bio.wikisort.org - Plant
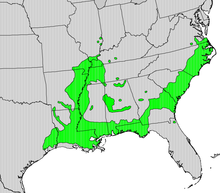
Nyssa aquatica, commonly called the water tupelo,[2] cottongum,[3] wild olive,[3] large tupelo,[3] tupelo-gum,[2] or water-gum,[2] is a large, long-lived tree in the tupelo genus (Nyssa) that grows in swamps and floodplains in the Southeastern United States.[4]
Nyssa aquatica trunks have a swollen base that tapers up to a long, clear bole, and its root system is periodically under water.[4] Water tupelo trees often occurs in pure stands.
Names
Nyssa aquatica's genus name (Nyssa) refers to a Greek water nymph;[5] the species epithet aquatica, meaning ‘aquatic’, refers to its swamp and wetland habitat.
One of the species' common names, tupelo, is of Native American origin, coming from the Creek words ito ‘tree’ and opilwa ‘swamp’; it was in use by the mid-18th century[6]
Uses
A large mature tree can produce commercial timber used for furniture and crates. The swollen base of the Nyssa aquatica is the source of a favored wood of wood carvers.
Many kinds of wildlife eat the fruit, and it is a favored honey tree.[4]


Gallery
- Branch with inflorescences
- Seeds
References
- Stritch, L. (2018). "Nyssa aquatica". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2018: e.T61990552A61990555. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-1.RLTS.T61990552A61990555.en. Retrieved 20 November 2021.
- "Nyssa aquatica". Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN). Agricultural Research Service (ARS), United States Department of Agriculture (USDA). Retrieved 10 January 2018.
- Bailey, L.H.; Bailey, E.Z.; the staff of the Liberty Hyde Bailey Hortorium (1976). Hortus third: A concise dictionary of plants cultivated in the United States and Canada. New York: Macmillan. ISBN 978-0-02-505470-7.
- Johnson, R. L. (1990). "Nyssa sylvatica". In Burns, Russell M.; Honkala, Barbara H. (eds.). Hardwoods. Silvics of North America. Washington, D.C.: United States Forest Service (USFS), United States Department of Agriculture (USDA). Vol. 2 – via Southern Research Station.
- Werthner, William B. (1935). Some American Trees: An intimate study of native Ohio trees. New York: The Macmillan Company. pp. xviii + 398 pp.
- New Oxford American Dictionary (2nd ed.).
External links
- Louisiana State University: page on Nyssa aquatica in America,
- bioimages.vanderbilt.edu - Nyssa aquatica images
- woodworkingnetwork.com: "All About Tupelo Wood"
На других языках
[de] Wasser-Tupelobaum
Der Wasser-Tupelobaum (Nyssa aquatica) ist eine Pflanzenart aus der Gattung der Tupelobäume (Nyssa) innerhalb der Familie der Hartriegelgewächse (Cornaceae).- [en] Nyssa aquatica
Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии