily confined to it. Compare endemic.
- natural hybrid
- A hybrid taxon produced by chance in the wild.
- naturalised
- Describing a plant, introduced from another region, that grows and reproduces readily in competition with the natural flora.
- nectar
- A usually sweet, nutrient-rich fluid produced by the flowers of many plants and collected by bees and other pollinators.
- nectary
A specialized gland that secretes nectar.
- neophyte
- A plant that has recently been introduced to a geographic area. Contrast archaeophyte.
- nerve
- Another name for a vein.
- node
- The part of a stem from which leaves or branches arise.
- nomen conservandum
- (Latin) A conserved name, usually a name that became so much better known than the correct name, that a substitution was made.
- nomen illegitimum
- A name that is either superfluous at its time of publication because the taxon to which it was applied already has a name, or the name has already been applied to another plant (a homonym).
- nomen invalidum
- A name that is not validly published, and technically is therefore not a botanical name. Abbreviation: nom. inval. See valid publication.
- nomen nudum
- A name not published in accordance with the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants, usually without a diagnosis or description of the entity to which it applies, and without reference to either; such a name should not be used.
- nomenclature
- The naming of things; often restricted to the correct use of scientific names in taxonomy; a system that sets out provisions for the formation and use of names.
- noxious
- Of plants, containing harmful or unwholesome qualities. Applied in conjunction with 'weed' to specifically describe a plant which legislation deems harmful to the environment. Each state and territory in Australia has specific legislation governing noxious weeds.
- nucellus
- The tissue of the ovule of a seed plant that surrounds the female gametophyte. It is enclosed by integuments and is not of epidermal origin.
- numerous
- Stamens are described as numerous when there are more than twice as many as sepals or petals, especially when there is no set number of them. Compare indefinite.
- nut
- A hard, dry, indehiscent fruit containing only one seed.
- nutlet
- 1. A small nut.
- 2. One of the lobes or sections of the mature ovary of some members of the Boraginaceae, Verbenaceae, and Lamiaceae.

Hoya carnosa secretes so much nectar that it fall in drops if no pollinators remove it.

The small green petals of Helleborus argutifolius act as floral nectaries. The sepals function as petals.

Some Senna species have extrafloral nectaries that attract ants to defend them from pests.

O
- ob-
- A prefix meaning "inversely"; usually the same shape as that described by the word stem, but attached by the narrower end. See obcordate, oblanceolate and obovate.
- obconic
- (of a fruit, hypanthium, pistil, or calyx) Shaped like an inverted cone, attached at the apex.
- obcordate
- (of a leaf blade) Broad and notched at the tip; heart-shaped but attached at the pointed end.
- obdiplostemonous
- Having stamens arranged in two whorls, and having twice as many stamens as petals, with the outer whorl being opposite the petals. Compare diplostemonous, haplostemonous.
- oblanceolate
- Having a lanceolate shape but broadest in the upper third.
- oblate
- Having a spherical shape but flattened at the poles.
- obligate
- (of parasites) Unable to survive without a host. Contrast facultative.
- oblique
- Slanting; of a leaf or stem, larger on one side of the midrib than the other, in other words asymmetrical.
- obloid
- Having a three-dimensional oblong shape, e.g. a fruit.
- oblong
- Having a length a few times greater than the width, with sides almost parallel and ends rounded.
- obovate
- (of a leaf) Having a length about 1.5 times the width, and widest above the centre.
- obsolete
- Not evident, or at most rudimentary or vestigial.
- obtrapeziform
- trapeziform, but attached by the narrower trapezoidal base (e.g. of a leaf)
- obtuse
- Blunt or rounded; having converging edges that form an angle of more than 90°. Compare acute.
- ocrea
A sheath formed from two stipules encircling the node in members of the Polygonaceae.
- odd-pinnate
Having an odd number of leaflets in a compound pinnate leaf, such that there is only one terminal leaflet.
- oft.
- An abbreviation of "often". Compare usu. and s.t..
- -oideae
- A suffix added to the stem of a generic name to form the name of a subfamily, e.g. Fumaria → Fumarioideae.
- olim
- Formerly, e.g. "olim B", formerly in the Berlin herbarium (Herbarium Berolinense).
- ontogeny
- The sequence of developmental stages through which an organism passes as it grows.
- operculum (calyptra)
- A lid or cover that becomes detached at maturity, e.g. in Eucalyptus, a cap covering the bud and formed by the fusion or cohesion of perianth parts.
- opposite
- 1. Describing leaves or flowers borne at the same level but on directly opposite sides of their common axis.
- 2. Describing the occurrence of something on the same radius as something else, e.g. anthers opposite sepals. Compare alternate.
- opus utique oppressum
Listed after the botanical name of a plant, or the name of a publication, this indicates that a publication is listed in the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants as a suppressed work. Botanical names of the specified rank in the publication are considered not validly published (article 34).
- orbicular
- Flat and more or less circular.
- order
- A group of one or more families sharing common features, ancestry, or both.
- ortet
- The original single parent plant from which a clone ultimately derives.
- orthotropous
- Describes an ovule that is erect, with the micropyle directed away from the placenta; atropous. Compare amphitropous, anatropous, campylotropous.
- oval
- See elliptical.
- ovary
- The basal portion of a carpel or group of fused carpels, enclosing the ovules.
- ovate
- Shaped like a section through the "long axis" of an egg and attached by the wider end.
- ovoid
- Egg-shaped, with wider portion at base; 3-dimensional object, ovate in all sections through long-axis.
- ovule
- Loosely, the seed before fertilization; a structure in a seed plant within which one or more megaspores are formed (after fertilization it develops into a seed).




Obtuse leaves of Dovyalis zeyheri

Open flower of Eucalyptus macrocarpa, next to a shed operculum

Opposite arrangement (phyllotaxis) of leaves

Orbicular leaves of Dombeya rotundifolia

P
- pachycaul
- with a disproportionately thick trunk
- pachycladous
- with disproportionately thick stems
- palea
1. The upper of two bracts enclosing a grass flower, major contributors to chaff in harvested grain.
- 2. Chaffy scales on the receptacles of many Asteraceae.
- 3. Chaffy scales on the stipe of many ferns.
- paleate
- Bearing paleae or chaffy scales, as in description of the receptacle of a capitulum of a plant in the Asteraceae.
- paleaceous
- Chaff-like in texture.
- palmate
- 1. leaf with veins radiating out from a central point (usually at the top of a petiole), resembling spread out fingers pointing away from the palm.
- 2. A compound palmate leaf has leaflets that radiate from a central point (usually at the top of a petiole).
- palmatifid
- Deeply divided into several lobes arising from more or less the same level.
- palmatisect
- Intermediate between palmate and palmatifid, i.e. the segments are not fully separated at the base; often more or less digitate.
- pandurate
- shaped like the body of a fiddle (mainly, of plant leaves)
- panicle
A compound raceme; an indeterminate inflorescence in which the flowers are borne on branches of the main axis or on further branches of these.
- papilionate
- Butterfly-like; having a corolla like that of a pea.
- papilla
A small, elongated protuberance on the surface of an organ, usually an extension of one epidermal cell.
- pappus
- In daisy florets, a tuft or ring of hairs or scales borne above the ovary and outside the corolla (representing the reduced calyx); a tuft of hairs on a fruit.
- paracarpel
- Ill-defined term, variously interpreted and applied to: organs attached to carpels; staminodes close to the gynoecium; and to a pistillode in a staminate flower
- paraperigonium
An anomalous secondary outgrowth of the perianthal meristem with ramifying vasculature. See also perigonium, perianth, and corona.[30]
- parasite
- An organism living on or in a different organism, from which it derives nourishment. Some plant species are parasitic. Compare saprophyte and epiphyte.
- parenchyma
- A versatile ground tissue composed of living primary cells which performs a wide variety of structural and biochemical functions in plants.
- parietal
- Attached to the marginal walls of a structure, e.g. ovules attached to placentas on the wall of the ovary. See placentation.
- paripinnate
- Having an even number of leaflets (or pinnae), i.e. terminated by a pair of pinnae as opposed to a single pinna. Compare imparipinnate.
- parthenocarpy
- The development or production of fruit without fertilization. Compare stenospermocarpy.
- patent
Spreading; standing at 45–50° to the axis. See also erecto-patent.
- patulous
- See patent.
- pauciflor
- Having few flowers per inflorescence. Compare pluriflor and uniflor.
- pectinate
- Pinnately divided with narrow segments closely set like the teeth of a comb.
- pedate
- Having a terminal lobe or leaflet, and on either side of it an axis curving outward and backward, bearing lobes or leaflets on the outer side of the curve.
- pedicel
The stalk of a flower; may also be applied to the stalk of a capitulum in the Asteraceae.
- peduncle
The stalk of an inflorescence.
- peltate
- Shield-like, with the stalk attached to the lower surface and not to the margin.
- pellucid
- Transmitting light; for example, said of tiny gland dots in the leaves of e.g. Myrtaceae and Rutaceae that are visible when held in front of a light.
- pendulous
- Hanging, for example an ovule attached to a placenta on the top of the ovary. Compare suspended.
- penicillate
- Tufted like an artist's brush; with long hairs toward one end.
- penninervation
With pinnately arranged veins.
- pentamerous
- In five parts, particularly with respect to flowers, five parts in each whorl. See also trimerous and tetramerous.
- pepo
- A type of berry formed from an inferior ovary and containing many seeds, usually large with a tough outer skin (e.g. a cucumber, pumpkin or watermelon.)
- perennating
- Of an organ that survives vegetatively from season to season. A period of reduced activity between seasons is usual.
- perennial
- A plant whose life span extends over several years.
- perfect
- (of a flower) Bisexual; containing both male and female reproductive parts in the same inflorescence. Contrast imperfect.
- perfoliate
- With its base wrapped around the stem (so that the stem appears to pass through it), e.g. of leaves and bracts.
- perforate
- With many holes. Used to describe the texture of pollen exine, and also to indicate that tracheary elements have a perforation plate. See also fenestrate.
- perforation plate
- in a tracheary element, part of the cell wall that is perforated; present in vessel members but not in tracheids. Should not be confused with a pit.
- perianth
- The collective term for the calyx and corolla of a flower (generally used when the two are too similar to be easily distinguishable). Abbreviation: P; for instance, P 3+3 indicates the calyx and corolla each have 3 elements, i.e. 3 sepals + 3 petals.
- pericarp
- The wall of a fruit, developed from the ovary wall.
- periclinal
- Curved along parallel to a surface. Compare anticlinal.
- pericycle
- A cylinder of parenchyma or sclerenchyma cells that lies just inside the endodermis and is the outer most part of the stele of plants.
- perigonium
- In flowering plants, synonym of perianth.
- 2. In mosses, the leaves surrounding the antheridia, also called a splash-cup, e.g. in Polytrichum juniperinum.
- perigynium
- A sac from a modified tubular bract, or when fully closed an utricle, around the pistillate flower of sedges
- perigynous
- Borne around the ovary, i.e. of perianth segments and stamens arising from a cup-like or tubular extension of receptacle (free from the ovary but extending above its base). Compare epigynous, hypogynous.
- persistent
- Remaining attached to the plant beyond the usual time of falling, for instance sepals not falling after flowering, flower parts remaining through maturity of fruit. Compare deciduous, caducous.
- perule
1. The scales covering a leaf or flower bud, or a reduced scale-like leaf surrounding the bud. Buds lacking perulae are referred to as "naked".
- 2. In Camellias the final bracts and sepals become indistinguishable and are called perules.
- 3. A kind of sac formed by the adherent bases of the two lateral sepals in certain orchids.
- petal
- In a flower, one of the segments or divisions of the inner whorl of non-fertile parts surrounding the fertile organs, usually soft and conspicuously coloured. Compare sepal.
- petalody
- The transformation of reproductive organs of flower into petals.
- petaloid
- Like a petal; soft in texture and coloured conspicuously.
- petiolary (or petiolar)
- Associated with a petiole, as in petiolary glands.
- petiolate
- (of a leaf) Having a petiole. Contrast sessile.
- petiole
- The stalk of a leaf.
- petiolule
- The stalk of a leaflet.
- petricolous
- Rock-dwelling; living on or among rocks.
- phaneranthous
- Showy, as in showy flowers that advertise to pollinators, as opposed to aphananthous (unshowy)
- phanerogam
- Gymnosperms and angiosperms; plants producing stamens and gynoecia; literally plants with conspicuous sexual reproductive organs. Compare cryptogams.
- phenology
- The study of the timing of seasonal biological phenomena, such as flowering, leaf emergence, fruit ripening and leaf fall.
- phloem
- A specialised conducting tissue in vascular plants that transports sucrose from the leaves to other plant organs.
- photobiont
- In a lichen, the component that does the photosynthesis, the green algae (Chlorophyta) or blue-green algae (Cyanobacteria). (compare to mycobiont, the fungal component.) Also called the phycobiont.
- photosynthesis
- The process by which energy from sunlight is used to convert carbon dioxide and water into simple sugars in cells containing chloroplasts. All plants, except certain parasites, can perform photosynthesis.
- phycobiont
- In a lichen, a synonym for photobiont.
- phyllary
- An individual bract within an involucre or involucel.
- phyllid
- A leaf-like extension of the stem in Bryophytes
- phyllode
A leaf with the blade much reduced or absent, and in which the petiole and or rachis perform the functions of the whole leaf, e.g. many acacias. Compare cladode.
- phyllopodium
- (in ferns) A short outgrowth of the stem on which the frond is borne and which remains attached to the rhizome after the frond has been shed.
- phylloplane
- the surface of a leaf, considered as a habitat for organisms.
- phyllosphere
- The above-ground surface of plants as a habitat for epiphytic microorganisms.
- phylum
- A level of classification or taxonomic rank below kingdom and above class. Traditionally, in botany the term division has been used instead of phylum.
- phytomelan
A black, inert, organic material that forms a crust-like covering of some seeds, commonly found in Asparagales, Asteraceae, etc.
- pileate
- Having a cap, a pileus.
- pileus
- A cap or cap-shaped structure, such as the cap of mushrooms or the plumule of some monocotyledons.
- piliform
- Having the shape of a cap, a pileus.
- pilose
- covered with soft, weak, thin and clearly separated hairs, which are usually defined as long and sometimes ascending.
- pinna
- (plural pinnae) a primary segment of a compound leaf.
- pinnate
- a compound leaf with leaflets arranged on each side of a common petiole or axis; also applied to how the lateral veins are arranged in relation to the main vein.
- pinnatifid
- Pinnately lobed.
- pinnatisect
- pinnately divided almost to midrib but segments still confluent.
- pinnule or pinnula
- Usage varies:
ultimate free division (or leaflets) of a compound leaf,
or
a pinnate subdivision of a multipinnate leaf. - pistil
- 1. a single carpel when the carpels are free.
- 2. a group of carpels when the carpels are united by the fusion of their walls.
- pistillate flower
- a flower containing one or more pistils but no fertile stamens. Sometimes called a female flower. Contrast with staminate flower
- pistillode
- A sterile or rudimentary pistil such as may appear in a staminate flower.
- pit
- In tracheary elements, a section of the cell wall where the secondary wall is missing, and the primary wall is present. Pits generally occur in pairs and link two cells.
- pith
- The central region of a stem, inside the vascular cylinder; the spongy parenchymatous central tissue in some stems and roots.
- placenta
- The tissue within an ovary to which the ovules are attached.
- placentation
- The arrangement of ovules inside ovary; for example axile, free-central, parietal, marginal, basal, or apical.
- placodioid
- The form of a lichen thallus which radiates outward with the ends of the radiating arms peeling up from the substrate, but which lack a cortex on the underside (unlike foliose lichens).
- Plant Breeders Rights (PBR)
- These rights, governed by Plant Breeder's Rights Acts give the plant breeder legal protection over the propagation of a cultivar, and the exclusive rights to produce and to sell it, including the right to license others to produce and sell plants and reproductive material of a registered, deliberately bred variety. Cf. UPOV.
- Plant Variety Rights (PVR)
- Governed by the Plant Variety Rights the registration of new varieties is now governed by Plant Breeders Rights.
- plastochron
- The time between successive leaf initiation events.
- pleiochasium
- pl. pleiochasia. An inflorescence in which several buds come out at the same time. cf. monochasium, dichasium.
- plicate
- Pleated; folded back and forth longitudinally like a fan, such as the leaves of fan palm species. The concept often appears in specific names in forms such as Kumara plicatilis and Acacia plicata. Commonly such names are not correctly appropriate, but are applied to distichous structures rather than plicate.
- -plinerved
- (of leaves) A suffix indicating that the main nerves are lateral and arise from a point distinctly above the base of the leaf. Combined with a numerical prefix to form words like 3-plinerved, 5-plinerved, and so on. Such leaves are especially characteristic of the family Melastomataceae. See for example Dissotis.
- plumose
- Like a feather; with fine hairs branching from a main axis.
- plumule
- The part of an embryo that gives rise to the shoot system of a plant. Compare radicle.
- pluriflor
- Having many flowers per inflorescence. See also pauciflor and uniflor.
- pluriovulate
- Having many ovules as in placentae, carpels, or ovaries.
- pneumatophore
- A vertical appendage, aerial at low tide, on the roots of some plants. Pneumatophore functions are unclear, but possibly related to gas exchange, or to root anchoring. Pneumatophores typically occur on mangrove roots, but some versions occur on species of conifers, such as some in the Taxodioideae.
- pod
- 1. A legume, the fruit of a leguminous plant, a dry fruit of a single carpel, splitting along two sutures.
- 2. A siliqua and silicula, the fruit of Brassicaceae, a dry fruit composed of two carpels separated by a partition.
- podocarpium
- In 4 genera of the coniferous family Podocarpaceae: (Acmopyle, Dacrycarpus, Falcatifolium, or Podocarpus), a group of fleshy fused bracts beneath the female cone, often brightly-coloured, which swell to enclose the developing seeds above, and attract fruit-eating animals. Eckenwalder, James E. (2009). "Conifers of the World: the complete reference.". ″Timber Press, Inc., London.″. pp. 648–61. ISBN 978-0-88192-974-4.
- pollen
- powdery mass shed from anthers (of angiosperms) or microsporangia (of gymnosperms); the microspores of seed plants; pollen-grains.
- pollen-mass
- pollen-grains cohering by a waxy texture or fine threads into a single body; pollinium, e.g. in orchids.
- pollen transmitting tissue
- the tissue in the style of a flower through which the pollen tubes grow.
- pollination
- The transfer of pollen from a male organ (such as an anther) to the receptive region of a female organ (such as a stigma).
- pollinium
- See pollen-mass.
- polygamodioecious
- Having bisexual and male flowers on some plants and bisexual and female flowers on others. Compare androdioecious, andromonoecious, dioecious, monoecious, polygamomonoecious, polygamous.
- polygamomonoecious
- having male, female, and bisexual flowers on the same plant. Compare androdioecious, andromonoecious, polygamodioecious, polygamous.
- polygamous
- having bisexual and unisexual flowers on the same plant.
- polymorphic
- Of several different kinds (in respect to shape and/or size), hence polymorphism. See also monomorphic (a single type) and dimorphic (two types)
- polyphyllous
- having many leaves or perianth segments. Compare symphyllous, gamophyllous, apophyllous.
- polyploid
- with more than two of the basic sets of chromosomes in the nucleus; any sporophyte with cells containing three or more complete sets of chromosomes. Various combinations of words or numbers with '-ploid' indicate the number of haploid sets of chromosomes, e.g. triploid = 3 sets, tetraploid = 4 sets, pentaploid = 5 sets, hexaploid = 6 sets, and so on.
- polystemonous
- having numerous stamens; the number of stamens being at least twice the number of sepals or petals, but not strictly three or four times that number.
- pome
- A fruit that has developed partly from the ovary wall but mostly from the hypanthium (e.g. an apple).
- population
- 1. All individuals of one or more species within a prescribed area.
- 2. A group of organisms of one species, occupying a defined area and usually isolated to some degree from other similar groups.
- 3. In statistics, the whole group of items or individuals under investigation.
- poricidal
- Opening by pores, as with the capsule of a poppy or the anthers in several families of plants. Compare longicidal.
- posterior
- Positioned behind or toward the rear. Contrast anterior.
- prickle
A hard, pointed outgrowth from the surface of a plant (involving several layers of cells but not containing a vein); a sharp outgrowth from the bark, detachable without tearing wood. Compare thorn.
- primary species
- In lichens, a species reproducing mainly by sexual reproduction rather than by vegetative reproduction.
- primary vein
- The single vein or array of veins that is conspicuously larger than any others in a leaf. In pinnate venation, the single primary vein can generally be found in the middle of the leaf; in palmate venation, several such veins radiate from a point at or near the base of the leaf.
- propagule
- In lichens, a part of the thallus that has both fungal and algal parts and can break off for vegetative reproduction, e.g. an isidium, phyllidium, phyllocladium, or soredium).
- prophyll
- A leaf formed at the base of a shoot, usually smaller than those formed later.
- pro parte
- In part. In nomenclature, used to denote that the preceding taxon includes more than one currently recognized entity, and that only one of those entities is being considered.
- procumbent
- Spreading along the ground but not rooting at the nodes; not as close to the ground as prostrate.
- propagule
- Any structure capable of generating a new plant; includes seeds, spores, bulbils, etc.
- prostrate
- Lying flat on the ground; commonly rooting at nodes that touch the soil surface.
- protandrous
- Having male sex organs which mature before the female ones, e.g. a flower shedding pollen before the stigma is receptive. Compare protogynous.
- proteranthous
- With new leaves appearing before flowers. See also hysteranthous and synanthous.
- prothallus
- A gametophyte plant, usually flattened and delicate, e.g. in ferns and fern allies.
- protogynous
- Having female sex organs which mature before the male ones, e.g. a flower shedding pollen after the stigma has ceased to be receptive. Compare protandrous.
- proximal
- Near the point of origin or attachment. Compare distal.
- pruinose
- Covered with a powdery, waxy material; having a bloom.
- pseudanthium
- A type of inflorescence occurring in the Asteraceae and Euphorbiaceae, in which multiple flowers are grouped together to form a flower-like structure, commonly called a head or capitulum.
- pseudo-
- A prefix meaning "false, not genuine", e.g. a pseudo-bulb is a thickened, bulb-like internode in orchids, but not an actual bulb.
- pseudobasifixed
- (of an anther) Connected to the filament of the stamen by connective tissue which extends in a tube around the filament tip. See also basifixed and dorsifixed.
- pseudostipule
- An enlarged, persistent axillary bud scale that resembles a stipule; common in Bignoniaceae.
- pseudoverticillate
- Having the appearance of being whorled (verticillate), without actually being so.
- puberulous
Covered with minute soft erect hairs.
- pubescent
- Downy; covered with short, soft hairs, especially erect hairs.
- pulverulent
- Having powdery or crumbly particles as if pulverized.
- pulvinate
- Having a pulvinus.
- pulvinus
- a swelling at either end of a petiole of a leaf or petiolule of a leaflet, e.g. in Fabaceae, that permits leaf movement.
- punctate
- (from Latin puncta= puncture or prick-mark) marked with an indefinite number of dots, or with similarly small items such as translucent glands or tiny hollows.
- punctiform
- Dot-like or in the shape of a prick-mark.
- pungent
- Having a sharp, hard point.
- pustule
- A blister-like swelling.
- pustulate
- Having pustules.
- pyramidal
- (of a growth habit) Conical or pyramid-shaped. Most familiar in some coniferous trees, especially species adapted to snowy climates
- pyrene
- The stone of a drupe, consisting of the seed surrounded by the hardened endocarp.
- pyriform
- Pear-shaped; a term for solid shapes that are roughly conical in shape, broadest one end and narrowest at the other. As a rule the distal third of their length is the broadest, and they are narrowest near the proximal end, the base, where the stalk, if any, attaches.
- pyrophile
- Plants which need fire for their reproduction.
- pyrophyte
- Plants which have adapted to tolerate fire.

The thick trunk of Brachychiton rupestris accumulates moisture as a means of survival of droughts, and presents a marked example of a pachycaul habit.

This Curio articulatus is pachycladous in that it has a disproportionately thick stem.

A maple (Acer platanoides) leaf has palmate venation, as its veins radiate out from a central point, like fingers from the palm of a hand.



Doubly paripinnate leaves of Delonix regia


Stephania japonica is a vine with peltate leaves.

Perfoliate leaves of Smyrnium perfoliatum with stems passing through them

The leaves of Aponogeton madagascariensis are perforate.

The perigonium of a moss (red in this case), also called a splash-cup, surrounds the antheridia and aids in dispersal of sperm.

Liquidambar styraciflua bud emerging from its protective brown imbricate cataphyll scales, also known as perules

Petiolary glands on the petiole of a cherry leaf

Rock-splitting roots of the petricolous large-leaved rock fig, Ficus abutilifolia

The phaneranthous habit of the red flowering gum, Corymbia ficifolia, can attract pollinators such as the honey eater, Anthochaera chrysoptera, from a considerable distance.

Seedlings of Acacia fasciculifera bear leaves that illustrate the ancestral function of their phyllodes as petioles.

Pileus of the fruiting body of the fungus Pluteus admirabilis

Glandular pilose hairs on the stem of Aquilegia grata




Electron micrographs of sections of wood of a conifer (Picea abies) show pits in the tracheid walls.

This crustose lichen, Caloplaca thallincola, is placodioid, with radiating "arms" in its growth pattern.


The corolla of Datura discolor is plicate.

Longitudinal section of maize kernel, scale=1.4mm:
A=pericarp, B=aleurone
C=stalk, D=endosperm
E=coleorhiza, F=radicle
G=hypocotyl, H=plumule
I=scutellum, J=coleoptile
A=pericarp, B=aleurone
C=stalk, D=endosperm
E=coleorhiza, F=radicle
G=hypocotyl, H=plumule
I=scutellum, J=coleoptile

Pneumatophores on a species of mangrove

The sharp projections on the trunk of the knobthorn, Senegalia nigrescens, are prickles rather than thorns, botanically speaking.

Procumbent growth habit of Sagina procumbens, growing mainly along the soil surface, but without rooting

Carpobrotus and other prostrate plants growing on sand in Sicily, striking root and binding the soil as they grow




Punctiform glands on the undersurface of a Plectranthus leaf


Q
R
- raceme
An indeterminate inflorescence in which the main axis produces a series of flowers on lateral stalks, the oldest at the base and the youngest at the top. Compare spike. Also racemiform or racemoid - having the form of a raceme
- rachilla (rhachilla)
- 1. the axis of a grass spikelet, above the glumes; see spikelet
- 2. the rachis of higher order in leaves that are compound more than once
- rachis
The axis of an inflorescence or a pinnate leaf; for example ferns; secondary rachis is the axis of a pinna in a bipinnate leaf distal to and including the lowermost pedicel attachment.
- radial
- With structures radiating from a central point as spokes on a wheel (e.g. the lateral spines of a cactus).
- radiate
- (of daisies, of a capitulum) With ray floret surrounding disc florets.
- radical
- Springing from the root; clustered at base of stem.
- radicle
- The part of an embryo giving rise to the root system of a plant. Compare plumule.
- rainforest
- A moist temperate or tropical forest dominated by broad-leaved trees that form a continuous canopy.
- ramet
- An individual member of a clone.
- ramicaul
- a single-leafed stem, as in Pleurothallis orchids.[31]
- ray
- 1. zygomorphic (ligulate) flowers in a radiate flowerhead, that is, ray-florets/flowers, for example Asteraceae.
- 2. each of the branches of an umbel.
- receptacle
- the axis of a flower, in other words, floral axis; torus; for example in Asteraceae, the floral base or receptacle is the expanded tip of the peduncle on which the flowers are inserted.
- recumbent
- bent back toward or below the horizontal.
- recurved
- bent or curved backward or downward.
- reduplicate
- folded outward, or with the two abaxial surfaces together.
- reflexed
- bent sharply back or down.
- registered name
- a cultivar name accepted by the relevant International Cultivar Registration Authority.
- registration
- 1. the act of recording a new cultivar name with an International Cultivar Registration Authority.
- 2. recording a new cultivar name with a statutory authority like the Plant Breeder’s Rights Office.
- 3. recording a trademark with a trade marks office.
- regular
- See actinomorphic.
- reniform
- Kidney-shaped.
- replum
- a framework-like placenta to which the seeds attach, and which remains after each valve drops away.
- resupinate
- 1. In botany, describing leaves or flowers that are in an inverted position because the petiole or pedicel, respectively, is twisted 180 degrees. compare: hyper-resupinate.
- 2. In lichenology, referring to either having or being a fruiting body that lies flat on the substrate, with the hymenium either over the whole surface or at the periphery.
- reticulate
- forming a network (or reticulum), e.g. veins that join one another at more than one point.
- retrorse
- Bent backward or downward. Compare antrorse.
- retuse
- Having a blunt (obtuse) and slightly notched apex.
- revision
- an account of a particular plant group, like an abbreviated or simplified monograph. Sometimes confined to the plants of a particular region. Similar to a monograph in clearly distinguishing the taxa and providing a means for their identification. Compare monograph.
- revolute
- rolled under (downward or backward), for example when the edges of leaves are rolled under toward the midrib. Compare involute.
- rhachis
- See rachis.
- rhizine
- The "root" or "trunk" projection of a foliose lichen that attaches the lichen to the substrate (what the lichen is growing on)
- rhizodermis
- the root epidermis, the outermost primary cell layer of the root
- rhizome
- a perennial underground stem usually growing horizontally. See also stolon. Abbreviation: rhiz.
- rhizomatous
- adj. a plant whose above ground stem is derived from a below ground stem (rhizome). cf. arhizomatous (arhizomatic)
- rhizosphere
- the below-ground surface of plants and adjacent soil as a habitat for microorganisms.
- rhytidome
- the dead region of the bark and root that lies outside the periderm.
- rhombic
- like a rhombus: an oblique figure with four equal sides. Compare trapeziform, trullate.
- rhomboid
- a four-sided figure with opposite sides parallel but with adjacent sides an unequal length (like an oblique rectangle); see also rhombic.
- rhomboidal
- a shape, for instance of a leaf, that is roughly diamond-shaped with length equal to width.
- rimose
- with many cracks, as in the surface of a crustose areolate lichen.
- root
- a unit of a plant's axial system which is usually underground, does not bear leaves, tends to grow downward, and is typically derived from the radicle of the embryo.
- root hairs
- outgrowths of the outermost layer of cells just behind the root tips, functioning as water-absorbing organs.
- root microbiome
- the dynamic community of microorganisms associated with plant roots.
- rootstock
- 1. the part of a budded or grafted plant which supplies the root system, also simply called a stock.
- 2. plants selected to produce a root system with some specific attribute, e.g. a virus-free rootstock.
- rosette
- when parts are not whorled or opposite but appear so, due to the contractions of internodes, e.g. the petals in a double rose or a basal cluster of leaves (usually close to the ground) in some plants.
- rostellate
- possessing a beak (rostellum). Synonym of rostrate.
- rostrate
- with a beak.
- rotate
- circular and flattened; for example a corolla with a very short tube and spreading lobes (for instance some Solanaceae).
- ruderal
- a plant that colonises or occupies disturbed waste ground. See also weed.
- rudiment
- In the structure of a plant, an item that is at best hardly functional, either because it is immature and has not yet completed its development (such as a leaf still incompletely formed inside a bud), or because its role in the organism's morphology cannot be completed and therefore is futile (such as the leaf rudiment at the tip of a phyllode, that will be shed while immature, because the leaf function will be taken over by the phyllode). Compare cataphyll, vestige.
- rudimentary
- Being of the nature of a rudiment; at most barely functional because incompletely developed; begun, but far from completed, either temporarily or permanently. Compare vestigial.
- rugose
- Wrinkled, either covered with wrinkles, or crumpled like a wrinkled leaf, either as a stiffening structure, or in response to disease or insect damage.
- rugulose
- Finely wrinkled.
- ruminate
- (usually applied to endosperm) Irregularly grooved or ridged; appearing chewed, e.g. the endosperm in certain members of Myristicaceae.
- runcinate
- Sharply pinnatifid or cleft, with the segments directed downward.
- runner
- See stolon.
- rupicolous
- Rupestral, saxicolous, growing on or among rocks. Compare epilithic and lithophytic.
- rush
- A plant of the family Juncaceae or, more loosely, applied to various monocotyledons.

Bulbinella latifolia racemes. The flowers are already open at the bottom; at the top, the axis is still growing and budding.

Rachis of Vachellia karroo bipinnate leaf, with components labelled as follows:
A. Rachilla (the diminutive of rachis)B. Pinnule
C. Jugary glands
D. Juga (plural of jugum)
E. Base of petiole
F. Petiolary gland
G. Rachis

Radicles emerging from germinating seeds

Reniform kidney bean seeds

A leaf of Ficus carica, illustrating reticulate venation


Typical rhizome. This one is a specimen of Iris pseudacorus.



Rugose leaves of Alocasia are stiffer than flat leaves of the same size and thickness would be.

Unidentified Crassula bearing rugulose leaves with fine wrinkles in the epidermis

S
- saccate
- Pouched or shaped like a sack.
- sagittate
- Shaped like the head of an arrow; narrow and pointed but gradually enlarged at the base into two straight lobes directed downward; may refer only to the base of a leaf with such lobes. Compare hastate.
- salverform
- Shaped like a salver - Trumpet-shaped; having a long, slender tube and a flat, abruptly expanded limb
- samara
- A dry, indehiscent fruit with its wall expanded into a wing, e.g. in the genus Acer.
- samphire
- A common name given to various edible coastal plants, such as Salicornia spp. (Amaranthaceae), Crithmum maritimum (Apiaceae) and Limbarda crithmoides (Asteraceae).
- sanguine
- from Latin sanguineus, blood-coloured: crimson; the colour of blood.
- saprophyte
A plant, or loosely speaking, a fungus or similar organism, deriving its nourishment from decaying organic matter such as dead wood or humus, and usually lacking chlorophyll. Compare parasite, saprotroph and epiphyte.
- saprotroph
An organism deriving its nourishment from decaying organic matter. Contrast parasite and epiphyte.
- sarment
- A long, slender, prostrate stolon, commonly called a runner.
- sarmentose
- Reproducing by sarments; strawberry plants are the most familiar example.
- saxicolous
- Growing on stone, like some lichens.
- scabrid .
Rough to the touch, with short hard protrusions or hairs.
- scalariform
- Ladder-like in structure or appearance.
- scale
- 1. A reduced or rudimentary leaf, for example around a dormant bud.
- 2. A flattened epidermal outgrowth, such as those commonly found on the leaves and rhizomes of ferns.
- scandent
- Climbing, by whatever means. See also: scandent in Wiktionary.
- scape
A stem-like flowering stalk of a plant with radical leaves.
- scapose
- Having the floral axis more or less erect with few or no leaves; consisting of a scape.
- scarious
- Dry and membranous.
- schizocarp
- A dry fruit formed from more than one carpel but breaking apart into individual carpels (mericarps) when ripe.
- scion
- The aerial part of a graft combination, induced by various means to unite with a compatible understock or rootstock.
- sclereid
- A cell with a thick, lignified, cell wall that is shorter than a fiber cell and dies soon after the thickening of its cell wall.
- sclerenchyma
- A strengthening or supporting tissue composed of sclereids or of a mixture of sclereids and fibers.
- sclerophyll
A plant with hard, stiff leaves; any structure stiffened with thick-walled cells.
- scorpioid
- (of a cymose inflorescence) Branching alternately on one side and then the other. Compare helicoid.
- scrobiculate
- Having very small pits.
- scrubland
- Dense vegetation dominated by shrubs.
- scurf
- Minute, loose, membranous scales on the surface of some plant parts, such as leaves.
- secondary metabolite
- Chemicals produced by a plant that do not have a role in so-called primary functions such as growth, development, photosynthesis, reproduction, etc.
- secondary species
- In lichens, a "species" taxon of lichen reproducing only by vegetative means, whose components reproduce mainly by sexual means – cf. primary species.
- secretory tissue
- The tissues concerned with the secretion of gums, resins, oils and other substances in plants.
- section (sectio)
- The category of supplementary taxa intermediate in rank between subgenus and series. It is a singular noun always written with a capital initial letter, in combination with the generic name.
- secund
- Having all the parts grouped on one side or turned to one side (applied especially to inflorescences).
- sedge
- A plant of the family Cyperaceae.
- seed
- A ripened ovule, consisting of a protective coat enclosing an embryo and food reserves; a propagating organ formed in the sexual reproductive cycle of gymnosperms and angiosperms (together, the seed plants).
- segment
- A part or subdivision of an organ, e.g. a petal is a segment of the corolla. A term sometimes used when the sepals and petals are indistinguishable.
- self-pollination
- (also selfing) The acceptance by stigmas of pollen from the same flower or from flowers on the same plant, which means they are self-compatible.
- semaphyll
- A structure such as a bract or sepal (if the remainder of the perianth is inconspicuous) which has become modified to attract pollinators.
- semelparity
- When a plant flowers once then dies.
- semiterete
- Rounded on one side but flat on the other. See also terete.
- senecioid
- See anthemoid.
- sensitive
- A descriptive term for stigmas that, in response to touch, close the two lobes of the stigma together, ending the receptivity of the stigma, at least for the time that the lobes are closed together. Mimulus is perhaps the best-known example.
- sensu
- In the sense of.
- sensu auct.
- (of a plant group or name) As cited by a named authority.
- sensu amplo
- (of a plant group or name) In a generous or ample sense.
- sensu lato
- (of a plant group) In a broad sense.
- sensu strictissimo
- (of a plant group) In the narrowest sense.
- sensu stricto
- (of a plant group) In a narrow sense.
- sepal
- In a flower, one of the segments or divisions of the outer whorl of non-fertile parts surrounding the fertile organs; usually green. Compare petal.
- septicidal
- (of a fruit) Dehiscing along the partitions between loculi. Compare loculicidal.
- septum
A partition, e.g. the membranous wall separating the two valves of the pod of Brassicaceae.
- seriate
- Arranged in rows.
- sericeous
- Silky with dense appressed hairs.
- series
- The category of supplementary taxa intermediate in rank between section and species. It is often used as a plural adjective, as in "Primula subgenus Primula sect. Primula series Acaules".
- serrate
- Toothed with asymmetrical teeth pointing forward; like the cutting edge of a saw.
- serrulate
- Finely serrate.
- sessile
- Attached without a stalk, e.g. of a leaf without a petiole or a stigma, when the style is absent.
- seta
A bristle or stiff hair (in Bryophytes, the stalk of the sporophyte). A terminal seta is an appendage to the tip of an organ, e.g. the primary rachis of a bipinnate leaf in Acacia.
- sheath
- A tubular or rolled part of an organ, e.g. the lower part of the leaf in most grasses.
- shoot
- The aerial part of a plant; a stem and all of its dependent parts (leaves, flowers, etc.).
- shrub
- A woody perennial plant without a single main trunk, branching freely, and generally smaller than a tree.
- sigmoid
- Shaped like the letter 'S'.
- silicula or silicle
- A fruit like a siliqua, but stouter, not more than twice as long as wide.
- silique
- siliqua
- A dry, dehiscent fruit (in contrast to a silicula, more than twice as long as wide) formed from a superior ovary of two carpels, with two parietal placentas and divided into two loculi by a 'false' septum.
- silky
- Densely covered with fine, soft, straight, appressed hairs, with a lustrous sheen and satiny to the touch.
- silviculture
- The science of forestry and the cultivation of woodlands for commercial purposes and wildlife conservation.
- simple
- Undivided or unsegmented, e.g. a leaf not divided into leaflets (note, however, that a simple leaf may still be entire, toothed or lobed) or an unbranched hair or inflorescence.
- sinuate
- Having deep, wave-like depressions along the margins, but more or less flat. Compare undulate.
- sinus
- A notch or depression between two lobes or teeth in the margin of an organ.
- solitary
- Single, of flowers that grow one plant per year, one in each axil, or widely separated on the plant; not grouped in an inflorescence.
- soralia
- In a lichen, the structure that bears soredia for non sexual reproduction.
- soredium
In a lichen, a small groups of algal cells surrounded by fungal filaments that form in soralia, which break off and grow new lichens without sexual reproduction after being dispersed by wind. Compare to an isidium, which breaks off and is dispersed by mechanical means.
- sorus
A cluster of sporangia. Sori typically occur in ferns, some Algae and some fungi. In many fern species the sorus is covered by a protective indusium.
- sp.
- An abbreviation of species (singular), often used when the genus is known but the species has not been determined, as in "Brassica sp." See spp..
- spp.
- An abbreviation of species (plural), often used to collectively refer to more than one species of the same genus, as in "Astragalus spp." See sp..
- spadix
- A spicate (spike-like) inflorescence with the flowers crowded densely, even solidly, around a stout, often succulent axis. Particularly typical of the family Araceae
- spathe
A large bract ensheathing an inflorescence. Traditionally any broad, flat blade.
- spathulate or spatulate
- Spoon-shaped; broad at the tip with a narrowed projection extending to the base.
- species
- A group, or populations of individuals, sharing common features and/or ancestry, generally the smallest group that can be readily and consistently recognized; often, a group of individuals capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring. The basic unit of classification, the category of taxa of the lowest principal rank in the nomenclatural hierarchy. Strict assignment to a species is not always possible, as it is subject to particular contexts, and the species concept under consideration.
- specific epithet
- Follows the name of the genus, and is the second word of a botanical binomial. The generic name and specific epithet together constitute the name of a species; i.e. the specific epithet is not the species name.
- speirochoric
- Unintentional introduction by seeds.[32] Compare agochoric.
- spica
Another name for a spike.
- spike
An unbranched, indeterminate inflorescence in which the flowers are without stalks. Compare raceme.
- spikelet
- A subunit of a spike inflorescence, especially in grasses, sedges, and some other monocotyledons, consisting of one to many flowers and associated bracts or glumes.
- spine
A stiff, sharp structure formed by the modification of a plant organ that contains vascular tissue, e.g. a lateral branch or a stipule; includes thorns.
- spinescent
- Ending in a spine; modified to form a spine.
- spiral
- Of arrangement, when plant parts are arranged in a succession of curves like the thread of a screw, or coiled in a cylindrical or conical manner.
- splash-cup (sporangia)
- A cup-like structure in fungi such as Nidulariaceae and in cryptogams such as some mosses. The cups function in spore dispersal, in which the energy of raindrops falling into the cup causes the water to splash outward carrying the spores.[33]
- sporangium (sporangia)
- A structure in which spores are formed and from which the mature spores are released
- sporangiophore
- An organ bearing sporangia, e.g. the cones of Equisetum.
- spore
- A haploid propagule, produced by meiosis in diploid cells of a sporophyte that can germinate to produce a multicellular gametophyte.
- sporocarp
- A fruiting body containing spores.
- sporophyll
- In pteridophytes, a modified leaf that bears a sporangium or sporangia.
- sporophyte
- The diploid multicellular phase in the alternation of generations of plants and algae that produces the spores. Compare gametophyte.
- sport
- A naturally occurring variant of a species, not usually present in a population or group of plants; a plant that has spontaneously mutated so that it differs from its parent plant.
- spreading
- Extending horizontally, e.g. in branches. Standing out at right angles to an axis, e.g. in leaves or hairs.
- spur
- 1. a short shoot.
- 2. a conical or tubular outgrowth from the base of a perianth segment, often containing nectar.
- squamule
- (plural squamules, squamulae) small scales; In lichens, squamules are overlapping plate-like forms, sometimes overlapping so much as to become leaf-like, but which lack a lower cortex, unlike the leafy forms of foliose lichens – adjective: squamulose.
- squamulose
- Covered with small scales (squamules). In lichens, being composed of squamules.
- squarrose
- Having tips of leaves, stems, etc. radiating or projecting outward, e.g. in the moss Rhytidiadelphus squarrosus.
- s.t.
- An abbreviation for "sometimes". Compare usu. and oft..
- stalk
- The supporting structure of an organ, usually narrower in diameter than the organ itself.
- stamen
The male organ of a flower, consisting (usually) of a stalk called the filament and a pollen-bearing head called the anther.
- staminate flower
A flower with stamens but no pistil.
- staminode
- A sterile stamen, often rudimentary, sometimes petal-like. Commonly has a function in attracting pollinators that feed on the staminodes.
- staminophore
- A structure, around the apex of eucalypt, myrtaceae hypanthia, that supports the stamens.
- standard
- The large posterior petal of pea-flowers.
- standard specimen
- A representative specimen of a cultivar or other taxon which demonstrates how the name of that taxon should be used.
- stele
- The primary vascular system (including phloem, xylem, and ground tissue) of plant stems and roots.
- stellate
- Star-shaped.
- stem
- The plant axis, either aerial or subterranean, which bears nodes, leaves, branches, and flowers.
- stem-clasping
- See amplexicaul.
- stenospermocarpy
- The development or production of fruit that is seedless or has minute seeds because of the abortion of seed development. Compare parthenocarpy.
- sterile
- Infertile, as with a stamen that does not bear pollen or a flower that does not bear seed.
- stigma
- The pollen-receptive surface of a carpel or group of fused carpels, usually sticky; usually a point or small head at the summit of the style.
- stipe
- Generally a small stalk or stalk-like structure. The stalk of a frond of a fern; the stalk supporting the pileus of a mushroom; the stalk of a seaweed such as a kelp; the stalk-like support of a gynaecium or a carpel
- stipella
One of two small secondary stipules at the base of leaflets in some species.
- stipitate
- stalked; borne on a stipe; of an ovary, borne on a gynophore.
- stipulate
- Bearing stipules.
- stipule
- A small appendage at the bases of leaves in many dicotyledons.
- stock
- See rootstock.
- stolon
A slender, prostrate or trailing stem, producing roots and sometimes erect shoots at its nodes. See also rhizome.
- stoloniferous
- Having stolons.
- stoma
A pore or small hole in the surface of a leaf (or other aerial organ) allowing the exchange of gases between tissues and the atmosphere.
- stone cell
- a sclereid cell, such as the cells that form the tissue of nut shells and the stones of drupes.
- striate
- Striped with parallel, longitudinal lines or ridges.
- strigose
- Covered with appressed, straight, rigid, bristle-like hairs; the appressed equivalent of hispid.
- strobilus
A cone-like structure consisting of sporophylls (e.g. conifers and club mosses) or sporangiophores (e.g. in Equisetopsida) borne close together on an axis.
- style
- An elongated part of a carpel or a group of fused carpels between the ovary and the stigma.
- stylodium
- An elongate stigma that resembles a style; a false style, e.g. commonly found in the Poaceae and Asteraceae.
- stylopodium
- A swelling on top of the ovary, at the base of the styles commonly found in flowers of the Apiaceae.
- stylulus
- The elongated apex of a free carpel which functions like the style of a syncarpous ovary, allowing pollen tubes from its stigma to enter the locule of only that carpel.
- subcoriaceous
- Slightly leathery or coriaceous.
- subgenus
- A category of supplementary taxa intermediate between genus and section. The name of a subgenus is a singular noun, always has a capital initial letter and is used in combination with the generic name, e.g. Primula subgenus Primula.
- subglobose
- Inflated, but less than spherical. See also globose.
- suborbicular
- nearly orbicular, flat and almost circular in outline. See also orbicular.
- subpetiolate
- (of a leaf) Having an extremely short petiole, and may appear sessile.
- subquadrangular
- Not quite square. Compare quadrangular.
- subshrub
A small shrub which may have partially herbaceous stems, but generally a woody plant less than 1 metre (3.3 ft) high.
- subspecies
- A taxonomic category within a species, usually used for geographically isolated or morphologically distinct populations of the same species. Its taxonomic rank occurs between species and variety.
- subtend
- To stand beneath or close to, as in a bract at the base of a flower.
- subulate
- Narrow and tapering gradually to a fine point.
- succulent
- 1. Juicy or fleshy.
- 2. A plant with a fleshy habit.
- sucker
- A shoot of more or less subterranean origin; an erect shoot originating from a bud on a root or a rhizome, sometimes at some distance from the stem of the plant.
- suffrutex
A subshrub or undershrub.
- sulcate
- Furrowed; grooved. May be single (monosulcate), two (bisulcate) or many (polysulcate).
- superficial
- On the surface.
- superior ovary
- An ovary borne above the level of attachment of the other floral parts, or above the base of a hypanthium. Compare inferior ovary and half-inferior ovary.
- suspended
- Of an ovule, when attached slightly below the summit of the ovary. Compare pendulous.
- suture
- A junction or seam of union. See fissure and commissure.
- sward
- Extensive, more or less even cover of a surface, e.g. a lawn grass. Compare tussock.
- sympatric
- Having more or less similar or overlapping ranges of distribution.
- sympodial
- A mode of growth in which the main axis is repeatedly terminated and replaced with a lateral branch. Examples occur in the family Combretaceae, including the genera Terminalia and Combretum. cf. monopodial.
- syconium
- A hollow infructescence containing multiple fruit, such as that of a fig.
- syn-
A prefix meaning "with, together".
- symmetrical
- Capable of being divided into at least two equal, mirror-image halves (e.g. zygomorphic) or having rotational symmetry (e.g. regular or actinomorphic). Compare irregular and asymmetrical.
- sympetalous
- Having united (connate or fused) petals, not free (apopetalous). See also syntepalous (having fused tepals).
- symphyllous
- a single perianth-whorl of united segments. Compare gamophyllous (synonym), apophyllous, polyphyllous
- synangium
- A fused aggregate of sporangia, e.g. in the trilocular sporangia of the whisk fern Psilotum.
- synanthous
- A type of growth in which new leaves and flowers appear and die back at the same time. See also hysteranthous and proteranthous.
- synaptospermy
- The dispersal of diaspores as units, where each bears more than one seed, for example where each diaspore comprises an entire inflorescence, as in Brunsvigia or multi-seeded fruit as in Tribulus zeyheri. Ephemeral synaptospermy is the term for when the diaspores split into units containing fewer or single seeds each, as in most tumbleweeds. True synaptospermy is when the diaspore generally remains entire until germination, as commonly happens in species of Grielum.
- syncarpous
- (of a gynoecium) Composed of united carpels.
- synonym
- An outdated or 'alternative' name for the same taxon.
- synoecious
- A synonym of bisexual.
- syntepalous
- Having fused tepals. See also sympetalous (having fused petals).

Sagittate leaves of an Alocasia plant




This Caloplaca marina lichen is saxicolous because it grows on stone.

Micrograph of the scabrid undersurface of the leaf of Stipa pulcherrima.

Involucral bracts of Syncarpha species are as scarious as tissue paper, but look like live petals for years, so they are known as "Everlastings" and valued for dried arrangements.

Isolated sclereid or stone cell in plant tissue
Sclereids in gritty particles of pear tissue


Sericeous leaves of Podalyria sericea, the silver sweet pea bush

The fruits of Lepidium bonariense are silicles, green and circular, with a notch at the apex.

Silky foliage of the silvertree, Leucadendron argenteum










Staminate flowers of Shepherdia canadensis








T












- taproot
- The primary descending root of a plant with a single dominant root axis.
- tartareous
- Having a surface that is course, thick, rough, and crumbling.
- taxon
A group or category in a system of biological classification.
- taxonomy
- The study of the principles and practice of classification.
- tegmen
- The inner layer of the testa (seed coat). It develops from the inner integument of the ovule.
- tendril
- Any slender organ modified from a stem, leaf, leaflet, or stipule and used by climbing plants to cling to an object.
- tepal
- A segment of a perianth, either sepal or petal; usually used when all perianth segments are indistinguishable in appearance.
- terete
Circular in cross-section; more or less cylindrical without grooves or ridges.
- terminal
- Situated at the tip or apex.
- ternate
- In groups of three; of leaves, arranged in whorls of three; of a single leaf, having the leaflets arranged in groups of three.
- terrestrial
- Of or on the ground; of a habitat, on land as opposed to in water (aquatic), on rocks (lithophytic), or on other plants (epiphytic).
- testa
- The seed coat.
- tetrad
- A group of four; usually used to refer to four pollen grains which remain fused together through maturity (e.g. in the Epacridaceae).[34]
- tetragonal
- Square; having four corners; four-angled, e.g. the cross-sections of stems of herbaceous Lamiaceae.
- tetramerous
- In four parts, particularly with respect to flowers; four parts in each whorl. See also trimerous and pentamerous.
- tetraploid
- Having four complete sets of chromosomes in each sporophyte cell.
- tetraspore
- The asexual spore of red algae. It is so named because each sporangium produces just four spores. See Rhodophyceae.[35]
- thalamus
1. A synonym for receptacle.
- 2. The inflorescence disk of members of the Asteraceae.
- 3. A calyx, as used by Carl Linnaeus.
- having a thallus-like structure; in the form of a thallus; thalloid
- thallus
- A vegetative structure that is not differentiated into stem and leaves, as in lichens, algae, thallose liverworts and certain vascular plants (e.g. Lemna; plural thalli
- theca
- One of the usually two synangia in which pollen is produced in flowering plants. It consists of two fused sporangia known as pollen sacs. The wall between the pollen sacs disintegrates before dehiscence, which is usually by a common slit.
- thorn
- A sharp, stiff point, usually a modified stem, that cannot be detached without tearing the subtending tissue; a spine. Compare prickle.
- throat
- The opening of a corolla or perianth.
- thyrse
- A branched inflorescence in which the main axis is indeterminate (racemose) and the lateral branches determinate (cymose).
- tomentum
- A dense covering of short, matted hairs. Tomentose is often used as a general term for bearing an indumentum, but this is not a recommended use.
- toothed
- Having a more or less regularly incised margin.
- torus
- See receptacle.
- transmitting tissue
- See pollen transmitting tissue.
- trapeziform
- 1. Like a trapezium (a four-sided figure with two parallel sides of unequal length).
- 2. Like a trapezoid (a four-sided figure, or quadrilateral, with neither pair of sides equal); sometimes used erroneously as a synonym for rhombic.
- tree
- A woody plant, usually with a single distinct trunk and generally more than 2–3 metres (6.6–9.8 ft) tall.
- triad
- A group of three.
- triangular
- Planar and with 3 sides.
- tribe
- A taxonomic grouping that ranks between genus and family.
- trichome
- In non-filamentous plants, any hair-like outgrowth from the epidermis, e.g. a hair or bristle; sometimes restricted to unbranched epidermal outgrowths.
- trifid.
- Split into three parts. See also bifid.
- trifoliate
- A compound leaf of three leaflets; for example, a clover leaf.
- trifoliolate
- See trifoliate.
- trigonous
- Triangular in cross-section and obtusely angled. Compare triquetrous.
- trimerous
- In three parts, particularly with respect to flowers; having three parts in each whorl. See also tetramerous and pentamerous.
- trinerved
- Having three nerves or veins.
- triplinerved
- (of leaves) Having three main nerves with the lateral nerves arising from the midnerve above the base of the leaf.
- triporate
- (of pollen) Having three pores
- triquetrous
- More or less triangular in cross-section, but acutely angled (with 3 distinct longitudinal ridges). Compare trigonous.
- trivalve
- Divided into three valves. Also trivalvar. See also bivalve.
- trivial name
- The second word in the two-part scientific name of an organism. Compare specific epithet.
- trophophyll
- A vegetative, nutrient-producing leaf or microphyll whose primary function is photosynthesis. It is not specialized or modified for some other function. Compare sporophyll.
- trullate
- Ovate but angled, as with a bricklayer's trowel; inversely kite-shaped. Compare rhombic.
- truncate
- Cut off squarely; having an abruptly transverse end.
- trunk
- The upright, large and typically woody main stem of a tree.
- truss
- A compact cluster of flowers or fruits arising from one centre; evident in many rhododendrons.
- tuber
- Any of many types of specialised vegetative underground storage organs. They accumulate food, water, or in protection from death by fire, drought, or other hard times. Tubers generally are well differentiated from other plant organs; for example, informally a carrot is not generally regarded as a tuber, but simply a swollen root. In this they differ from the tuber of a sweet potato, which has no special root-like function. Similarly, corms are not generally regarded as tubers, even though they are underground storage stems. Tubers store food for the plant, and also have important roles in vegetative reproduction. They generally are of two main types: stem tubers form by the swelling of an underground stem growing from a root, or from structures such as underground stolons. Stem tubers generally produce propagative buds at their stem nodes, forming a seasonal perennating organ, e.g. a potato. The main other class is the root tuber, also called tuberoid. They differ from stem tubers in features such as that, like any normal root, they do not form nodes.
- tubercle
- A small wart-like outgrowth or protuberance of tissue.
- tuberculate
- Covered in tubercles. See warty.
- tuberoid
- An alternative name for underground storage organ formed by the swelling of a root; occurs in many orchids.
- tuberous
- Resembling a tuber or producing tubers.
- tubular
- Having the form of a tube or cylinder.
- tufted
- Densely fasciculate at the tip.
- tunic
- The outer covering of some bulbs and corms.
- tunicate
- (of bulbs) Consisting of concentric coats.
- turbinate
- Shaped like a spinning top or beetroot.
- turgid
- Swollen with liquid; bloated; firm. Compare flaccid.
- tussock
- A dense tuft of vegetation, usually well separated from neighbouring tussocks, for example in some grasses. Compare sward.
- two-ranked
- Having leaves arranged in two rows in the same plane, on opposite sides of the branch. See distichous.
- type
- An item (usually an herbarium specimen) to which the name of a taxon is permanently attached, i.e. a designated representative of a plant name. Important in determining the priority of names available for a particular taxon.
- type genus
- In nomenclature, a single genus on which a taxonomic family is based.
U
- umbel
- A racemose inflorescence in which all the individual flower stalks arise in a cluster at the top of the peduncle and are of about equal length; in a simple umbel, each stalk is unbranched and bears only one flower. A cymose umbel looks similar to an ordinary umbel but its flowers open centrifugally.
- umbo
- A rounded elevation, such as in the middle of the top of an umbrella or mushroom; a central boss or protuberance, such as on the scale of a cone.
- umbonate
- Having an umbo, with a conical or blunt projection arising from a flatter surface, as on the top of a mushroom or in the scale of a pine cone.
- unciform
- Hook-shaped.
- uncinate
- Having a hook at the apex.
- undershrub
- A low shrub, often with flowering branches that die off in winter. Compare subshrub.
- understory
- Plant life growing beneath the forest canopy.
- undulate
- Wavy and not flat. Compare sinuate.
- uniflor
- Having a single flower (uniflory). Compare pauciflor (few) and pluriflor (many).
- unilocular
- Having one loculus or chamber, e.g. the ovary in the families Proteaceae and Fabaceae.
- uniserial
- Arranged in a single row or series. Unbranched. Uniseriate.
- uniseriate
- Arranged in a single row or series. Unbranched. Uniserial.
- unisexual
- Of one sex; bearing only male or only female reproductive organs, dioecious, dioicous. See Sexual reproduction in plants.
- unitegmic
- (of an ovule) Covered by a single integument. See also bitegmic, having two integuments.
- urceolate
- Shaped like an urn or pitcher, with a swollen middle and narrowing top. Examples include the pitchers of many species of the pitcher plant genera Sarracenia and Nepenthes.
- usu.
- An abbreviation of usually. Compare s.t. and oft..
- utricle
- 1. A small bladder; a membranous bladder-like sac from the ovary wall, thin pericarp, becomes more or less bladdery or inflated at maturity enclosing an ovary or fruit.
- 2. In sedges, a fruit in which the fruit is loosely encloses from a modified tubular bract, see perigynium.




V
- vallecular canal
- A resin canal coinciding with a longitudinal groove in the seeds of Asteraceae. A longitudinal cavity in the cortex of the stems of Equisetum, coinciding with a groove in the stem surface.
- valvate
- (of sepals and petals in bud) Meeting edge-to-edge but not overlapping.
- valve
- A portion of an organ that fragments or splits open, e.g. the teeth-like portions of a pericarp in a split (dehisced) capsule or pod when ripe.
- var.
- An abbreviation of varietas.
- variant
- A plant or group of plants showing some measure of difference from the characteristics associated with a particular taxon.
- variegated
- Irregularly marked with blotches or patches of another colour.
- varietas
A taxonomic rank below that of species and between the ranks of subspecies and form.
- vascular
- Referring to the conducting tissues (xylem and phloem) of vascular plants.
- vascular bundle
- A bundle of vascular tissue in the primary stems of vascular plants, consisting of specialised conducting cells for the transport of water (xylem) and assimilate (phloem).
- vasculum
- A container used by botanists for collecting field specimens.
- vein
A strand of vascular tissue, e.g. in the leaves of vascular plants.
- veinlet
- A small vein; the ultimate (visible) division of a vein.
- velamen
- A spongy tissue covering the aerial roots of orchids and some other epiphytes.
- velutinous
- See velvety.
- velvety
- Densely covered with fine, short, soft, erect hairs.
- venation
- The arrangement of veins in a leaf.
- ventral
- From Latin venter, meaning "belly". The opposite of dorsal. Partly because the term originally referred to animals rather than plants, usage in botany is arbitrary according to context and source. In general "ventral" refers to "the belly or lower part", but in botanical usage such concepts are not always clearly defined and may be contradictory. For example:
- facing toward the axis (adaxial) in referring to a lateral organ of an erect plant
- facing toward the substrate in any part of an erect plant, for example the lower surface of a more or less horizontal leaf (abaxial)
- facing toward the substrate in a prostrate or climbing plant.
- vernation
- The arrangement of unexpanded leaves in a bud; the order in which leaves unfold from a bud.
- vernonioid
- In the Compositae, style with sweeping hairs borne on abaxial surfaces of style branches.
- verruciform
- Wart-like in form.
- verrucose
- Having warts.
- verruculose
- Minutely verrucose; minutely warty.
- versatile
- (of anthers) Swinging freely about the point of attachment to the filament.
- verticillate
- Arranged in one or more whorls, i.e. several similar parts arranged at the same point of the axis, e.g. leaf arrangement. Compare pseudoverticillate (appearing whorled or verticillate but not actually so).
- verticillaster
- A type of pseudoverticillate inflorescence, typical of the Lamiaceae, in which pseudo-whorls are formed from pairs of opposite cymes.
- vesicular
- (of hairs) Bladder-like; vesciculous, bearing such hairs.
- vessel
- A capillary tube formed from a series of open-ended cells in the water-conducting tissue of a plant.
- vestigial
- Reduced in form and function from the normal or ancestral condition.
- villous
- Abounding in or covered with long, soft, straight hairs; shaggy with soft hairs.
- vine
- 1. Scandent plants climbing by means of trailing or twining stems or runners.
- 2. Such a stem or runner.[20][36]
- 3. A member of the genus Vitis.
- virgate
Wand-shaped, twiggy, especially referring to erect, straight stems. In mycology, referring to a pileus with radiating ribs or lines.
- Viridiplantae
- A clade of autotrophic organisms that includes the green algae, Charophyta and land plants, all of which have cellulose in their cell walls, chloroplasts derived from primary endosymbiosis with Cyanobacteria that contain chlorophylls a and b and lack phycobilins.
- viscid
- Sticky; coated with a thick, syrupy secretion.
- vitta
- An oil tube in the fruit of some plants.
- viviparous
- 1. Referring to seeds or fruits which germinate before being shed from the parent plant.
- 2. The development of plantlets on non-floral organs, e.g. leaves.

Photomicrograph of a cross section of a vascular bundle in the stem of a typical herbaceous dicotyledon
A: PhloemB: Cambium
C: Xylem
D: Fibrous sheath of vascular bundle



Flower stalks and sepal tubes of Pueraria phaseoloides are covered with velutinous (velvety) hairs.




Asparagus virgatus owes its specific epithet virgatus to the twiggy appearance of its virgate shoots.
W
- warty
- A surface covered with small round protuberances, especially in fruit, leaves, twigs and bark. See tuberculate.
- watershoot
- An erect, strong-growing, or epicormic shoot developing from near the base of a shrub or tree, but distinct from a sucker.
- weed
- 1. Any plant growing where it is not wanted; commonly associated with disrupted habitats. See also ruderal.
- 2. An unwanted plant which grows among agricultural crops.
- 3. A naturalised, exotic, or ecologically "out-of-balance" indigenous species outside of the agricultural or garden context, which, as a result of invasion, adversely affects the survival or regeneration of indigenous species in natural or partly natural vegetation communities.[37]
- wild
- Originating from a known wild or purely natural habitat (wilderness).
- whorl
- A ring of organs borne at the same level on an axis (e.g. leaves, bracts, or floral parts).
- wing
- 1. A membranous expansion of a fruit or seed which aids in dispersal, for instance on pine seeds.
- 2. A thin flange of tissue extending beyond the normal outline of a structure, e.g. on the column of some orchids, on stems, on petioles.
- 3. One of the two lateral petals of a flower of subfamily Faboideae of family Fabaceae, located between the adaxial standard (banner) petal and the two abaxial keel petals.
- woolly
- Very densely covered with long, more or less matted or intertwined hairs, resembling a sheep's wool.


The verticillate whorls of leaves on Brabejum stellatifolium are unusual among trees in its native region.

Winged seeds of Catalpa bignonioides are nearly all wing. Tufts at the tips increase aerodynamic drag, thereby improving wind dispersal.

Leaves of some species of Citrus have winged petioles.

Senecio haworthii leaves have an unusually dense woolly coat.
X
- xeromorph
- A plant with structural features (e.g. hard or succulent leaves) or functional adaptations that prevent water loss by evaporation; usually associated with arid habitats, but not necessarily drought-tolerant. Compare xerophyte.
- xerophyte
- A plant generally living in a dry habitat, typically showing xeromorphic or succulent adaptation; a plant able to tolerate long periods of drought. Compare xeromorph.
- xylem
- A specialised water-conducting tissue in vascular plants.
Z
- zonate
- Having light and dark circular bands or rings, typically on leaves or flowers.
- zygomorphic
- Bilaterally symmetrical; symmetrical about one vertical plane only; applies to flowers in which the perianth segments within each whorl vary in size and shape. Contrast actinomorphic and irregular.
- zygote
- A fertilized cell, the product of fusion of two gametes.

Zonate markings on the leaves of a garden variety of Pelargonium zonale

Like most of the genus Pelargonium, and unlike most members of the genus Geranium, Pelargonium quercifolium bears flowers that are bilaterally symmetrical. Accordingly, because the yoke of an ox is bilaterally symmetrical, such flowers are said to be zygomorphic, which literally means "yoke-shaped".
See also
- Glossary of biology
- Glossary of plant morphology
- Glossary of leaf morphology
- Glossary of scientific naming
- International scientific vocabulary
- Plant morphology
- Floral formula – abbreviations used in describing flower parts
- Plant anatomy
- Palynology
 Plants portal
Plants portal
References
- Harris & Harris 2001, p. 3.
- Shreve, Forrest; Wiggins, Ira. Vegetation and Flora of the Sonoran Desert. Stanford University Press, 1964. ISBN 978-0804701631
- Harris & Harris 2001, p. 4.
- Harris & Harris 2001, pp. 4–5.
- Harris & Harris 2001, p. 5.
- John Sims (1803). Curtis's Botanical Magazine, Or, Flower-garden Displayed: In which the Most Ornamental Foreign Plants, Cultivated in the Open Ground, the Green-house, and the Stove, are Accurately Represented in Their Natural Colours ... pp. 93–.
- Harris & Harris 2001, p. 6.
- Handbook of Plant Palaeoecology, Flora and Vegetation, p.95 By R. T. J. Cappers, R. Neef
- Pell & Angell 2016, p. 15.
- Pell & Angell 2016, p. 16.
- Pell & Angell 2016, p. 17.
- Pell & Angell 2016, p. 20.
- Pell & Angell 2016, p. 24.
- Pell & Angell 2016, p. 27.
- Pell & Angell 2016, p. 35.
- Pell & Angell 2016, p. 39.
- Pell & Angell 2016, p. 41.
- Pell & Angell 2016, p. 46.
- Pell & Angell 2016, p. 47.
- Jackson, Benjamin, Daydon; A Glossary of Botanic Terms with their Derivation and Accent; Published by Gerald Duckworth & Co. London, 4th ed 1928
- Jaeger, Edmund Carroll (1959). A source-book of biological names and terms. Springfield, Ill: Thomas. ISBN 978-0-398-06179-1.
- Pell & Angell 2016, p. 58.
- Hanzawa, F.; Beattie, A.; Holmes, A. (1985). "Dual Function of the Elaiosome of Corydalis aurea (Fumariaceae): Attraction of Dispersal Agents and Repulsion of Peromyscus maniculatus, a Seed Predator". American Journal of Botany. 72 (11): 1707–1711. doi:10.1002/j.1537-2197.1985.tb08442.x. JSTOR 2443727.
- Pell & Angell 2016, p. 78.
- Mosses Lichens & Ferns of Northwest North America, Dale H. Vitt, Janet E. marsh, Robin B. Bovey, Lone Pine Publishing Company, ISBN 0-295-96666-1
- Potentials and Limitations of Ecosystem Analysis, Extinction and Naturalization of Plant Species p.261, edited by Ernst-Detlef Schulze, Helmut Zwölfer
- Pell & Angell 2016, p. 83.
- Potentials and Limitations of Ecosystem Analysis, Extinction and Naturalization of Plant Species, p.261, edited by Ernst-Detlef Schulze, Helmut Zwölfer, 1987
- Field Guide to California Lichens, Stephen Sharnoff, Yale University Press, 2014, ISBN 978-0-300-19500-2, page 279
- Alan W. Meerow, Michael F. Fay, Charles L Guy, Qin-Bao Li, Faridah Q Zaman, Mark W. Chase. Systematics of Amaryllidaceae based on cladistic analysis of plastid sequence data. Am. J. Bot. September 1999 vol. 86 no. 9 1325-1345
- Pell & Angell 2016, p. 169.
- Selected aspects of tiny vetch [Vicia hirsuta (L.) Gray S.F. Seed ecology: generative reproduction and effects of seed maturity and seed storage on seed germination Magdalena Kucewicz, Katarzyna Maćkiewicz, Anna Źróbek-Sokolnik, Uniwersity of Warmia and Mazury, Department of Botany and Nature Protection. 5 September 2009.
- The Splash-Cup Dispersal Mechanism in Plants, Harold J. Brodie, Canadian Journal of Botany, 1951, 29(3): 224-234, 10.1139/b51-022,
- Beach, Chandler B., ed. (1914). . . Chicago: F. E. Compton and Co.
- Beach, Chandler B., ed. (1914). . . Chicago: F. E. Compton and Co.
- Brown, Lesley (1993). The New shorter Oxford English dictionary on historical principles. Oxford [Eng.]: Clarendon. ISBN 978-0-19-861271-1.
- Carr, G.W., in Foreman & Walsh, 1993.
Bibliography
- Allaby, Michael (2012). A Dictionary of Plant Sciences. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-960057-1.
- Henk Beentje (2010) The Kew Plant Glossary, an illustrated dictionary of plant terms. Revised edition (2012). Kew Publishing: Richmond, U.K. ISBN 978-1-84246-422-9.
- Ernest M. Gifford and Adriance S. Foster. 1989. Morphology and Evolution of Vascular Plants, 3rd edition. W. H. Freeman. ISBN 978-0-7167-1946-5
- Harris, James G.; Harris, Melinda Woolf (2001). Plant Identification Terminology: An Illustrated Glossary (2nd ed.). Spring Lake, UT, USA: Spring Lake Publishing. ISBN 0-9640221-6-8.
- Hickey, Michael; King, Clive (2000). The Cambridge illustrated glossary of botanical terms. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-79401-5.
- Hughes, Colin. "The virtual field herbarium". Oxford University Herbaria. Retrieved 4 March 2017.
- "Plant Characteristics" (Glossary). Retrieved 4 March 2017., in Hughes (2017)
- Benjamin D. Jackson. A Glossary of Botanic Terms. Duckworth: London. J.B. Lippincott Company: Philadelphia (1928).
- David B. Lellinger. 2002. A Modern Multilingual Glossary for Taxonomic Pteridology (Pteridologia, 3). American Fern Society. ISBN 978-0-933500-02-0.
- Pell, Susan K.; Angell, Bobbi (2016). A Botanist's Vocabulary: 1300 Terms Explained and Illustrated. Portland, OR: Timber Press. p. 169. ISBN 978-1-604-69563-2.
- Simpson, Michael G. (2011). Plant Systematics. Academic Press. ISBN 978-0-08-051404-8.
- Stearn, W.T. 1983. Botanical Latin. David & Charles, North Pomfret, Vermont.
- Glossary of botanical and medical terms, in Don G. W. A general system of gardening and botany. Founded upon Miller's Gardener's dictionary, and arranged according to the natural system. 1831
- "Glossary of botanical terms". Neotropikey. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. Retrieved 18 February 2017.
- "Glossary for Vascular Plants". The William & Lynda Steere Herbarium, New York Botanical Garden. Retrieved 20 September 2019.
External links
- Wiktionary
- Glossary at: APweb
- A glossary of botanical terms in English At: Flora, etc.
- Garden Web
- eFloras
- Categorical Glossary for the Flora of North America Project
Royal Botanical Gardens at Kew
Australia and New Zealand
- University of Sydney: Eflora – Glossary
- Florabase (Western Australia)
- Flora of Australia Online Glossary
- Flora of Australia Abbreviations
- Flora of S Australia
- Botany Word of the Day. Illustrated with New Zealand natives
- New Zealand Plant Conservation Network
Africa
- Herman, P P J (2015). "Botanical glossary" (PDF). SANBI. Retrieved 21 May 2020.
- Plants of southern Africa
Текст в блоке "Читать" взят с сайта "Википедия" и доступен по лицензии Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike; в отдельных случаях могут действовать дополнительные условия.
Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
2019-2025
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии
