bio.wikisort.org - Plant
Quercus imbricaria, the shingle oak, is a deciduous tree in the red oak group of oaks. It is native primarily to the Midwestern and Upper South regions of North America.
| Shingle oak | |
|---|---|
 | |
Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Fagales |
| Family: | Fagaceae |
| Genus: | Quercus |
| Subgenus: | Quercus subg. Quercus |
| Section: | Quercus sect. Lobatae |
| Species: | Q. imbricaria |
| Binomial name | |
| Quercus imbricaria Michx. 1801 not A.Gray ex A.DC. | |
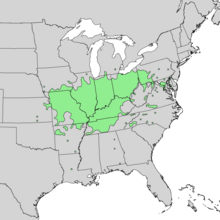 | |
| Natural range | |
| Synonyms[2] | |
|
List
| |
Description

A tree usually 15–18 meters (50–60 feet) high, maximum height 100 ft, with broad pyramidal head when young, becoming in old age broad-topped and open. Trunk up to 1 m (40 inches) in diameter (rarely 1.4 m or 56 in). It reaches its largest size in southern Illinois and Indiana, although the national champion is 104' by 68' in Cincinnati, Ohio.
- Bark: Light brown, scaly; on young stems light brown, smooth. Branchlets slender, dark green and shining at first, later become light brown, finally dark brown.[3]
- Wood: Pale reddish brown, sapwood lighter; heavy, hard coarse-grained, checks badly in drying; used for shingles and sometimes in construction. Sp. gr., 0.7529; weight of cu. ft., 46.92 lbs.[3]
- Winter buds: Light brown, ovate, acute, one-eight inch long.[3]
- Leaves: Alternate, oblong or obovate, four to six inches long, one to two inches wide, wedge-shaped or rounded at base, acute or rounded at apex, sometimes entire or with undulated margins, sometimes more or less three-lobed. They come out of the bud involute, bright red, covered with rusty down above and white tomentum below. When full grown are dark green, smooth and shining above, pale green or pale brown, downy below; midribs stout yellow, grooved above, primary veins slender. In autumn they become dark red above, pale beneath, midribs darken, then the leaf. Petioles stout, hairy, flattened, grooved. Stipules about one-half inch long, caducous.[3]
- Flowers: May, when leaves are half grown. Staminate flowers borne on tomentose aments two to three inches long. Bracts linear-lanceoate. Calyx pale yellow, downy, four-lobed; stamens four to five; anthers yellow. Pistillate flowers borne on slender tomentose peduncles. Involucres scales are downy, about as long as the calyx lobes; stigmas short, reflexed, greenish-yellow.[3]
- Acorns: Ripen in autumn of second year, about 18 months after pollination.[3] Stalked, solitary or in pairs; nut almost spherical, 9–18 millimeters or 1⁄2 to 2⁄3 in long; cup embraces one-half to two-thirds nut, is cup-shaped covered with light red brown, downy scales, rounded or acute at apex. Kernel very bitter.[4][3]
It is distinguished from most other oaks by its leaves, which are shaped like laurel leaves, 8–20 cm (4–10 in) long and 1.5–7.5 cm (1⁄2–3 in) broad with an untoothed margin; they are bright green above, paler and somewhat downy beneath.
Hybrids
Quercus × leana Nutt. (Q. velutina x Q. imbricaria) (Lea's hybrid oak), is a naturally occurring hybrid of the black oak and shingle oak, growing to 20 m, a native of south-eastern North America, also found in a few European collections.
Distribution and habitat
It is native primarily to the Midwestern and Upper South regions of North America, from southern New York west to northern Illinois and eastern Kansas, and south to central Alabama and Arkansas. It is abundant in the lower Ohio Valley and middle Mississippi Valley, and rare in the east.
It is most commonly found growing in uplands with good drainage, less often along lowland streams, at altitudes of 100–700 m (330–2,300 ft).
Ecology
The acorn is an important food for squirrels and some birds.
Uses
In the past, the wood was important for making shingles, from which the common name derives.
References
- Wenzell, K.; Kenny, L.; Jerome, D. (2017). "Quercus imbricaria". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2017: e.T194174A111278885. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-2.RLTS.T194174A111278885.en. Retrieved 13 November 2021.
- "Quercus imbricaria Michx.". World Checklist of Selected Plant Families (WCSP). Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew – via The Plant List.
- Nixon, Kevin C. (1997). "Quercus imbricaria". In Flora of North America Editorial Committee (ed.). Flora of North America North of Mexico (FNA). Vol. 3. New York and Oxford – via eFloras.org, Missouri Botanical Garden, St. Louis, MO & Harvard University Herbaria, Cambridge, MA.
- Keeler, Harriet L. (1900). Our Native Trees and How to Identify Them. New York: Charles Scribner's Sons. pp. 372–374.
External links
- Quercus imbricaria images from Vanderbilt University
- photo of herbarium specimen at Missouri Botanical Garden, collected in Missouri in 1948
На других языках
- [en] Quercus imbricaria
[ru] Дуб черепитчатый
Дуб черепитчатый, дуб лавровый (лат. Quercus imbricaria), — листопадное дерево рода Дуб семейства Буковые (Fagaceae).Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии
