bio.wikisort.org - Plant
Ipomoea purpurea, the common morning-glory,[2] tall morning-glory,[3] or purple morning glory, is a species in the genus Ipomoea, native to Mexico[4] and Central America.
Description
Like all morning glories, the plant entwines itself around structures, growing to a height of 2–3 m (6 ft 7 in – 9 ft 10 in) tall. The leaves are heart-shaped and the stems are covered with brown hairs. The flowers are trumpet-shaped, predominantly blue to purple or white, and 3–6 cm (1.2–2.4 in) in diameter.[5]
Distribution and habitat
The plant is predisposed to moist and rich soil, but can be found growing in a wide array of soil types.[6] It is naturalized throughout warm temperate and subtropical regions of the world. Although it is often considered a noxious weed, I. purpurea is also grown for its attractive purple and white flowers, and has many cultivars. Common cultivars include I. purpurea 'Crimson Rambler' (red-violet blossoms with white throats), 'Grandpa Ott's', 'Kniola's Black Knight', 'Star of Yelta' (blossoms in varying shades of deep purple with white or pale pink throats), and 'Milky Way' (white corolla with mauve accents).
Chemistry
The triangular seeds have some history of use as a psychedelic; they, like I. tricolor, may contain LSA.[6] Effects are reported to be somewhat similar to those of LSD.[7]
Flower color
Acylated cyanidin glycosides can be isolated from violet-blue flowers of I. purpurea. These anthocyanins were all based on cyanidin 3-sophoroside-5-glucoside, acylated with caffeic acid and/or p-coumaric acid.[8]
Acylated pelargonidin glycosides can be isolated from the red-purple flowers of I. purpurea. The acylated anthocyanins were all based on pelargonidin 3-sophoroside-5-glucoside, acylated with caffeic acid and/or glucosylcaffeic acid.[9]
Toxic treatments
Commercial morning glory seeds are commonly treated with toxic methylmercury, which serves as a preservative and a cumulative neurotoxic poison that is considered useful by some to discourage their recreational use. The US has no legal requirement to disclose to buyers that seeds have been treated with a toxic heavy metal compound.[10] According to the book Substances of Abuse, in addition to methylmercury, the seeds are commonly coated with a chemical [which?] that cannot be removed with washing that is designed to cause unpleasant physical symptoms, such as nausea and abdominal pain. The book states that this chemical is also toxic.[11]
Gallery
- Light blue I. purpurea
- Pink I. purpurea
- Pink I. purpurea close-up
- I. purpurea in Loganville, Georgia
- Pink I. purpurea
- Purple I. purpurea close-up
- Purple I. purpurea close-up
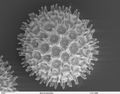
- Scanning electron micrograph of I. purpurea pollen
- Violet-blue I. purpurea
See also
- Morning glory
References
- USDA Plants Profile
- BSBI List 2007 (xls). Botanical Society of Britain and Ireland. Archived from the original (xls) on 2015-06-26. Retrieved 2014-10-17.
- USDA, NRCS (n.d.). "Ipomoea purpurea". The PLANTS Database (plants.usda.gov). Greensboro, North Carolina: National Plant Data Team. Retrieved 22 January 2016.
- Fang, Zhou (2013-01-12). "Tracing the Geographic Origins of Weedy Ipomoea purpurea in the Southeastern United States". Journal of Heredity. 104 (5): 666–77. doi:10.1093/jhered/est046. PMID 23894192 – via Oxford Journals.
- "Ipomoea purpurea". Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN). Agricultural Research Service (ARS), United States Department of Agriculture (USDA). Retrieved 17 December 2017.
- Richard H. Uva, Joseph C. Neal and Joseph M. Ditomaso, Weeds of The Northeast, (Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press, 1997), Pp. 214-217.
- Charles Savage, Willis W. Harman and James Fadiman, Ipomoea purpurea: A Naturally Occurring Psychedelic
- Norio Saito; Fumi Tatsuzawa; Kyoko Yoda; Masato Yokoi; Kichiji Kasahara; Shigeru Iida; Atsushi Shigihara & Toshio Honda (November 1995). "Acylated cyanidin glycosides in the violet-blue flowers of Ipomoea purpurea". Phytochemistry. 40 (4): 1283–1289. doi:10.1016/0031-9422(95)00369-I. PMID 7492373.
- Norio Saito; Fumi Tatsuzawa; Masato Yokoi; Kichiji Kasahara; Shigeru Iida; Atsushi Shigihara; Toshio Honda (December 1996). "Acylated pelargonidin glycosides in red-purple flowers of Ipomoea purpurea". Phytochemistry. 43 (6): 1365–1370. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(96)00501-8. PMID 8987912.
- Dunn Chace, Teri (2015). Seeing Seeds: A Journey into the World of Seedheads, Pods, and Fruit. Portland OR: Timber Press. ISBN 978-1604694925.
- Potter, James (2008). Substances of Abuse. Redding CA: Jubilee Enterprises. p. 157. ISBN 978-1930327467.
External links
На других языках
- [en] Ipomoea purpurea
[es] Ipomoea purpurea
Ipomoea purpurea, llamada popularmente gloria de la mañana, manto de María, don Diego de día, campanilla morada o quiebra platos (entre otros nombres), es una especie de la familia Convolvulaceae, nativa de México, América del Sur y de Centroamérica.[it] Ipomoea purpurea
Il campanello purpureo o campanella purpurea (nome scientifico Ipomoea purpurea) è una specie di pianta rampicante erbacea della famiglia delle Convolvulacee, originaria del Messico e dell'America centrale. È usata in Italia come pianta ornamentale annuale, per la bellezza dei fiori, sia pur effimeri, e la capacità di ricoprire bersò, pergolati, reti di recinzione e di salire lungo fili appositamente tesi.[ru] Ипомея пурпурная
Ипоме́я пурпу́рная[2][3], или Ипомея пурпу́ровая[4] (лат. Ipomoea purpurea) — однолетнее травянистое вьющееся растение, вид рода Ипомея (Ipomoea) семейства Вьюнковые (Convolvulaceae). Культивируется как декоративное растение.Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии