bio.wikisort.org - Plant
Vanilla planifolia is a species of vanilla orchid. It is native to Mexico and Belize.[1] It is one of the primary sources for vanilla flavouring, due to its high vanillin content. Common names include flat-leaved vanilla,[5] and West Indian vanilla (also used for the Pompona vanilla, V. pompona). Often, it is simply referred to as "the vanilla". It was first scientifically named in 1808. With the species' population in decline and its habitats being converted to other purposes, the IUCN has assessed Vanilla planifolia as Endangered.[1]
| Vanilla planifolia | |
|---|---|
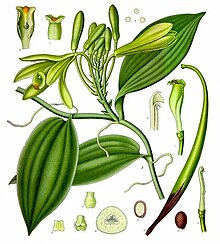 | |
| 1887 illustration from Köhler's Medicinal Plants | |
Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Monocots |
| Order: | Asparagales |
| Family: | Orchidaceae |
| Subfamily: | Vanilloideae |
| Genus: | Vanilla |
| Species: | V. planifolia |
| Binomial name | |
| Vanilla planifolia | |
| Synonyms[4] | |
| |
Habitat
It prefers hot, wet, tropical climates.[6]
It is cultivated and harvested primarily in Veracruz, Mexico, Tahiti, Indonesia, and Madagascar.[6]
Description
Like all members of the genus Vanilla, V. planifolia is a vine. It uses its fleshy roots to support itself as it grows.
Flowers

Flowers are greenish-yellow, with a diameter of 5 cm (2 in). They last only a day, and must be pollinated manually, during the morning, if fruit is desired. The plants are self-fertile, and pollination simply requires a transfer of the pollen from the anther to the stigma. If pollination does not occur, the flower is dropped the next day. In the wild, there is less than 1% chance that the flowers will be pollinated, so in order to receive a steady flow of fruit, the flowers must be hand-pollinated when grown on farms.
Fruit
Fruit is produced only on mature plants, which are generally over 3 m (10 ft) long. The fruits are 15–23 cm (6–9 in) long pods (often incorrectly called beans). Outwardly they resemble small bananas. They mature after about five months, at which point they are harvested and cured. Curing ferments and dries the pods while minimizing the loss of essential oils. Vanilla extract is obtained from this portion of the plant.
Chemistry
The major chemical components from the pods are vanillin, vanillic acid, 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde and 4-hydroxybenzoic acid.[7]
Contact dermatitis

When propagating vanilla orchids from cuttings or harvesting ripe vanilla pods, care must be taken to avoid contact with the sap from the plant's stems. The sap of most species of Vanilla orchid which exudes from cut stems or where pods are harvested can cause moderate to severe dermatitis if it comes in contact with bare skin. Washing the affected area with warm soapy water will effectively remove the sap in cases of accidental contact with the skin. The sap of vanilla orchids contains calcium oxalate crystals, which appear to be the main causative agent of contact dermatitis in vanilla plantation workers.[8][9][10][11][12]
See also
References
- Vega, M.; Hernández, M.; Herrera-Cabrera, B.E.; Wegier, A. (2020). "Vanilla planifolia". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2020: e.T103090930A172970359. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-2.RLTS.T103090930A172970359.en. Retrieved 19 November 2021.
- "Vanilla planifolia Andrews". Plants of the World Online. The Trustees of the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. n.d. Retrieved October 14, 2022.
- "Vanilla planifolia Andrews". Catalogue of Life. Species 2000. n.d. Retrieved October 14, 2022.
- The Plant List: A Working List of All Plant Species, retrieved 26 January 2016
- "Vanilla planifolia (Commercial Vanilla, Flat Leaved Vanilla): Go Orchids". goorchids.northamericanorchidcenter.org. Retrieved 2020-06-20.
- GRIN-Global Web v 1.9.4.2: Taxonomy of Vanilla planifolia
- Reinvestigation of vanillin contents and component ratios of vanilla extracts using high-performance liquid chromatography and gas chromatography. Scharrer A and Mosandl A, Deutsche Lebensmittel-Rundschau, 2001, volume 97, number 12, pages 449-456, INIST:14118840
- "Vanilla Orchid Care - OrchidsMadeEasy.com".
- "Cultural Requirements of the Vanilla Orchid" (PDF).
- "Growing Vanilla Bean Plants (Vanilla planifolia orchid). Vanilla Plants and seeds for sale. - NurseriesOnline". 8 August 2015.
- "Vanilla planifolia Andrews - Plants of the World Online - Kew Science". powo.science.kew.org.
- "Vanilla planifolia Vanilla PFAF Plant Database". pfaf.org.
External links
На других языках
[de] Gewürzvanille
Die Gewürzvanille – Aussprache: [.mw-parser-output .IPA a{text-decoration:none}vaˈnɪlə; -ljə]; schweizerisch und süddeutsch [ˈvanɪl] – (Vanilla planifolia) oder Echte Vanille ist eine Orchideenpflanze. Der Name stammt über das französische vanille vom spanischen vainilla (‚kleine Hülse oder Schote‘, zu lat. vagina). Gewürzvanille wird im Handel unter den Herkunftsbezeichnungen Bourbon-Vanille (von den Inseln Madagaskar und Reunion [ehemals Bourbon]), mexikanische Vanille und Vanille aus Tahiti angeboten (vergleiche Tahiti-Vanille). Die Pflanze besitzt grün-gelbliche Blüten und bringt Samenkapseln hervor, aus denen das Gewürz Vanille hergestellt wird.- [en] Vanilla planifolia
[es] Vanilla planifolia
Vanilla planifolia es una especie del género de orquídeas Vanilla, de hábito trepador y crecimiento rastrero, originaria de México y Centroamérica. Se cultiva de México a Paraguay y en Madagascar.[1][2] Del fruto de esta planta se extrae la vainilla.[fr] Vanilla planifolia
Vanilla planifolia est la principale espèce d'orchidées utilisée pour produire la vanille.[it] Vanilla planifolia
La vaniglia[2] o vainiglia[2] (Vanilla planifolia Jacks. ex Andrews, 1808) è un'orchidea originaria del Messico[3]. I suoi frutti, delle capsule, comunemente ed erroneamente chiamate baccelli, sono la spezia nota come vaniglia.[ru] Ваниль плосколистная
Ваниль плосколистная[2], или Ваниль душистая[3], иногда также просто Ваниль[4] (лат. Vanilla planifolia) — вид однодольных растений рода Ваниль (Vanilla) семейства Орхидные (Orchidaceae)[5][6]. Растение описано британским ботаником Генри Чарльзом Эндрюсом в 1808 году[7][8].Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии
