bio.wikisort.org - Plant
Symphyotrichum ascendens (formerly Aster ascendens) is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae known by the common names western aster,[3] long-leaved aster,[4] and Rocky Mountain aster.[5] Blooming July–September, it is native to western North America and can be found at elevations of 500–3,200 m (1,600–10,500 ft) in several habitats.
| Symphyotrichum ascendens | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Symphyotrichum ascendes | |
Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Asterids |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae |
| Tribe: | Astereae |
| Subtribe: | Symphyotrichinae |
| Genus: | Symphyotrichum |
| Subgenus: | Symphyotrichum subg. Ascendentes |
| Species: | S. ascendens |
| Binomial name | |
| Symphyotrichum ascendens | |
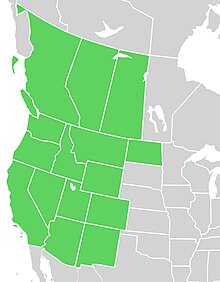 | |
| Native distribution by state and province[2] | |
| Synonyms[2] | |
|
Basionym
Alphabetical list
| |
Description
Symphyotrichum ascendens is a rhizomatous, perennial, and herbaceous plant growing a branching, erect stem to heights between 20 and 60 centimeters (8 and 24 inches). Leaves are widely lance-shaped to oblong and pointed, the largest ones near the base of the stem reaching up to 15 cm (6 in) long. The stem and leaves are roughly hairy in places.[6]
The inflorescence is an array of many flower heads with many narrow violet to nearly white ray florets around a center of golden disc florets that open July–September.[7] The fruit is a hairy cypsela with a long pappus.[6] S. ascendens is similar to Symphyotrichum chilense, which has smaller flower heads.[5]
Chromosomes
Symphyotrichum ascendens has a chromosome base number of x = 13.[8] There are diploid individuals (2n = 26) which occur in the western portion of its range, and tetraploid ones (2n = 52) found eastward.[9]
Taxonomy
S. ascendens is a member of the genus Symphyotrichum, sometimes called American-asters,[10] classified in the subgenus Ascendentes.[8] Its basionym (original scientific name) is Aster ascendens Lindl., and it has many taxonomic synonyms. Its name with author citations is Symphyotrichum ascendens (Lindl.) G.L.Nesom.[2] In 1834, English botanist John Lindley formally described the plant that now is named Symphyotrichum ascendens.[11]
This species is allopolyploid, derived from the hybridization of S. spathulatum (chromosome base number x = 8) with S. falcatum (x = 5),[6] each from a different subgenus, Symphyotrichum and Virgulus, respectively.[12] This produced a plant with a unique base number of x = 13,[8] also written x2 = 13 (8 + 5),[9] and it warranted its own subgenus, Ascendentes, and its own species name. One other species is placed within subgenus Ascendentes: S. defoliatum.[12]
Distribution and habitat

Western aster is native to western North America from British Columbia to Saskatchewan, south to the United States in Montana and North Dakota then south to New Mexico, west to California, north to Washington state, and all states in between.[2] It can be found at elevations of 500–3,200 meters (1,600–10,500 feet) in several habitats including grasslands, sagebrush steppe, and meadows.[6]
Citations
References
- Allen, G.A. (2012). "Symphyotrichum ascendens". In Jepson Flora Project (ed.). Jepson eFlora. The Jepson Herbarium, University of California, Berkeley. Retrieved 25 July 2021.
- Brouillet, L.; Semple, J.C.; Allen, G.A.; Chambers, K.L.; Sundberg, S.D. (2006). "Symphyotrichum ascendens". In Flora of North America Editorial Committee (ed.). Flora of North America North of Mexico (FNA). Vol. 20. New York and Oxford. Retrieved 22 July 2021 – via eFloras.
- BSBI List 2007 (xls). Botanical Society of Britain and Ireland. Archived from the original (xls) on 26 June 2015. Retrieved 17 October 2014.
- "Aster ascendens Lindl., Fl. Bor.-Amer. (Hooker) 2(7): 8 (1834)". International Plant Names Index (IPNI). Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew; Harvard University Herbaria & Libraries; Australian National Botanic Gardens. Retrieved 25 July 2021.
- Native Plant Trust (2021). "Symphyotrichum (American-aster): Go Botany". Go Botany (GoBotany.NativePlantTrust.org). Framingham, Massachusetts: Native Plant Trust. Archived from the original on 28 November 2020. Retrieved 24 July 2021.
- NatureServe (2 July 2021). "Symphyotrichum ascendens Western Aster". NatureServe Explorer (explorer.natureserve.org). Arlington, Virginia: NatureServe. Retrieved 17 July 2021.
- POWO (2021). "Symphyotrichum ascendens (Lindl.) G.L.Nesom". Plants of the World Online. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. Retrieved 22 July 2021.
- Semple, J.C. (n.d.a). "Symphyotrichum ascendens x". www.uwaterloo.ca. Ontario. Archived from the original on 22 July 2021. Retrieved 22 July 2021.
- Semple, J.C. (n.d.b). "Symphyotrichum subg. Ascendentes". www.uwaterloo.ca. Ontario. Archived from the original on 22 July 2021. Retrieved 22 July 2021.
- Semple, J.C. (14 May 2021). "Symphyotrichum ascendens — Long-leaved Aster, Intermountain Aster, Western Aster". www.uwaterloo.ca. Ontario. Archived from the original on 22 July 2021. Retrieved 22 July 2021.
- Taylor, Ronald J. (1992). Sagebrush Country: A Wildflower Sanctuary. Missoula, Montana: Mountain Press Publishing Company. ISBN 0-87842-280-3. OCLC 1036858077. Retrieved 20 January 2022.
- USDA, NRCS (2014). "Symphyotrichum ascendens". The PLANTS Database (plants.usda.gov). Greensboro, North Carolina: National Plant Data Team. Retrieved 22 July 2021.
External links
- Symphyotrichum ascendens in the CalPhotos photo database, University of California, Berkeley
- BONAP distribution map, Biota of North America Program, 2014
Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии




