bio.wikisort.org - Plant
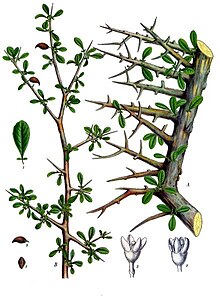
Commiphora myrrha, called myrrh,[1] African myrrh,[1] herabol myrrh,[1] Somali myrrhor,[1] common myrrh,[3] is a tree in the Burseraceae family. It is one of the primary trees used in the production of myrrh, a resin made from dried tree sap. The tree is native to the Arabian peninsula (Oman, Yemen) and to Africa (Djibouti, Ethiopia, Somalia, Northeast Kenya).[4] It is called 'mur' (المر) in Arabic, meaning bitter. It is the gum of the myrrh tree. Its oil is called oleoresin. It famously comes from Mecca, so it is called 'Mur Makki'.
| Commiphora myrrha | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Sapindales |
| Family: | Burseraceae |
| Genus: | Commiphora |
| Species: | C. myrrha |
| Binomial name | |
| Commiphora myrrha (Nees) Engl.[1] | |
| Synonyms[2] | |
|
List
| |

It is anti-bacterial, anti-fungal, anti-pest and can be used for fumigation or oral use. It has been used as an astringent, antiseptic, anti-parasitic, anti-tussive, emmenagogue, and anti-spasmodic agent.[citation needed] It was commonly included in mixtures used to treat worms, wounds, and sepsis.
Growth
Commiphora myrrha is very spiny and it grows to a height of about 4 m (13 ft). It grows at an altitude of between about 250 to 1,300 m (820 to 4,270 ft) with a yearly mean rainfall of about 23 to 30 cm (9.1 to 11.8 in). It does best in thin soil, primarily in areas with limestone.[5]
References
- "Commiphora myrrha". Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN). Agricultural Research Service (ARS), United States Department of Agriculture (USDA). Retrieved 2009-01-15.
- "The Plant List: A Working List of All Plant Species". Retrieved June 6, 2014.
- Sandra Kynes (8 November 2013). Mixing Essential Oils for Magic: Aromatic Alchemy for Personal Blends. Llewellyn Worldwide. pp. 191–. ISBN 978-0-7387-3715-7.
- "Commiphora myrrha". www.cactus-art.biz. Retrieved 2009-01-15.
- "Species Information". www.worldagroforestrycentre.org. Archived from the original on 2011-09-30. Retrieved 2009-01-15.
External links
- List of Chemicals Found in Commiphora myrrha (Dr. Duke's Databases)
- European Medicines Agency: Myrrha
На других языках
- [en] Commiphora myrrha
[es] Commiphora myrrha
Commiphora myrrha es una especie de la familia Burseraceae, natural de Somalia y otras regiones de África. De su resina se obtiene la mirra.[ru] Мирра (растение)
Ми́рра, Коммифора мирровая (лат. Commiphora myrrha) — вид растений из рода Коммифора семейства Бурзеровые (Burseraceae), из которого получают смолу мирра (другие названия — мирро, смирна), широко применяемую в религиозных ритуалах.Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии